Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 26, 2022; 10(18): 6156-6162
Published online Jun 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i18.6156
Published online Jun 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i18.6156
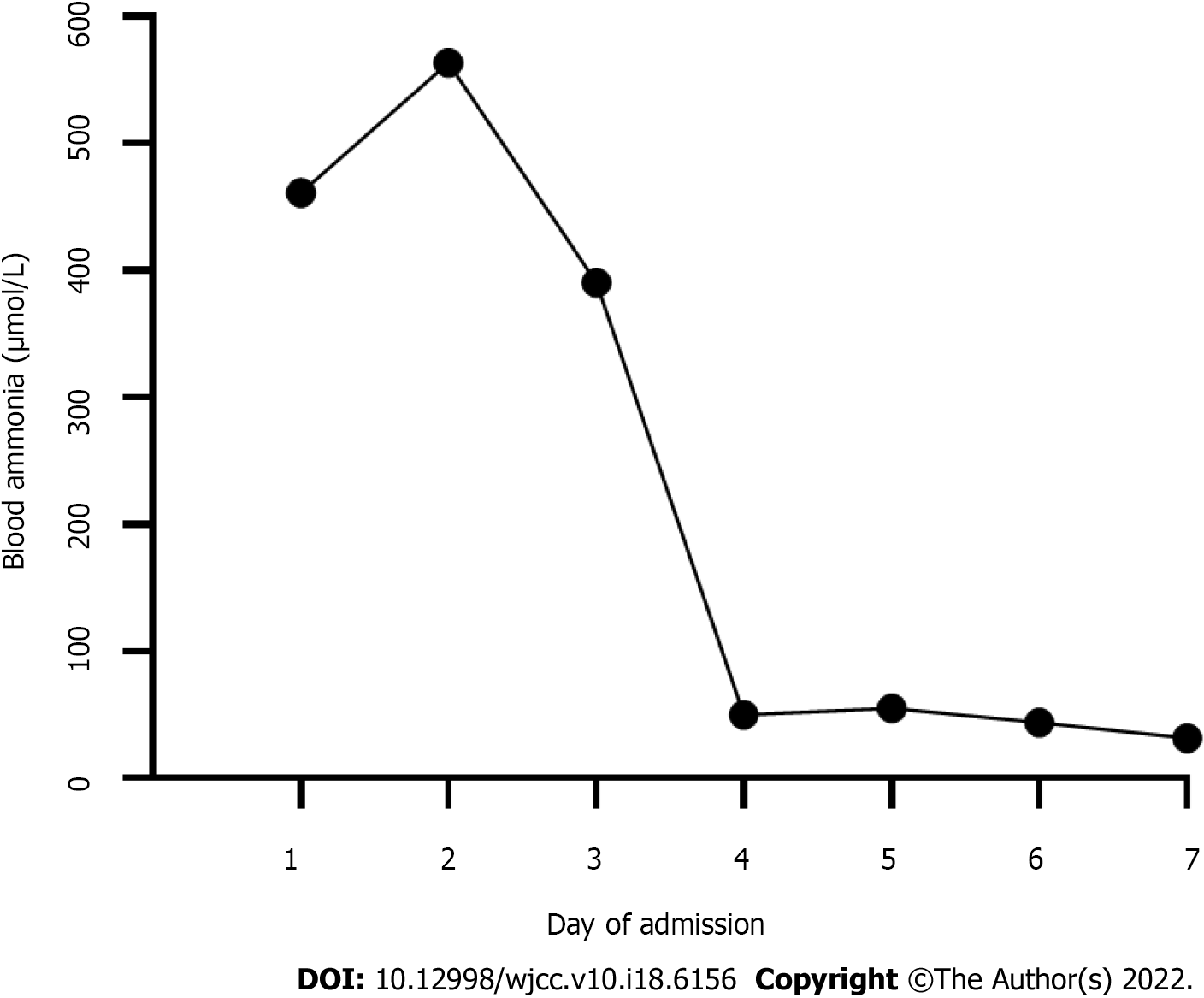
Figure 1 Blood ammonia changes during the first week of admission.
