Published online Sep 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i9.1644
Peer-review started: July 12, 2023
First decision: July 31, 2023
Revised: August 9, 2023
Accepted: August 21, 2023
Article in press: August 21, 2023
Published online: September 15, 2023
Processing time: 63 Days and 5.7 Hours
Endoscopic mucosal resection is an innovative method for treating early gastric cancer and has been widely used in clinical practice.
To analyze the factors associated with the development of heterochronic gastric cancer in patients with early gastric cancer who had undergone endoscopic mucosal dissection (EMD).
A cohort of patients with early gastric cancer treated using EMD was retro
Of the 300 patients with early gastric cancer, 150 patients developed heterochronic gastric cancer after EMD. Statistical analysis revealed that patient age (P value = XX), sex (P value = XX), tumor size (P value = XX), pathological type (P value = XX), and surgical technique (P value = XX) were significantly associated with the occurrence of heterochronic gastric cancer.
Age, sex, tumor size, pathological type, and surgical technique are key factors influencing the occurrence of heterochronic gastric cancer after EMD in patients with early gastric cancer. To address these factors, postoperative follow-up and management should be strengthened to improve the prognosis and survival rate of patients.
Core Tip: Factors affecting heterochronic gastric cancer after endoscopic mucosal dissection for early gastric cancer include age, gender, tumor size, pathological type, and surgical technique. Postoperative follow-up and management should be strengthened to improve the patient’s prognosis and survival rate.
- Citation: Xie B, Xia Y, Wang X, Xiong Y, Chen SB, Zhang J, He WW. Factors associated with heterochronic gastric cancer development post-endoscopic mucosal dissection in early gastric cancer patients. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2023; 15(9): 1644-1652
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v15/i9/1644.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v15.i9.1644
Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) is an innovative method for treating early gastric cancer and has been widely applied in clinical practice. EMR allows the local excision of early gastric cancer via endoscopic techniques while maximizing the preservation of the normal gastric wall. Thus, the treatment goal is achieved, and at the same time, the trauma and adverse effects are minimized[1-15].
Different technical approaches for endoscopic mucosal dissection (EMD), including the typical EMR and the large endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD), have been described. Their indications, operational difficulties, and risks of complications have been compared and analyzed. Furthermore, the advantages of ESD in treating early gastric cancer have been discussed. Compared with conventional surgical resection, EMD has the advantages of less trauma, faster recovery, and shorter hospital stays. Several clinical studies and retrospective analyses have evaluated the treatment outcomes and survival rates of EMD. In addition, complications and risk management of EMD have been examined. Although EMD is a relatively safe technique, complications such as bleeding, perforation, and infection can occur. Relevant preventive strategies and treatments to reduce the occurrence of complications have been presented[16-20]. The future direction of EMD has also been explored. With advances in technology and equipment, the application of EMD in treating early gastric cancer is expected to become more promising. Directions for further research, including postoperative follow-up and prognostic evaluation, application of new instruments and techniques, and exploration of individualized treatment strategies, have also been proposed.
Globally, gastric cancer is the fifth most common malignancy and has the third highest mortality rate[21-30]. With the improvements in diagnostic techniques and the popularization of endoscopic screening, the diagnosis rate of early gastric cancer has gradually increased. Early gastric cancer is defined as gastric cancer confined to the mucosa or submucosa, with or without regional lymph node metastasis. Several guidelines recommend endoscopic resection as the first-line treatment for early gastric cancer[31,32]. Unlike the surgical approach, endoscopic resection preserves a large portion of the gastric mucosa and is associated with an increased risk of metachronous gastric cancer (MGC) in the remaining gastric mucosa[33]. However, an increasing number of patients with early gastric cancer are treated via endoscopic resection. Identifying the risk factors for the development of MGC is therefore important to devise an appropriate surveillance strategy.
Endoscopic resection is extensively employed for treating superficial gastrointestinal tumors and has become the treatment of choice for patients with early gastric cancer without the risk of lymph node metastasis. EMR, ESD, and endoscopic submucosal tunnel dissection are the major endoscopic resection methods for early gastric cancer. The absolute indications for endoscopic dissection of early gastric cancer include the following: (1) Differentiated intramucosal carcinoma (cT1a) without ulcers; (2) differentiated intramucosal carcinoma (cT1a) with ulcers ≤ 3 cm in size; and (3) high-grade gastric intraepithelial neoplasia. Expanded indications include undifferentiated intramucosal carcinoma (cT1a) with a lesion size of ≤ 2 cm and no ulceration. The morphology, extent, nature, and depth of infiltration of the lesion must be accurately diagnosed preoperatively so that appropriate therapy can be selected according to the indication.
EMR can be grouped into two main categories: (1) Nonattractive methods: Submucosal injection-loop resection, submucosal injection-presection-excision, etc.; and (2) attractive methods: Transparent cap method and ligature method. EMR is suitable for the resection of lesions ≤ 2 cm in diameter with no surface ulceration and can also be used to obtain large histological specimens of superficial malignancies and provide accurate pathological staging[34,35]. Although endoscopic piecemeal mucosal resection can be performed on larger lesions, it may not be possible to obtain the entire lesion for accurate pathological assessment and the risk of local recurrence may be exacerbated.
Heterochronous gastric cancer refers to the progressive development of inflammatory mucosa outside the primary lesion in the direction of “atrophy-enterosis-heterogeneous hyperplasia”. This process is more prolonged than concurrent gastric cancer and takes at least V1 years. There are few studies on concurrent or heterochronic gastric cancer. Therefore, this study investigated the risk factors affecting the development of concurrent and heterochronic gastric cancer after ESD and serves as a reference for the clinical management of this condition.
A total of 300 patients diagnosed with early gastric cancer and treated using ESD at our gastrointestinal endoscopy center from 2016 to 2023 were selected for this study. The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) Preoperative evaluation meeting the indications for ESD surgery (differentiated intramucosal carcinoma without combined ulceration, differentiated intramucosal carcinoma of < 3 cm with ulceration, or high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia of gastric mucosa); (2) postoperative pathology suggestive of curative or relatively curative resection of differentiated intramucosal carcinoma of < 3 cm with combined ulceration or differentiated carcinoma of < 3 cm with a submucosal infiltration depth of < 500 μm; (3) repeat gastroscopy at 3, 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42, and 48 mo after ESD, with complete results; and (4) a follow-up period of 18 mo, and availability of complete clinical records. The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) Additional surgery, radiotherapy, or chemotherapy after the surgery; and (2) patients lost to follow-up. Clinical data, such as age, smoking history, family history, sex, degree of postoperative pathological differentiation, depth of tumor infiltration, first multifocal lesion, tumor size, initial lesion location, and degree of background mucosal atrophy and intestinalization, were retrospectively collected from patients who met the various inclusion criteria. Pathological staging was performed according to the Vienna classification criteria for epithelial tumors of the gastrointestinal tract[36], and histological staging and depth of infiltration were determined as per the criteria of the Japanese Gastric Cancer Society.
Gastroscopy was repeated at 3, 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42, and 48 mo postoperatively, and the findings were documented. A lesion detected at ≤ 12 mo and 1 cm from the original lesion was considered concurrent gastric cancer, whereas a new lesion detected at > 12 mo was considered heterochronic gastric cancer. The occurrence of concurrent or heterochronous gastric cancer during follow-up was collectively referred to as multiple gastric cancers, whereas the absence of concurrent and heterochronous gastric cancer signified single gastric cancer.
SPSS 26.0 was used for the statistical analysis of the data. Quantitative data that conformed to a normal distribution were expressed as mean ± SD, and a t-test was used for the comparison of means between groups. Statistical data were expressed as percentages, and the χ2 test was used for comparison between groups. The influential factors associated with tumor recurrence in the univariate analysis were substituted in the multifactor dichotomous logistic regression model for the analysis of independent risk factors. The test level was α = 0.05 (two-tailed).
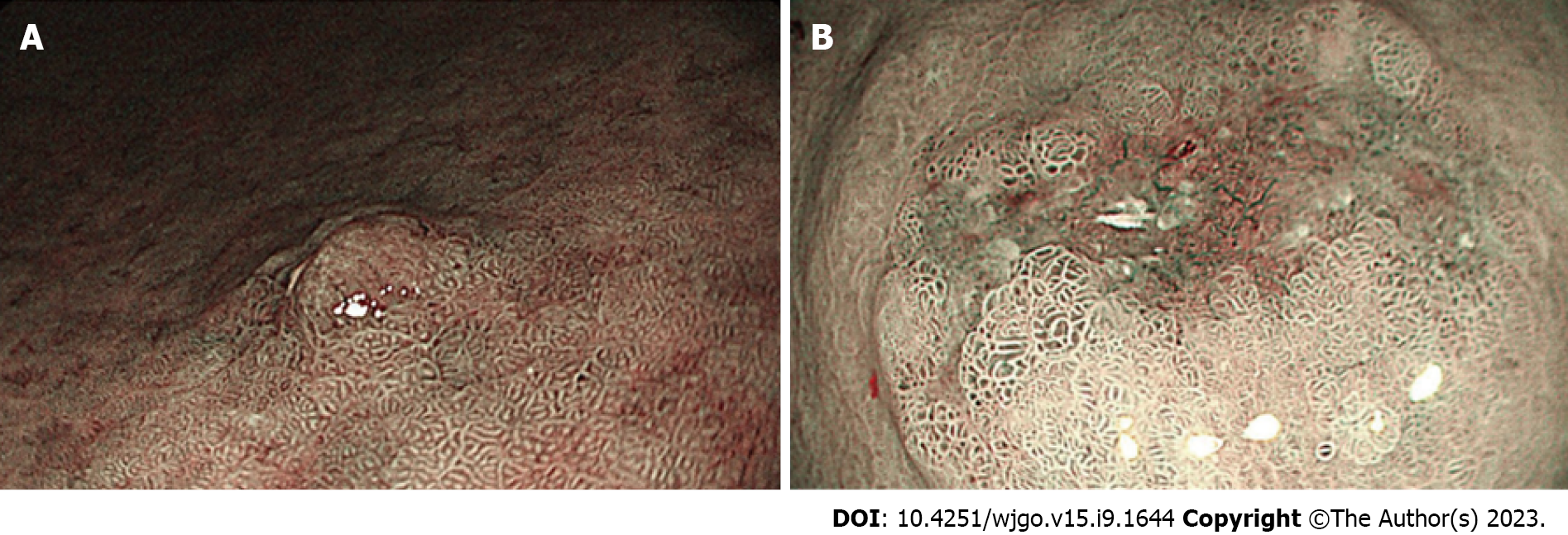
Of the 300 patients included in this study, 170 (56.7%) were men, 66 (22.0%) had a history of heavy smoking (BIW400), 15 (5.0%) had a family history of gastric cancer, and 10 (3.33%) were initially diagnosed with multiple early carcinoma lesions. The median age of the patients was 63 years, and the mean diameter of the initial lesions was 1.92 cm ± 0.89 cm. Furthermore, 58% (76/331) of the initial lesions were located in the lower third of the stomach, and 43.5% of the patients demonstrated severe intestinalization. In addition, of the 300 patients (331 lesions in total) with early gastric cancer, 265 had single (304 lesions), 74 had heterochronous (86 lesions) and 51 had concurrent (51 lesions) gastric cancer (Figure 1).
The results of the single factor analysis of multiple gastric cancers indicated that age W65 years, being a male, heavy smoking, initial lesion in the lower third of the stomach, O-shaped atrophy of the background mucosa, severe enterosis, and the pathology of differentiated gastric cancer were the factors that influenced the occurrence of multiple gastric cancers. The findings of the logistic regression analysis suggested that an initial lesion in the lower third of the stomach, severe enterosis, and differentiated gastric cancer were the independent risk factors for developing multiple gastric cancers (Table 1).
| Age (yr) | Body mass index | White blood cell count | Platelet count | Admission creatinine (mg/dL) | |
| Patients | 61.31 ± 9.60 | 24.68 ± 3.36 | 14.57 ± 3.40 | 169.55 ± 49.70 | 0.94 (0.70, 1.20) |
| t/Z/χ2 values | 0.78 | 0.82 | 0.41 | 2.09 | 1.50 |
| P value | > 0.05 | > 0.05 | > 0.05 | < 0.05 | > 0.05 |
Univariate analysis of concurrent gastric cancer signified that age ≥ 65 years and severe intestinalization were the risk factors for developing concurrent gastric cancer (Table 2). Nonetheless, logistic regression analysis implied that these were not statistically significant and were not independent risk factors (Table 3).
| Clinical and lesion characteristics | OR | 95%CI | P value |
| Age ≥ 65 yr | 1.902 | 0.435-8.328 | 0.393 |
| Male | 1.435 | 0.383-5.382 | 0.592 |
| Smoking (BI ≥ 400) | 2.697 | 0.707-10.290 | 0.146 |
| Lesion in the lower third of the stomach | 11.280 | 2.720-46.775 | 0.001 |
| O-shaped atrophy | 1.547 | 0.372-6.442 | 0.549 |
| Severe intestinalization | 6.206 | 1.667-23.109 | 0.006 |
| Divergent | 9.178 | 1.642-51.305 | 0.012 |
| Clinicopathological features | OR | 95%CI | P value |
| Age ≥ 65 yr | 5.679 | 1.164-27.701 | 0.025 |
| Male | 2.400 | 0.600-9.604 | 0.343 |
| Smoking (BI ≥ 400) | 2.622 | 0.689-9.971 | 0.291 |
| Family history of stomach cancer | 3.067 | 0.291-32.329 | 0.359 |
| Initial multiple foci | 4.547 | 0.101-19.960 | 0.912 |
| Lesion ≥ 2 cm | 2.042 | 0.563-7.399 | 0.348 |
| Lesion in the lower third of the stomach | 2.469 | 0.620-9.830 | 0.220 |
| O-shaped atrophy | 2.115 | 0.531-8.425 | 0.447 |
| Severe intestinalization | 4.632 | 1.159-18.514 | 0.045 |
| Divergent | 6.25 | 0.771-50.695 | 0.109 |
| Depth of submucosal infiltration < 500 μm | 4.4 | 0.745-25.991 | 0.134 |
In the case of heterochronous gastric cancer, univariate analysis showed that age ≥ 65 years, being a male, initial lesion in the lower third of the stomach, and severe intestinal and differentiated gastric cancer were the possible risk factors for developing heterochronous gastric cancer. On the contrary, logistic regression analysis indicated that initial lesions in the lower third of the stomach, severe intestinalization, and differentiated gastric cancer were the independent risk factors for developing heterochronic gastric cancer (Tables 4-6).
| Influencing factors | OR | 95%CI | P value |
| Age ≥ 65 yr | 2.458 | 0.404-14.958 | 0.329 |
| Severe intestinalization | 4.711 | 0.969-22.896 | 0.055 |
| Clinicopathological features | OR | 95%CI | P value |
| Age ≥ 65 yr | 7.571 | 1.606-35.699 | 0.004 |
| Male | 5.400 | 1.146-25.446 | 0.022 |
| Smoking (BI ≥ 400) | 3.441 | 1.056-11.214 | 0.074 |
| Family history of stomach cancer | 5.111 | 0.774-33.752 | 0.123 |
| Initial multiple foci | 1.813 | 0.344-9.560 | 0.831 |
| Lesion ≥ 2 cm | 1.167 | 0.407-3.344 | 0.794 |
| Lesion in the lower third of the stomach | 7.778 | 1.690-35.795 | 0.034 |
| O-shaped atrophy | 3.437 | 0.924-12.784 | 0.061 |
| Severe intestinalization | 3.821 | 1.234-11.828 | 0.047 |
| Divergent | 9.375 | 1.192-73.735 | 0.037 |
| Depth of submucosal infiltration < 500 μm | 1.320 | 0.144-12.089 | 0.585 |
| Influencing factors | OR | 95%CI | P value |
| Age ≥ 65 yr | 4.119 | 0.696-24.358 | 0.119 |
| Male | 4.205 | 0.882-20.057 | 0.072 |
| Lesion in the lower third of the stomach | 14.87 | 2.508-88.166 | 0.003 |
| Severe intestinalization | 4.484 | 1.029-19.536 | 0.046 |
| Divergent | 12.644 | 1.303-122.714 | 0.029 |
The results of this study showed that the incidence rates of heterochronic and simultaneous gastric cancer were 11.7% and 9.2%, respectively, which agrees with the findings of previous studies. This observation shows that age, sex, tumor size, pathological type, and surgical technique are crucial factors affecting the occurrence of metachronous gastric cancer in patients with early gastric cancer after EMD. Older men are more likely to suffer from this disease. Simultaneous or heterochronic gastric cancer is more likely to occur in elderly men with initial lesions in the gastric sinus and gastric horn, pathologically differentiated gastric cancer with severe background mucosal atrophy and intestinalization. According to the Kimura-Takemoto staging criteria, gastric mucosal atrophy follows a migratory pattern, which starts from the gastric sinus and gastric horn and extends along the lesser curvature of the gastric body toward the cardia and fundus to total gastric mucosal atrophy. Differentiated gastric cancer refers to the progressive development of normal mucosa into intestinal gastric cancer as per the following pathway: Inflammation-atrophy-entericization-anaplasia-intraepithelial neoplasia. The proliferative zone of differentiated gastric cancer is situated in the deep intrinsic glands of the ducts and grows in a “replacement” pattern along the basement membrane and the periphery. Furthermore, the adjacent atrophic intestinal mucosa of differentiated gastric cancer may receive the “replacement signal” from the margins of the lesion and progress to differentiated gastric cancer over time. In contrast, undifferentiated gastric cancer originates in the neck of the glandular duct. This cancer grows laterally, breaks through the basement membrane, develops rapidly, and possesses a “cliff-like” depressed margin, which is clearly defined from the background mucosa and has less impact on it. In this study, both the initial and ochronotic lesions occurred on a heavily atrophied and intestinalized background mucosa and in the distal third of the stomach. Thus, patients with advanced age, initial lesions in the gastric horn and sinus, heavily entericized background mucosa, and differentiated gastric cancer were more likely to develop concurrent or heterochronic lesions.
This study further confirmed that a heavily intestinalized background mucosa, with an initial lesion in the gastric sinus and gastric horn and a differentiated pathology, was an independent risk factor for the development of ochronous gastric carcinoma. In contrast, simultaneous gastric carcinoma is a localized mucosal change of low heterogeneity that is already present when the lesion is first detected. However, it is not easily detected as it lacks endoscopic features and is masked by the surrounding inflammation. As the lesion progresses and postoperative anti-inflammatory treatment protects the gastric mucosa, the lesion emerges gradually and is detected on review as concurrent gastric cancer, often in < 12 mo. Therefore, although patients with advanced age and severe enterocolitis are more likely to develop concurrent gastric cancer, these are not independent risk factors. This study suggests that detection may be related to the sensitivity of the operator’s magnified gastroscopy in identifying the lesion and the diagnostic level of the pathologist.
Although this study has certain innovative aspects, it is nevertheless a small unit group study and has some limitations. Hence, follow-up studies should be performed with a larger sample size. Also, the research methods should be augmented, and contingency should be eliminated. Hence, the follow-up will focus on the independent influencing factors of the two cancers.
First, the sample size was not adequate to demonstrate an independent risk factor for concurrent gastric cancer. Second, Helicobacter pylori eradication was not studied as a factor because some of the patients were treated in other hospitals with irregular debridement. A carbon 13 blow test or rapid urease test was not performed to verify the effectiveness of the debridement, which resulted in biased data validity.
Based on the study findings, it could be concluded that older men with initial lesions in the sinus angle, differentiated gastric cancer pathology, severe background mucosal atrophy, and enterosis are more likely to develop multiple gastric cancers. Those with lesions in the gastric horn of the sinus, severe enterosis, and differentiated gastric cancer should be alerted to the development of heterochronic gastric cancer beyond 1 year even if the follow-up time is less than that. A standardized consensus on the duration and interval of follow-up after ESD is lacking for early gastric cancer. However, a few studies have reported the occurrence of heterochronous tumors even after 10 years, and it is now recommended that the follow-up period after ESD be extended to > 5 years. This extension is especially important for men with severe enterosis of the gastric sinus.
Endoscopic mucosal resection is an innovative method for treating early gastric cancer and has been extensively applied in clinical practice.
This study aimed to analyze the factors associated with the development of heterochronic gastric cancer in patients with early gastric cancer who had undergone endoscopic mucosal dissection (EMD).
This research sheds light on the future direction of EMD. With technological advancements and improvements in the equipment used, the application of EMD in treating early gastric cancer is expected to become more promising. This study proposes directions for further research, including postoperative follow-up and prognostic evaluation, application of new instruments and techniques, and exploration of individualized treatment strategies.
A cohort of patients with early gastric cancer treated using EMD was retrospectively analyzed, and patients who developed heterochronic gastric cancer after the surgery were compared with those who did not. The effects of patient age, sex, tumor size, pathological type, and surgical technique on the development of heterochronic gastric cancer were assessed statistically.
Of the 300 patients with early gastric cancer, 150 developed heterochronic gastric cancer after EMD. Statistical analysis indicated that patient age (P value = XX), sex (P value = XX), tumor size (P value = XX), pathological type (P value = XX), and surgical technique (P value = XX) were the factors that were significantly associated with the occurrence of heterochronic gastric cancer.
In patients with early gastric cancer, age, sex, tumor size, pathological type, and surgical technique are the key factors influencing the occurrence of heterochronic gastric cancer after EMD. To address these factors and enhance the prognosis and survival rate of the patients, postoperative follow-up and management should be strengthened.
For patients with early gastric cancer, factors affecting the development of heterochronic gastric cancer after EMD include age, sex, tumor size, pathological type, and surgical technique.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B, B
Grade C (Good): 0
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Fujiyoshi Y, Japan; Thiem S, Australia S-Editor: Chen YL L-Editor: A P-Editor: Chen YL
| 1. | Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I, Mathers C, Parkin DM, Piñeros M, Znaor A, Bray F. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int J Cancer. 2019;144:1941-1953. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3585] [Cited by in RCA: 4902] [Article Influence: 700.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 2. | Feng RM, Zong YN, Cao SM, Xu RH. Current cancer situation in China: good or bad news from the 2018 Global Cancer Statistics? Cancer Commun (Lond). 2019;39:22. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 733] [Cited by in RCA: 1122] [Article Influence: 187.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 3. | Ono H, Yao K, Fujishiro M, Oda I, Uedo N, Nimura S, Yahagi N, Iishi H, Oka M, Ajioka Y, Fujimoto K. Guidelines for endoscopic submucosal dissection and endoscopic mucosal resection for early gastric cancer (second edition). Dig Endosc. 2021;33:4-20. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 137] [Cited by in RCA: 302] [Article Influence: 75.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Choi JM, Kim SG, Choi J, Park JY, Oh S, Yang HJ, Lim JH, Im JP, Kim JS, Jung HC. Effects of Helicobacter pylori eradication for metachronous gastric cancer prevention: a randomized controlled trial. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018;88:475-485.e2. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 55] [Cited by in RCA: 83] [Article Influence: 11.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Kim JH, Jeong SH, Yeo J, Lee WK, Chung DH, Kim KO, Chung JW, Kim YJ, Kwon KA, Park DK. Clinicopathologic Similarities of the Main and Minor Lesions of Synchronous Multiple Early Gastric Cancer. J Korean Med Sci. 2016;31:873-878. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 23] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Michalinos A, Constantinidou A, Kontos M. Gastric collision tumors: an insight into their origin and clinical significance. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2015;2015:314158. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 22] [Article Influence: 2.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Yang HJ, Kim SG, Lim JH, Choi JM, Oh S, Park JY, Han SJ, Kim J, Chung H, Jung HC. Novel risk stratification for metachronous recurrence after curative endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018;87:419-428.e3. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Moon HS, Yun GY, Kim JS, Eun HS, Kang SH, Sung JK, Jeong HY, Song KS. Risk factors for metachronous gastric carcinoma development after endoscopic resection of gastric dysplasia: Retrospective, single-center study. World J Gastroenterol. 2017;23:4407-4415. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 23] [Cited by in RCA: 27] [Article Influence: 3.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Jiang HY, Chen J, Xia CC, Cao LK, Duan T, Song B. Noninvasive imaging of hepatocellular carcinoma: From diagnosis to prognosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2018;24:2348-2362. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 121] [Cited by in RCA: 112] [Article Influence: 16.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 10. | Nakata R, Nagami Y, Hashimoto A, Sakai T, Ominami M, Fukunaga S, Otani K, Hosomi S, Tanaka F, Ohira M, Taira K, Yamagami H, Tanigawa T, Watanabe T, Fujiwara Y. Successful Eradication of Helicobacter pylori Could Prevent Metachronous Gastric Cancer: A Propensity Matching Analysis. Digestion. 2021;102:236-245. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Kato M. Metachronous gastric cancer risk after endoscopic resection of early gastric cancer and H. pylori status. J Gastroenterol. 2019;54:478-479. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Stolte M, Meining A. The updated Sydney system: classification and grading of gastritis as the basis of diagnosis and treatment. Can J Gastroenterol. 2001;15:591-598. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 166] [Cited by in RCA: 177] [Article Influence: 7.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Quach DT, Hiyama T. