Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Jul 26, 2022; 10(21): 7242-7255
Published online Jul 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i21.7242
Published online Jul 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i21.7242
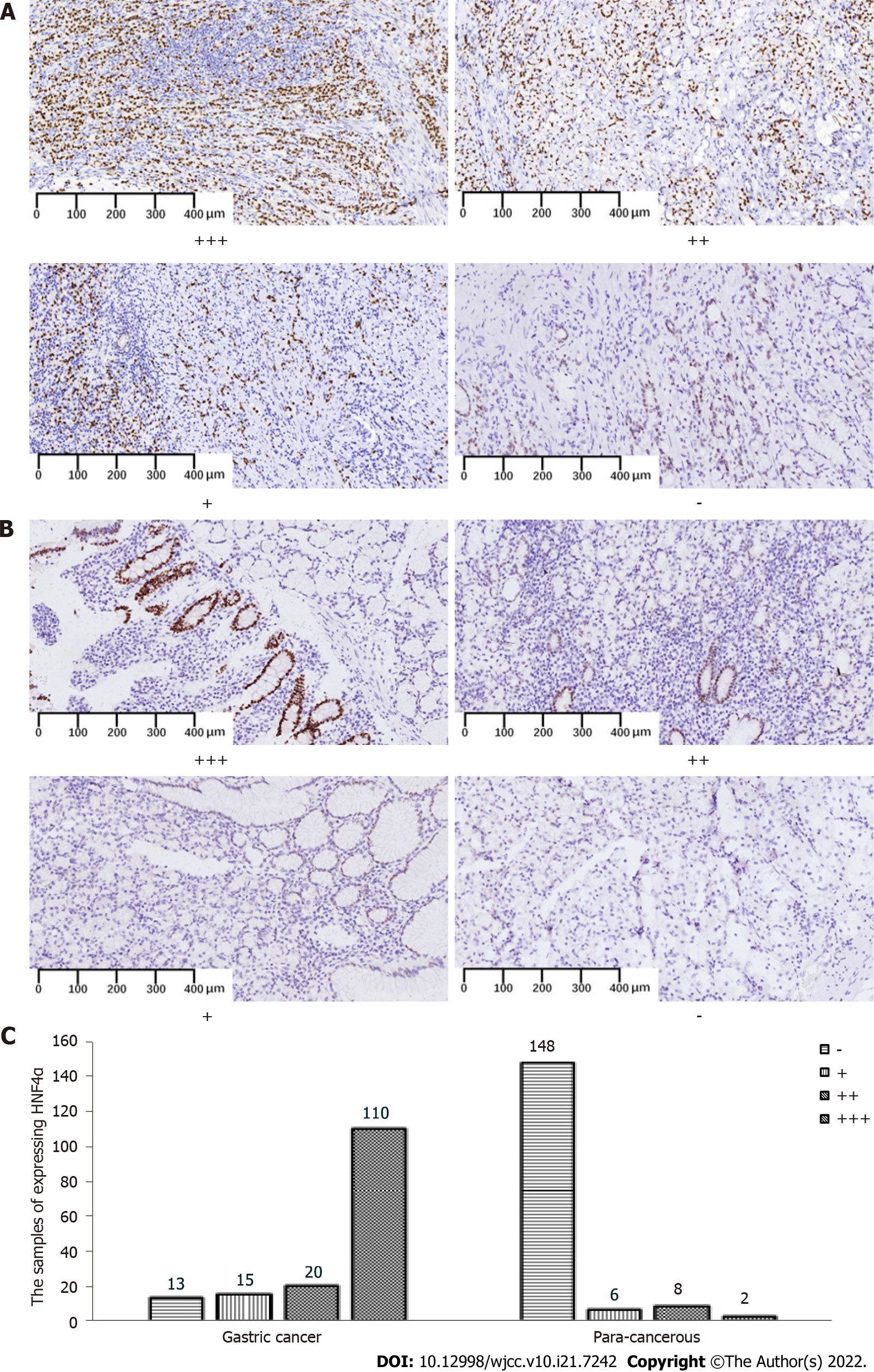
Figure 1 Expression of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha in gastric cancer tissues and para-cancerous tissues.
A, B: Representative figures of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha (HNF4α) expression (nuclear staining) at different grades of pathological scores in gastric cancer tissues (GC) (A) and para-cancerous (PC) tissues (B); C: Numbers of samples expressing HNF4α in GC and PC groups. Specimens were examined under a light microscope (200 × magnification). HNF4: Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha.
