Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 6, 2022; 10(22): 7785-7793
Published online Aug 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i22.7785
Published online Aug 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i22.7785
Figure 1 Endoscopic views of endoscopic papillectomy and autorelease biliary supporter placement in a patient with a laterally spreading tumors of the major duodenal papilla.
A: Duodenal papilla tumor was examined by duodenoscopy with indigo carmine staining; B: Submucosal injection was performed to lift the lesion; C: Muscularis propria wound after piecemeal submucosal resection with duodenal papilla; D: The wound was closed with endoscopic hemoclips, and the novel autorelease bile stent was inserted via a guide wire by endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography; E: Fibrin glue was sprayed to cover the wound; F: Specimen of piecemeal papilla polypectomy; G: X-ray image showed autorelease biliary stents were successfully placed; H: The autorelease biliary supporter fell off naturally and arrived in colon about 10 d after this operation.
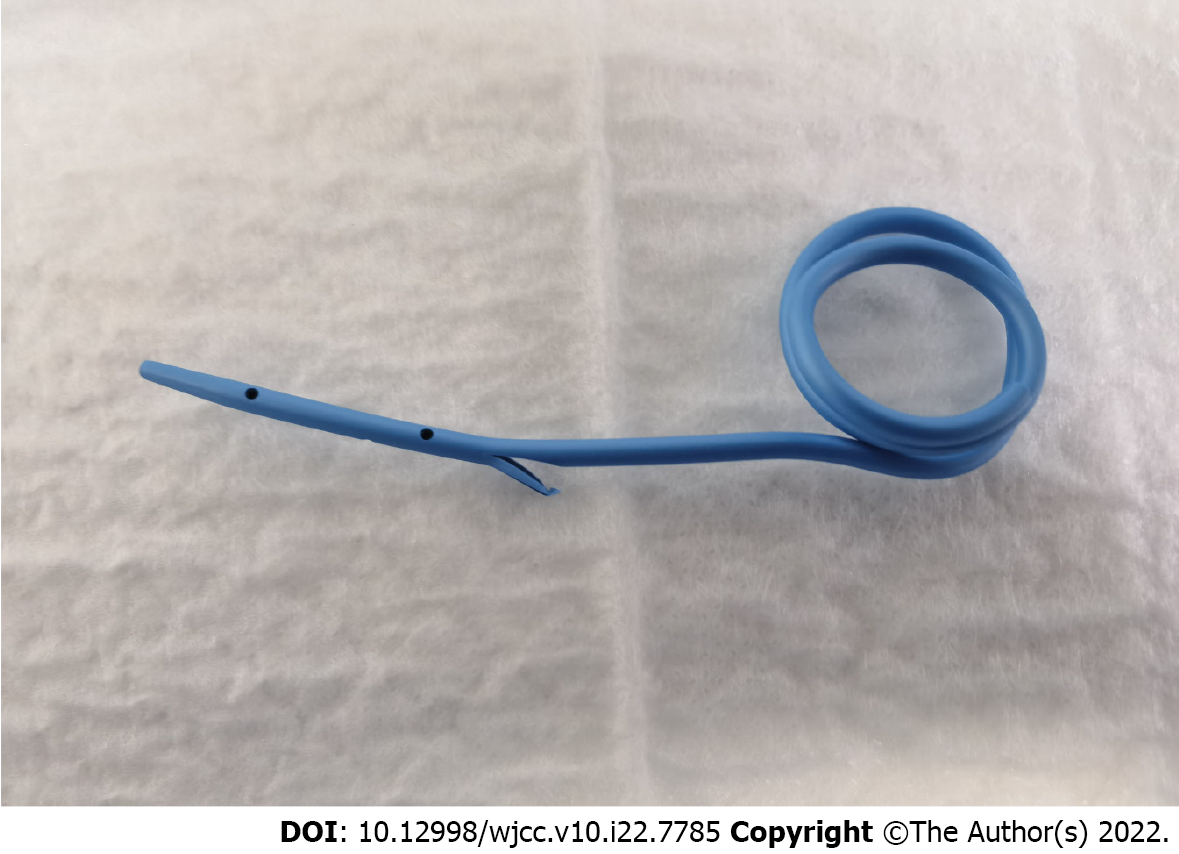
Figure 2 The novel autorelease bile supporter was inserted through a guide wire using endoscopic retrograde cholangiopan
- Citation: Liu SZ, Chai NL, Li HK, Feng XX, Zhai YQ, Wang NJ, Gao Y, Gao F, Wang SS, Linghu EQ. Prospective single-center feasible study of innovative autorelease bile duct supporter to delay adverse events after endoscopic papillectomy. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(22): 7785-7793
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i22/7785.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i22.7785