Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Diabetes. May 15, 2015; 6(4): 598-612
Published online May 15, 2015. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i4.598
Published online May 15, 2015. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i4.598
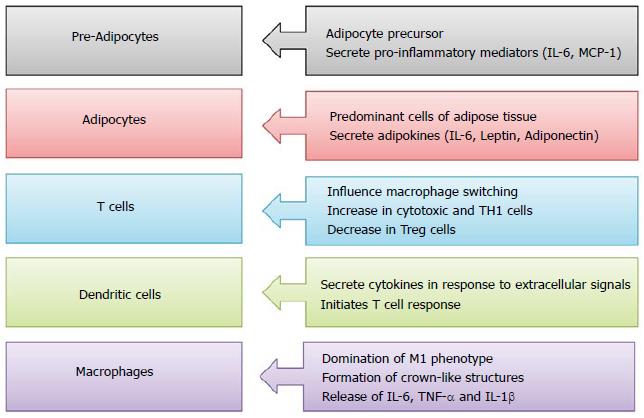
Figure 1 Functions of various immune cell types in pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes.
IL: Interleukin; MCP-1: Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor α.
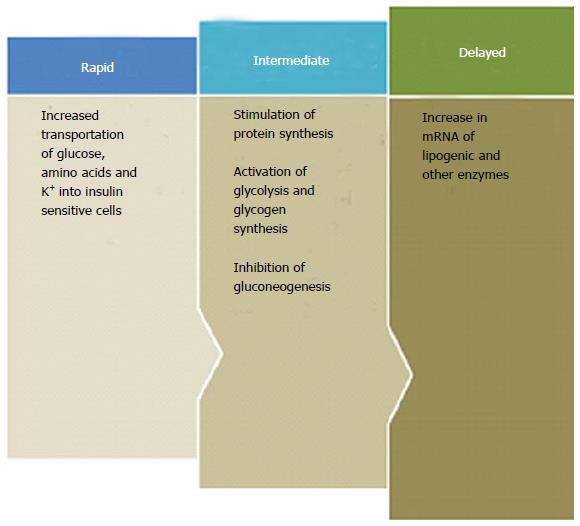
Figure 2 Various hormone functions of insulin.
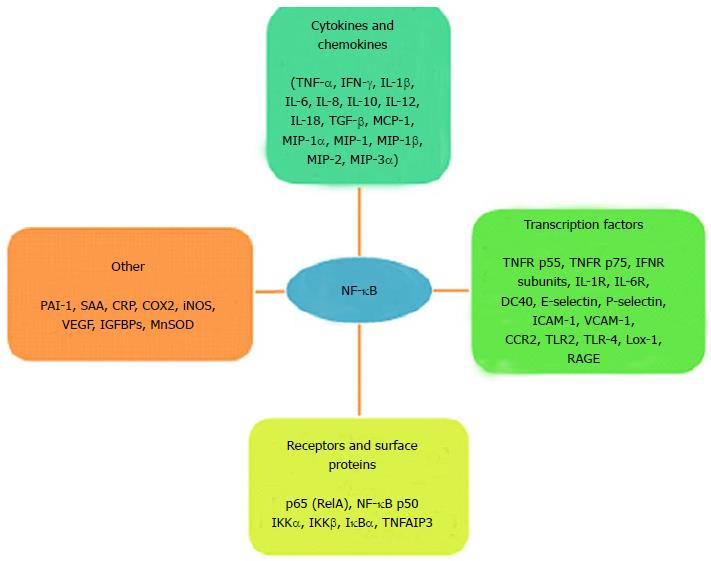
Figure 3 Target genes activated by NF-κB.
TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; IFN-γ: Interferon-gamma; IL: Interleukin; TGF-β: Tumor growth factor-beta; MCP-1: Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; MIP: Major intrinsic protein; TNFR: Tumor necrosis factor receptor; INFR: Interferon receptor; IL-R: Interleukin receptor; CD: Cluster of differentiation; ICAM: Intracellular cell adhesion molecule; VCAM: Vascular cell adhesion molecule; CCR: Chemokine CC receptor; TLR: Toll-like receptor; Lox: Lysyl oxidase; RAGE: Receptor advanced glycation end product; PAI: Plasminogen inhibitor activator; SAA: Serum amyloid; CRP: C-reactive protein; COX: Cyclo-oxygenase; iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; IGFBPs: Insulin-like growth factor binding protein; MnSOD: Manganese superoxide dismutase; RelA: Reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog A; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappa B; IKK: Inhibitor Kappa B kinase; IκBα: Inhibitor of NF-κB; TNFAIP3: TNF-α induced protein 3.
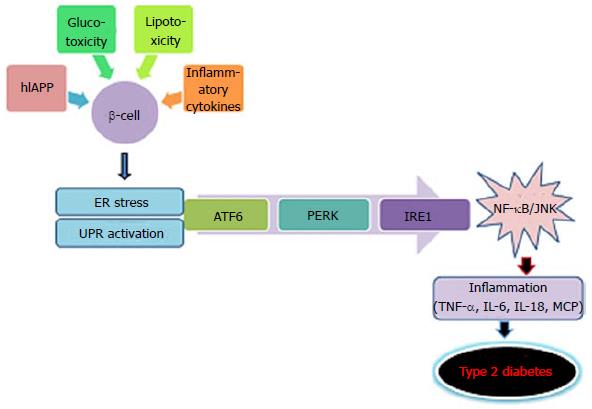
Figure 4 Mechanism of endoplasmic reticulum stress.
ER: Endoplasmic-reticulum; ATF6: Activating transcription factor 6; PERK: Double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase (PKR)-like ER kinase; IRE1: Inositol-requiring kinase 1; IL: Interleukin; MCP: Monocyte chemoattractant protein; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor α; JNK: c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase; NF-κB: Nuclear factor κB.
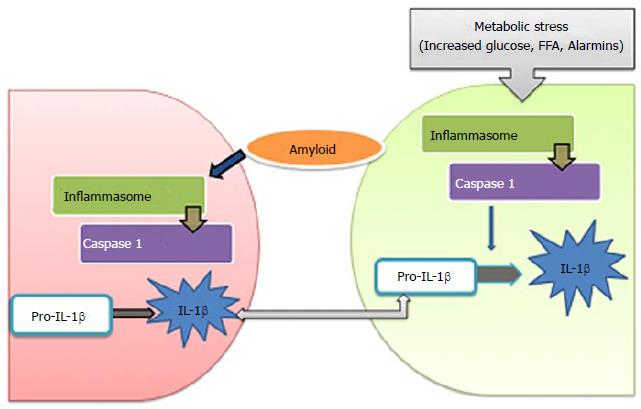
Figure 5 Activation of inflammasomes in type 2 diabetes (metabolic stress activates multiprotein complex, inflammasome in β-cells that induce caspase-1 to cleave pro-interleukin-1β (pro-IL-1β) into active IL-1β.
β-cell-derived IL-1β promote the release of chemokines and recruitment of macrophages that are activated by human islet amyloid polypeptide, leading to deleterious concentrations of IL-1β. FFA: Free fatty acid; IL: Interleukin.
- Citation: Hameed I, Masoodi SR, Mir SA, Nabi M, Ghazanfar K, Ganai BA. Type 2 diabetes mellitus: From a metabolic disorder to an inflammatory condition. World J Diabetes 2015; 6(4): 598-612
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v6/i4/598.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v6.i4.598