Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Apr 16, 2022; 10(11): 3630-3638
Published online Apr 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i11.3630
Published online Apr 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i11.3630
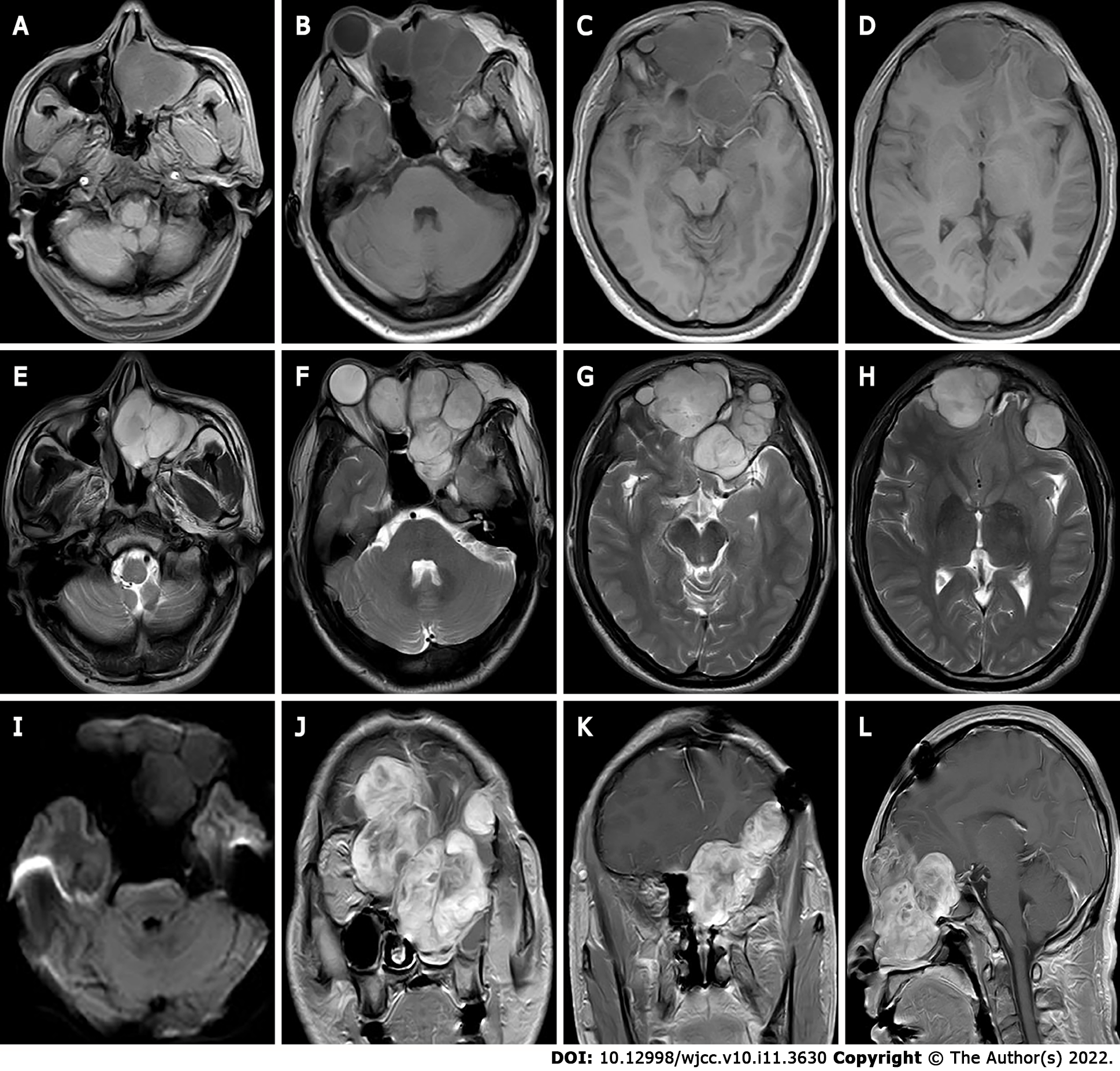
Figure 1 The first preoperative Magnetic resonance imaging findings.
A-I: Magnetic resonance imaging shows multiple masses with T1 weighted imaging (WI) inhomogeneous low signals (A-D) and T2WI inhomogeneous high signals (E-H) in the bilateral frontal, bilateral septal sinuses, bilateral frontal sinuses, left orbit, left nasal cavity, left pterygoid sinus and left maxillary sinus, the lesion showed equal or slightly lower signals on diffusion WI with poorly defined borders (I); J-L: Bilateral frontal lobe and right orbital compression resulted in a localized left shift of the frontal midline, and right shift of the nasal cavity. After enhancement, the lesion showed significant heterogeneous progressive enhancement.