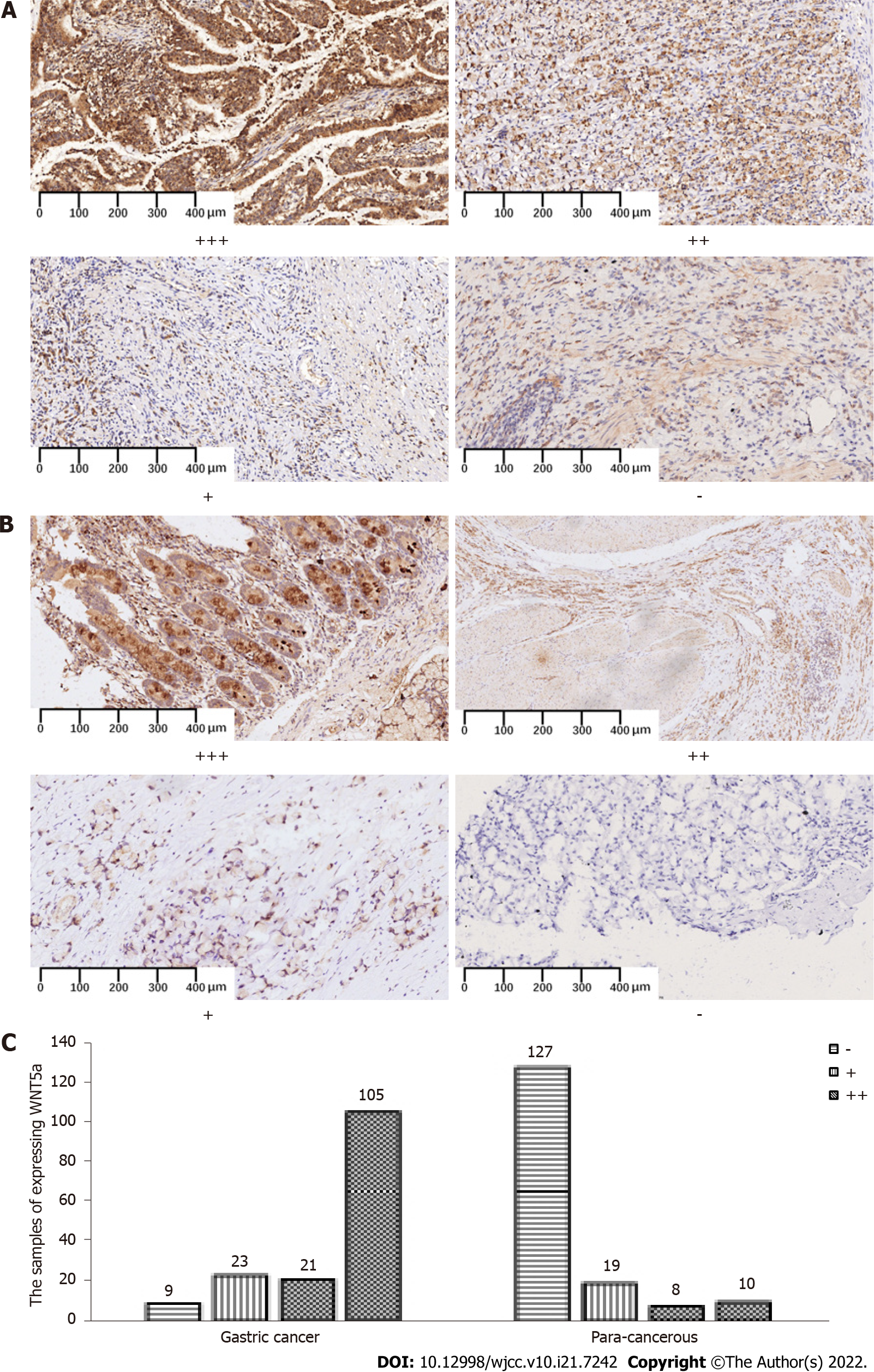
Figure 2 Expression of wingless-related integration site in gastric cancer tissues and para-cancerous tissues.
A, B: Representative figures of wingless-related integration site (WNT5a) expression (cytoplasmic staining) at different grades of pathological scores in gastric cancer tissues (GC) (A) and para-cancerous (PC) tissues (B); C: Numbers of samples expressing WNT5a in GC and PC groups. Specimens were examined under a light microscope (200 × magnification). WNT5a: Wingless-related integration site.
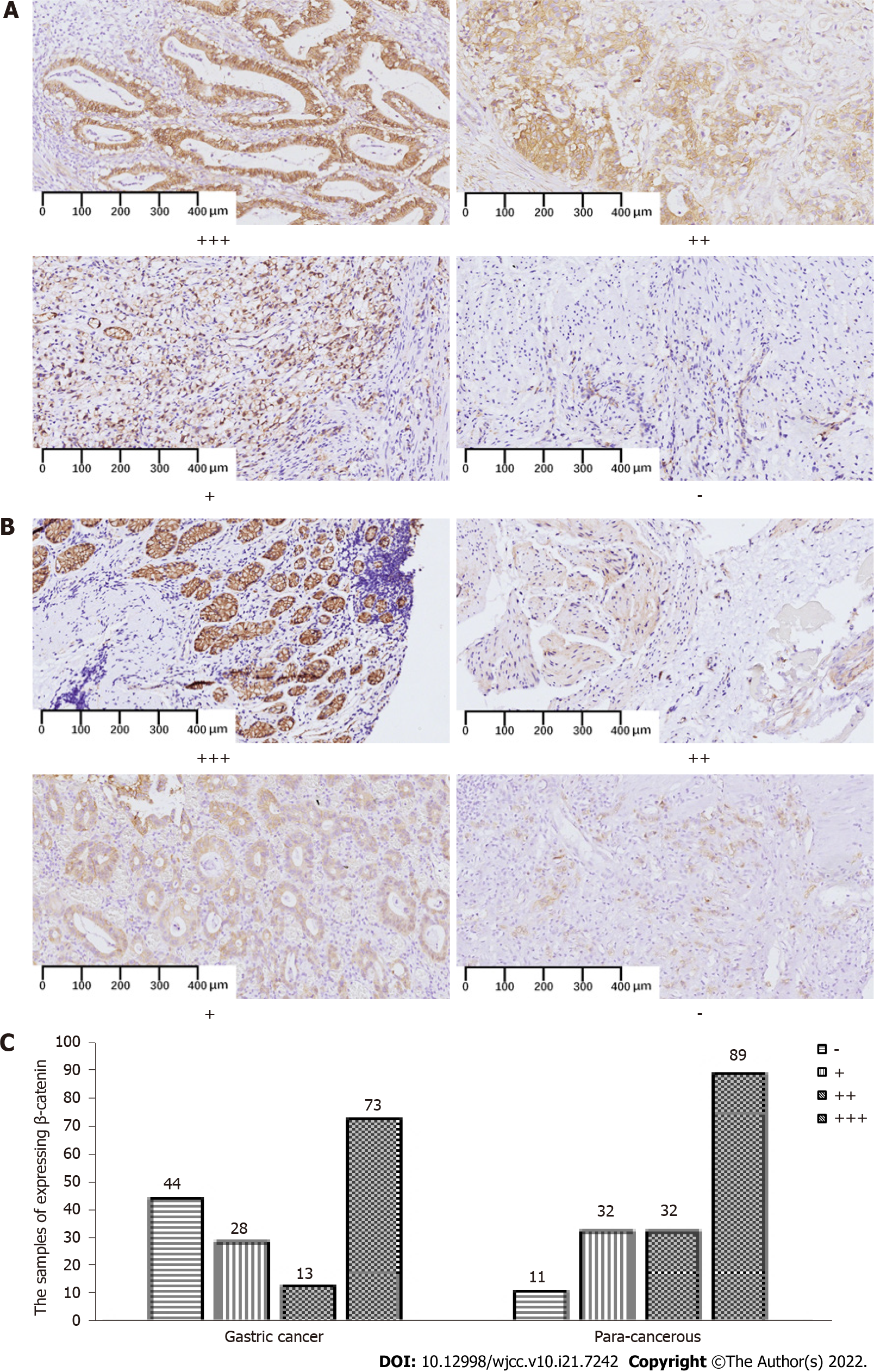
Figure 3 Expression of β-catenin in gastric cancer tissues and para-cancerous tissues.
A, B: Representative figures of β-catenin expression (membranous and cytoplasmic staining) at different grades of pathological scores in gastric cancer (GC) (A) and para-cancerous (PC) tissues (B); C: Numbers of samples expressing β-catenin in GC and PC groups. Specimens were examined under a light microscope (200 × magnification).
- Citation: Hu Q, Li LL, Peng Z, Yi P. Expression of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha, wingless-related integration site, and β-catenin in clinical gastric cancer. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(21): 7242-7255
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i21/7242.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i21.7242