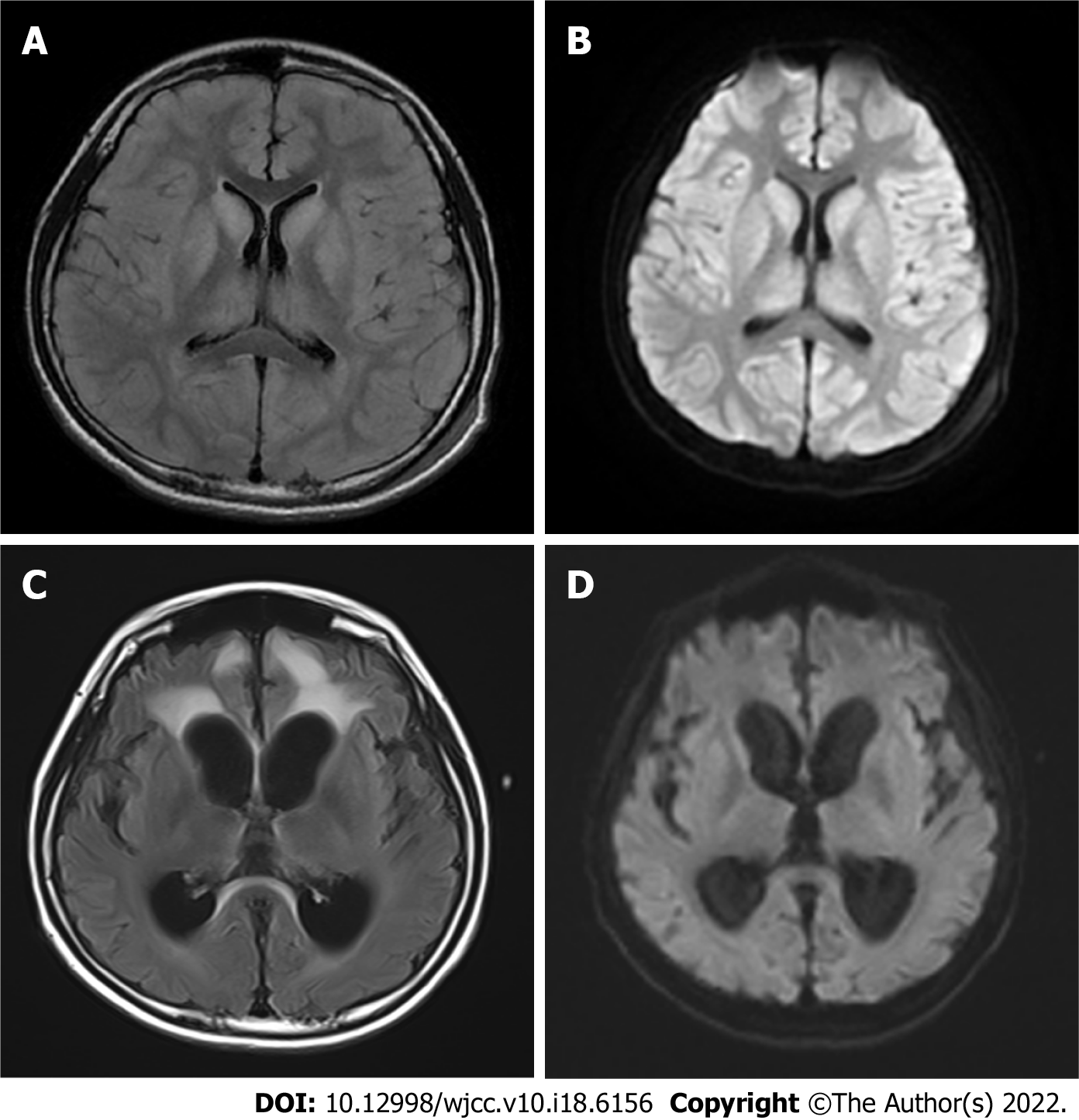
Figure 2 Brain magnetic resonance imaging.
A: On admission, brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), T2 fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) imaging showed a large symmetrical high signal, more pronounced in the bilateral dorsal thalamus, caudate nucleus, lenticular nucleus, insula, cingulate gyrus and frontal lobe into the cortex at the falx; B: On admission, a high signal was observed on diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) of bilateral dorsal thalamus, caudate nucleus, lenticular nucleus, insula, frontal lobe into the cortex at the falx; C: Two months after liver transplantation (LT), brain MRI, T2 FLAIR imaging showed that the cerebral sulcus fissure was widened and deepened bilaterally in the cerebral hemispheres, and the cortex was atrophied, with a patchy high signal in the frontal lobes bilaterally; D: Two months after LT, brain MRI, DWI did not show any significant abnormal signal, and the abnormal signal in the original bilateral cerebral hemispheric cortex, dorsal thalamus, basal ganglia area, insula, cingulate gyrus, and frontal and temporal lobes was no longer obvious.
- Citation: Fu XH, Hu YH, Liao JX, Chen L, Hu ZQ, Wen JL, Chen SL. Liver transplantation for late-onset ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(18): 6156-6162
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i18/6156.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i18.6156