Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Oncol. Apr 24, 2025; 16(4): 104061
Published online Apr 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i4.104061
Published online Apr 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i4.104061
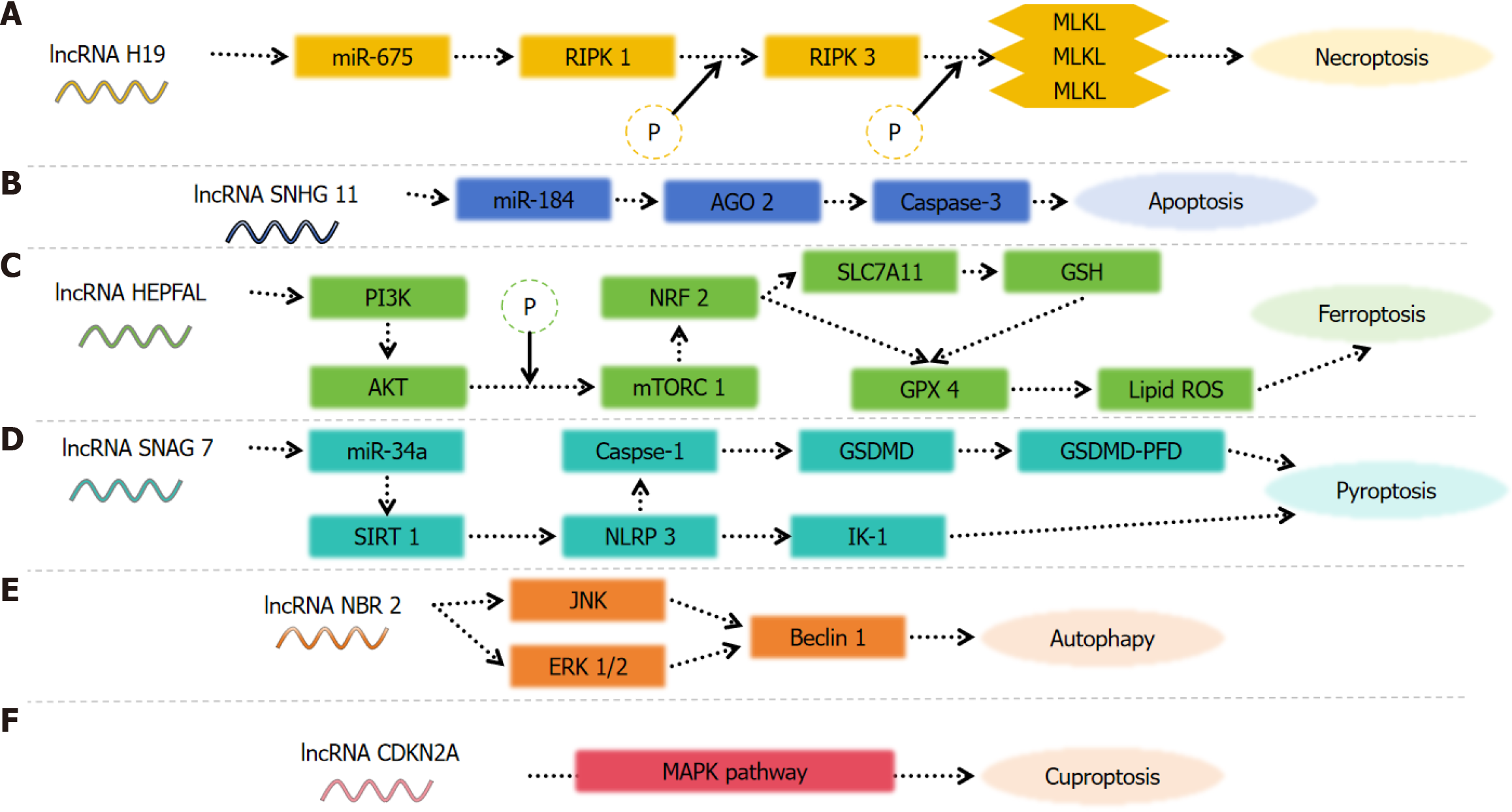
Figure 1 Effect of aberrantly expressed long non-coding RNAs on cell death in different modes.