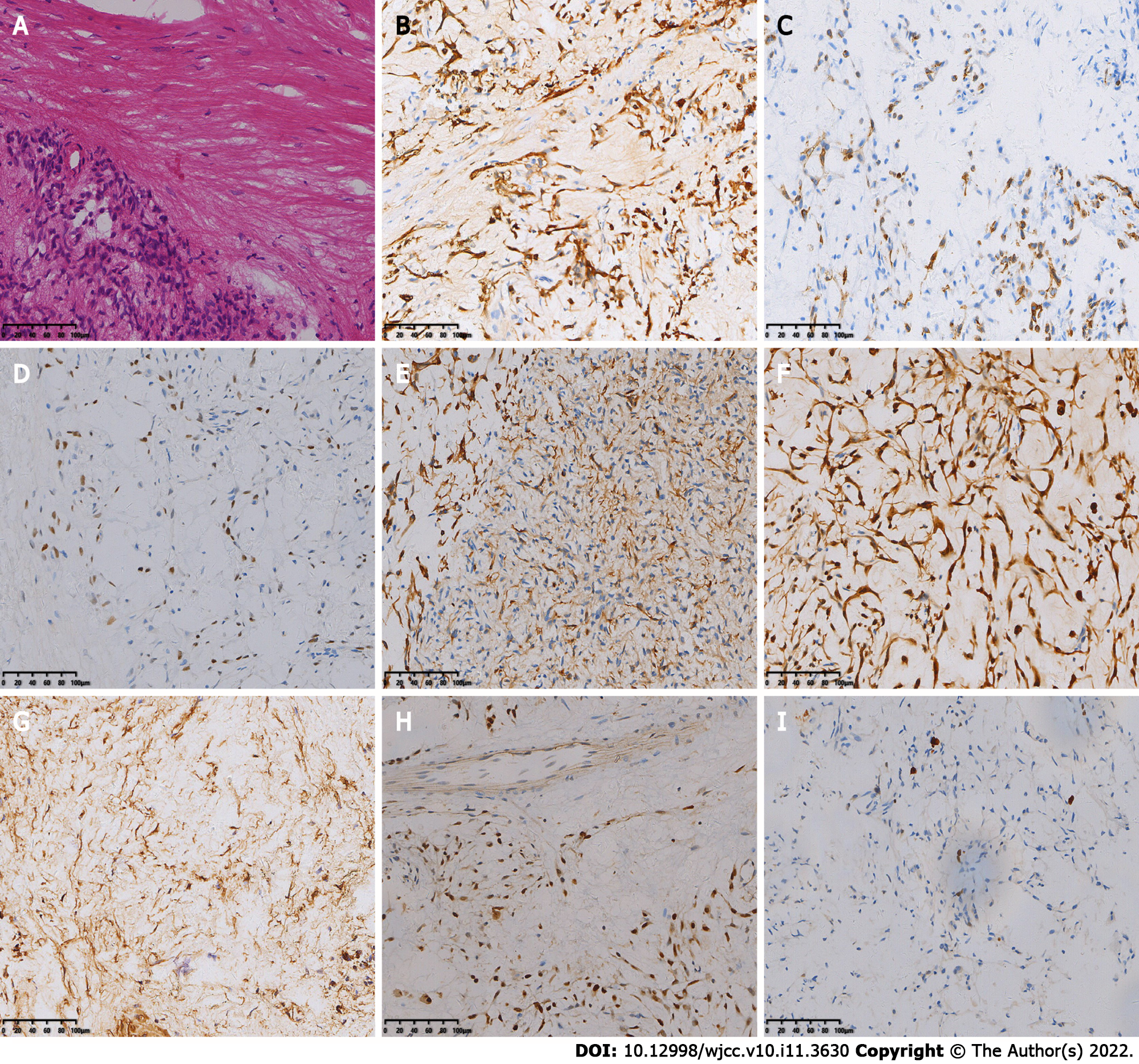
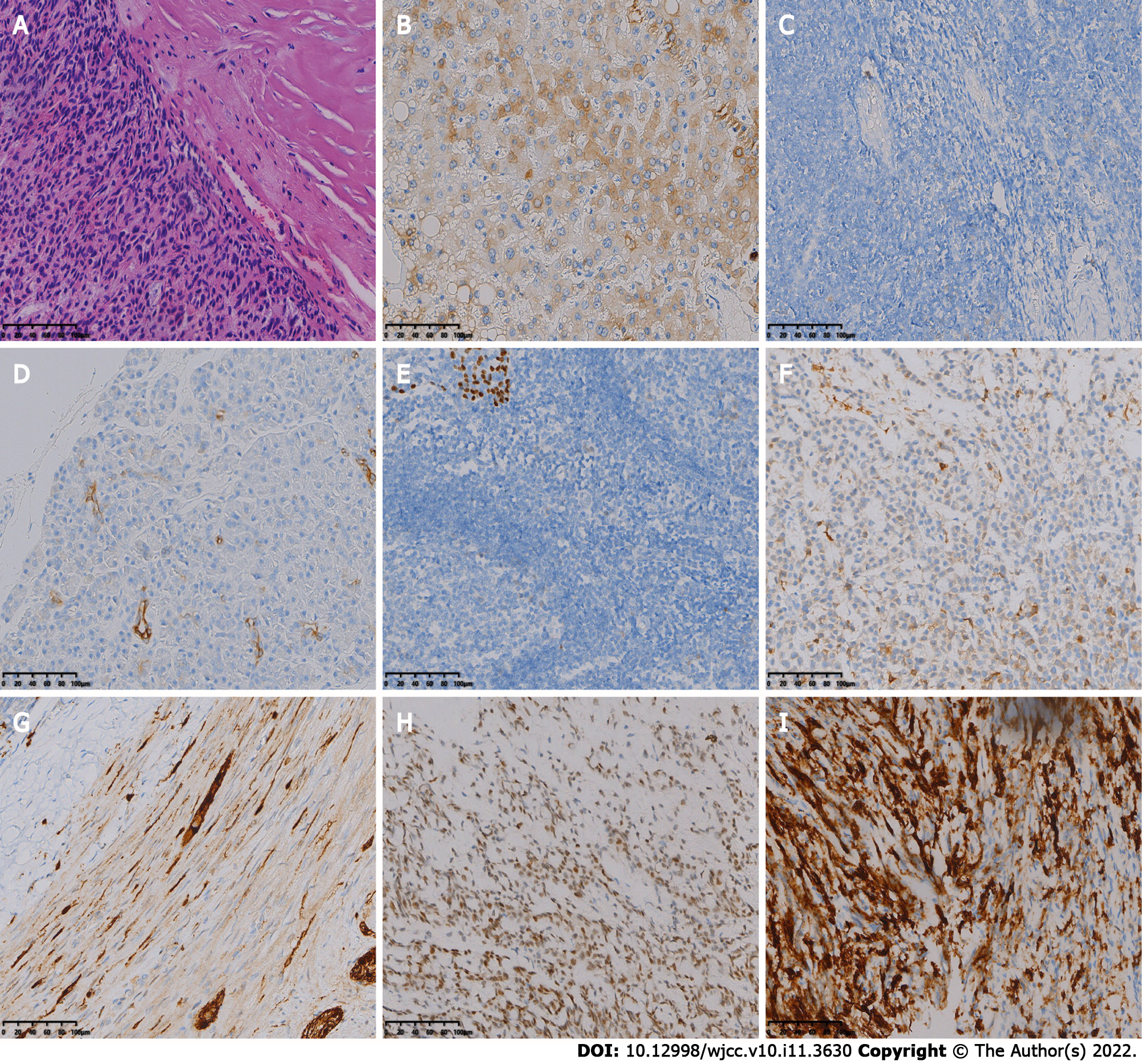
Figure 2 The first postoperative immunohistochemistry results.
A: Hematoxylin-eosin staining shows spindle-shaped tumor cells, mucinous mesenchyme and foci of necrosis, with nuclear schizophrenia and marked nuclear anisotropy, and a small localized pleomorphic adenomatous component in the tumor (magnification × 200); B-I: Immunohistochemistry showed that the tumor cells were positive for CK (B), CK7 (C), P63 (D), Calponin (E), S-100 (F), SMA (G), SOX-10 (H) and 5% of cells were positive for Ki-67 (I) [Envision (B-I) × 200].
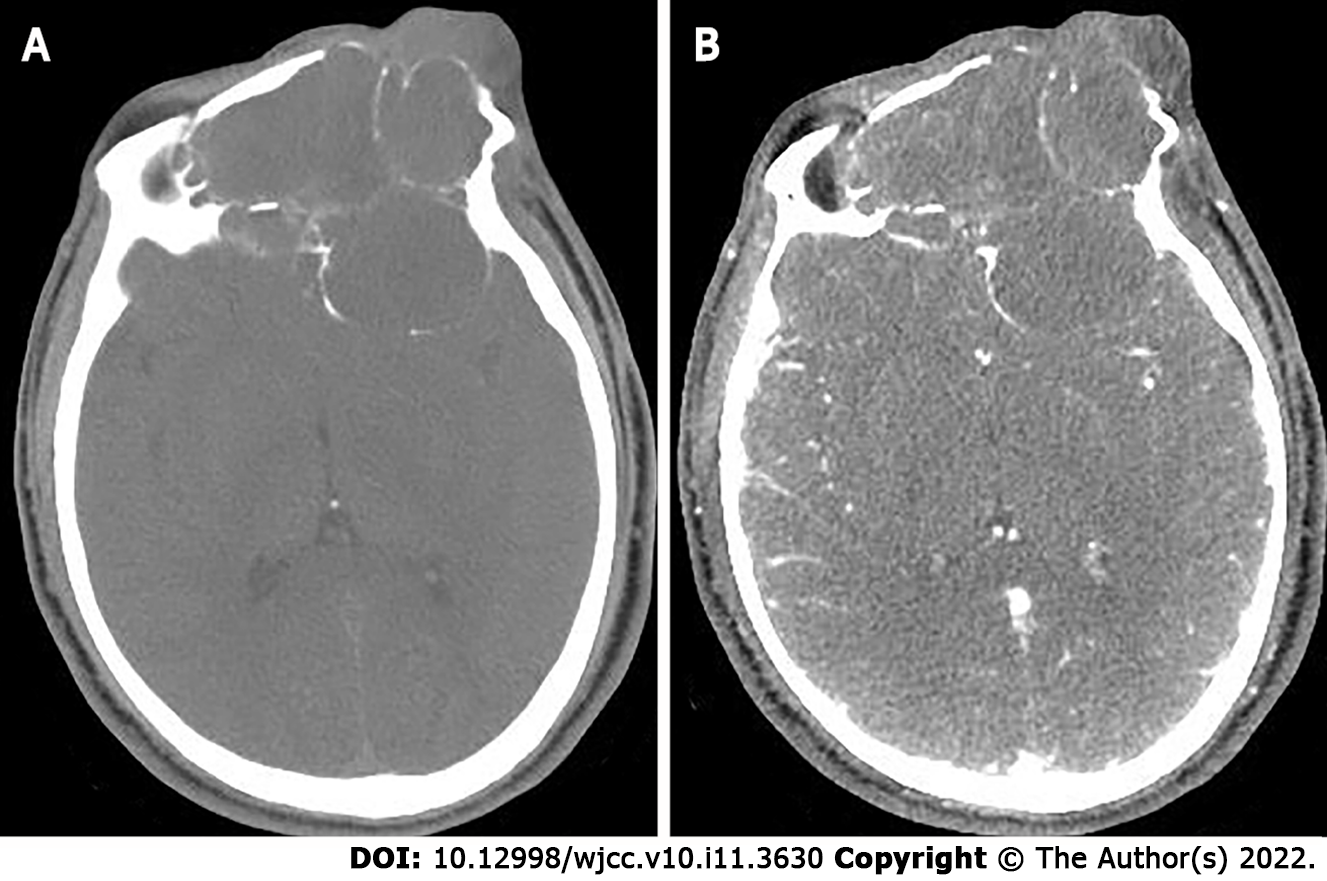
Figure 3 The second preoperative computed tomography findings.
A: Computed tomography (CT) scan shows large lamellar soft tissue density masses in the left orbit, bilateral frontal areas, bilateral septal sinuses, pterygoid sinuses, left maxillary sinus, and anterior skull base, with CT attenuation of approximately 22 Hounsfield units (HU), peripheral multiple osteolytic destruction of bone; B: Arterial phase shows moderate enhancement of the lesion, with CT attenuation of approximately 58 HU.
