Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Sep 27, 2022; 14(9): 887-895
Published online Sep 27, 2022. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v14.i9.887
Published online Sep 27, 2022. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v14.i9.887
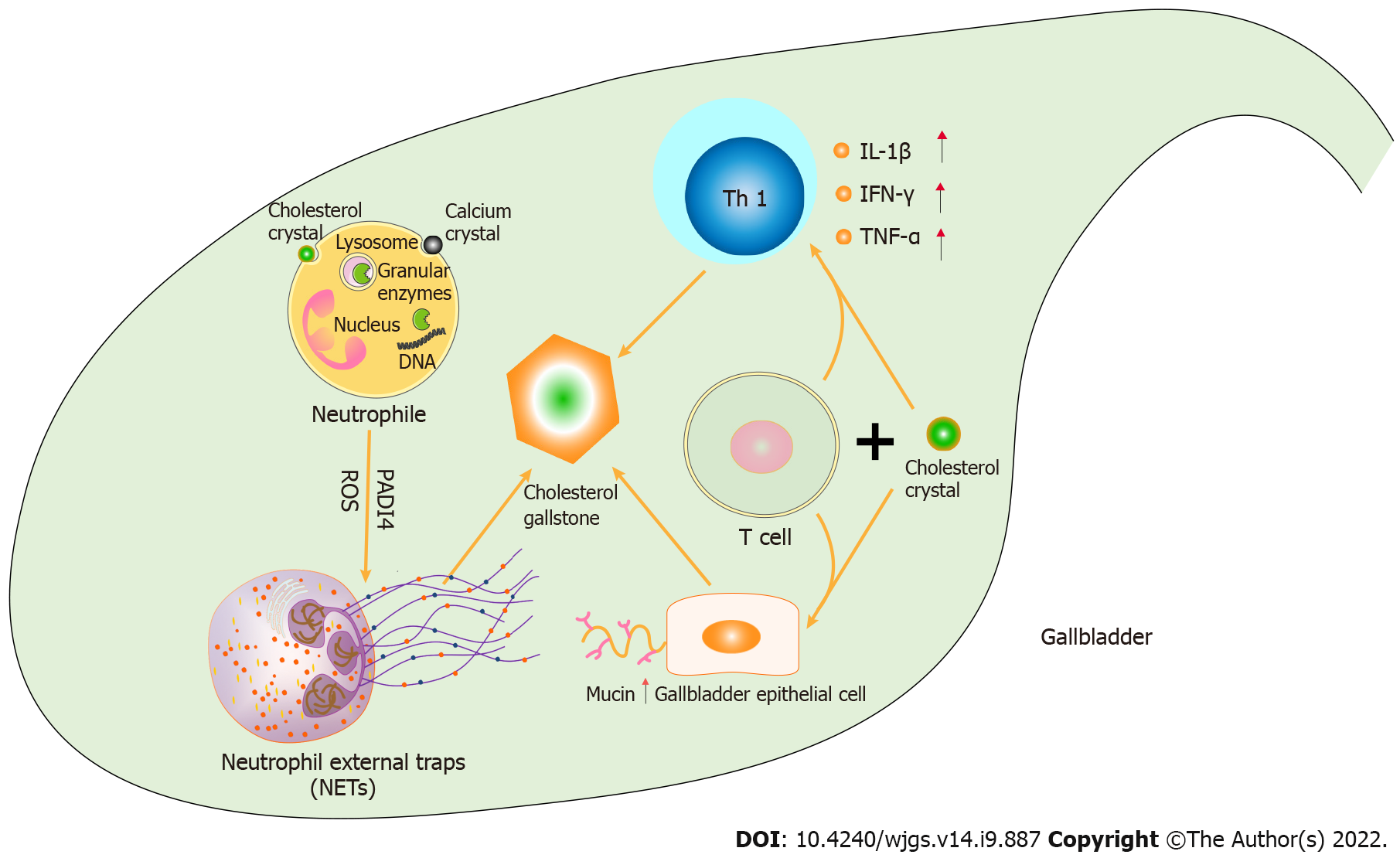
Figure 1 Role of neutrophils and T cells in cholesterol gallstone formation.
In gallbladder bile, cholesterol or calcium crystals are ingested by neutrophils as pinocytosis, inducing leakage of lysosomes and granular enzymes in neutrophils. The intracellular chromatin of neutrophils is decondensed by granular enzymes and externalized to extrachromosomal DNA, resulting in the formation of neutrophil external traps (NETs). Cholesterol crystals and calcium crystals in the bile of the gallbladder are aggregated to form cholesterol gallstones by the “glue” role of NETs. On the other hand, mucin gene expression and mucin gel accumulation in gallbladder epithelial cells can be induced by the joint action of T cells and cholesterol crystals, promoting the formation of cholesterol gallstones. T cells and cholesterol crystals can also induce T helper type 1 cytokines (such as interleukin-1 beta, interferon gamma, tumor necrosis factor-alpha), which cause gallbladder inflammation, gallbladder tissue damage, and gallbladder dysfunction, leading to cholesterol gallstones.
- Citation: Jiao JY, Zhu XJ, Zhou C, Wang P. Research progress on the immune microenvironment of the gallbladder in patients with cholesterol gallstones. World J Gastrointest Surg 2022; 14(9): 887-895
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v14/i9/887.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v14.i9.887