A: H19 promotes the phosphorylation of MLKL by RIPK 3 through the miR-675 pathway, and MLKL forms a complex and translocates to the plasma membrane, ultimately leading to necroptosis; B: SNHG 11 binds miR-184 and targets AGO2; Caspase 3 expression increases and promotes apoptosis; C: HEPFAl promotes ferroptosis by modifying SLC7A11 ubiquitination; D: SNHG7 inhibits NLRP3-dependent pyroptosis by targeting the miR-34a/SIRT1 axis in liver cancer; E: NBR2 inhibits autophagy-induced cell proliferation through the ERK and JNK pathways; F: CDKN2A involved in the MAPK signaling pathway. LncRNAs: Long non-coding RNA.
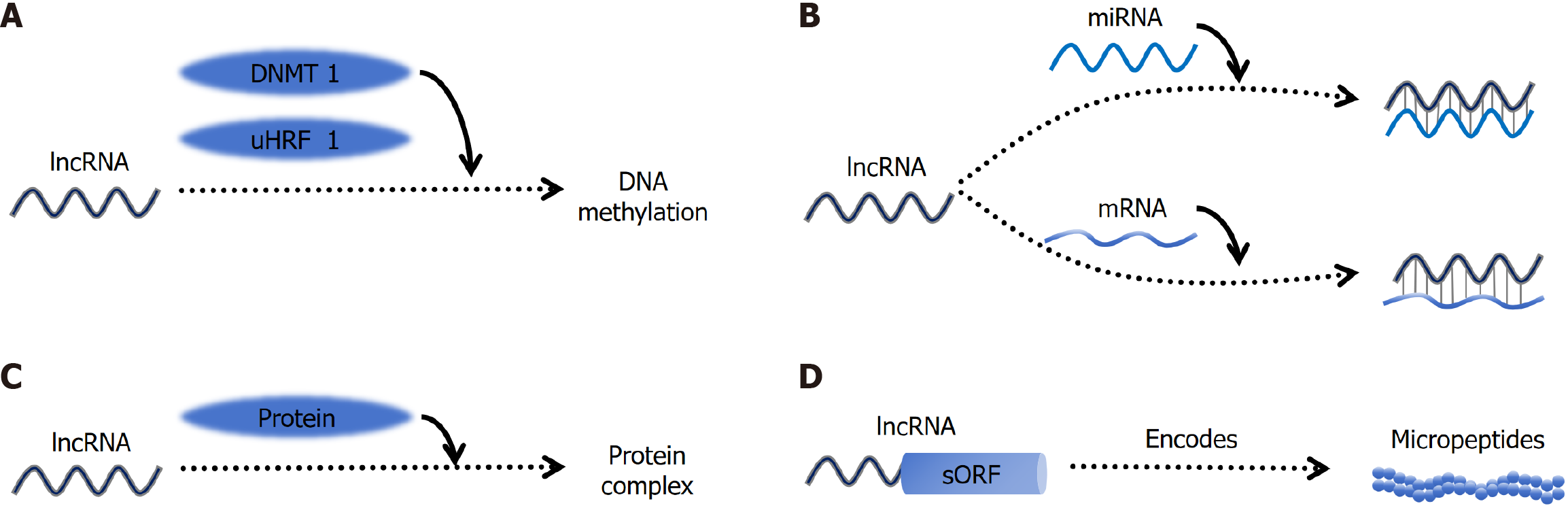
Figure 2 Functional mechanisms of long non-coding RNA in hepatocellular carcinoma.
A: UHRF1 drives hepatocellular carcinoma by inducing global DNA hypomethylation; B: Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) bind to mRNAs and miRNAs to regulate their stability, thereby regulating gene expression; C: LncRNAs interact with proteins to regulate their stability or facilitate the formation of protein complex; D: Several lncRNAs hold the potential to encode small peptides, through which they exhibit their biological functions. lncRNAs: Long non-coding RNA.
- Citation: Wang J, Liu ZX, Huang ZH, Wen J, Rao ZZ. Long non-coding RNA in the regulation of cell death in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Clin Oncol 2025; 16(4): 104061
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v16/i4/104061.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v16.i4.104061