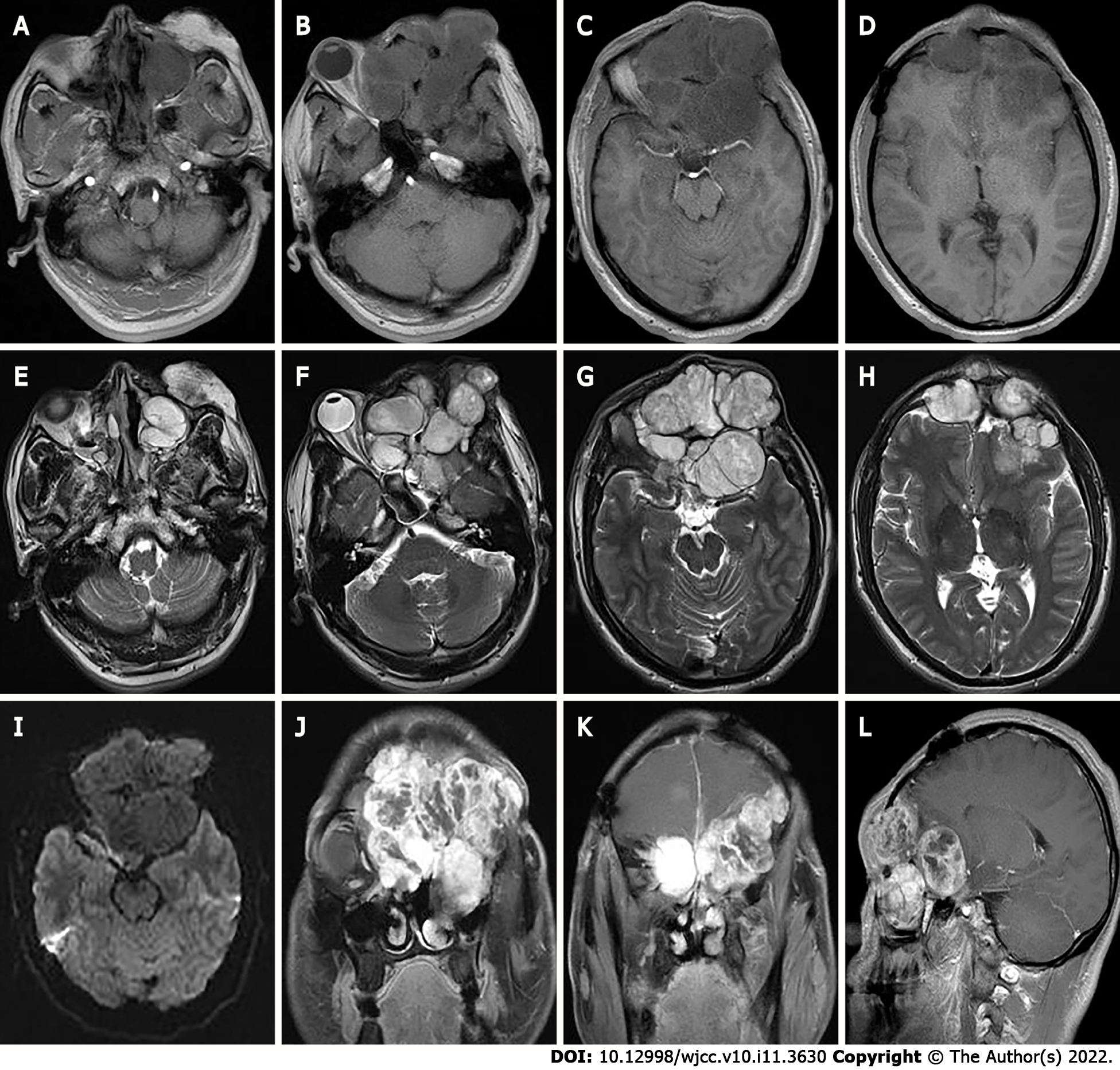
Figure 4 The second preoperative magnetic resonance imaging findings.
A-H: Magnetic resonance imaging shows multiple masses of T1 weighted imaging (WI) low signals (A-D) and T2WI inhomogeneous high signals (E-H) in the left orbit, bilateral frontal areas, bilateral septal sinuses, pterygoid sinuses, left maxillary sinus, and anterior skull base; I: Slightly lower signals on diffusion WI, and lesion borders were not well defined; J-L: After enhancement, the lesion showed significant heterogeneous enhancement.
Figure 5 The second postoperative immunohistochemistry results.
A: Hematoxylin-eosin staining shows diffuse distribution of spindle-shaped tumor cells (magnification × 200); B-I: Immunohistochemistry showed that the tumor cells were positive for CK (B), CK5/6 (C), CK7 (D), P63 (E), Calponin (F), S-100 (G), SOX-10 (H) and SSTR2 (I) [Envision (B-I) × 200].
- Citation: Huang WP, Li LM, Gao JB. Pleomorphic adenoma of the left lacrimal gland recurred and transformed into myoepithelial carcinoma after multiple operations: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(11): 3630-3638
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i11/3630.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i11.3630