Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Oncol. Jul 24, 2024; 15(7): 806-810
Published online Jul 24, 2024. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v15.i7.806
Published online Jul 24, 2024. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v15.i7.806
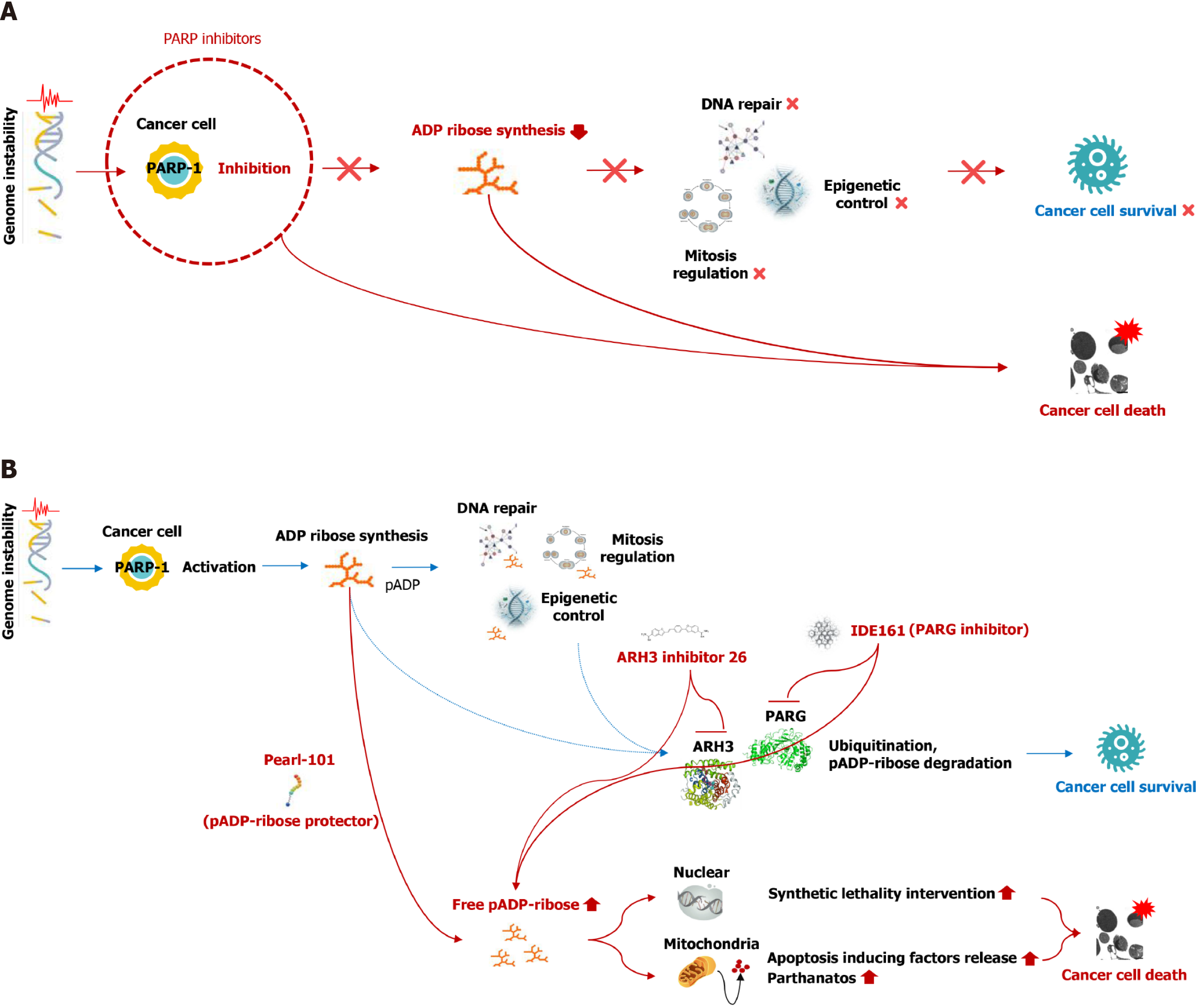
Figure 1 Strategies for inducing cancer cell death through poly (ADP-ribose) regulation.
A: The anticancer effect is achieved by diminishing the synthesis of poly (ADP-ribose) (PAR), a process mediated by the inhibition of PAR polymerase-1; B: Promising strategies for the development of innovative anticancer treatments focused on PAR accumulation. The enzymes responsible for PAR degradation, such as PAR glycohydrolase or (ADP-ribosyl)hydrolase 3 (ARH3), are inhibited by IDE161 (IDEAYA Biosciences) or ARH3 inhibitor 26. Pearl-101, a molecule currently under development by PearlsInMires, plays a crucial role in maintaining the structural integrity of the PAR chain. The accumulation of PAR can lead to the death of cancer cells through a process known as synthetic lethality intervention and the release of apoptosis-inducing factors. PAR: Poly (ADP-ribose); PARG: PAR glycohydrolase; ARH3: (ADP-ribosyl)hydrolase 3; PARP-1: Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1; pADP: Poly(ADP-ribose).
- Citation: Jeong KY, Kang JH. Poly (ADP-ribose): A double-edged sword governing cancer cell survival and death. World J Clin Oncol 2024; 15(7): 806-810
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v15/i7/806.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v15.i7.806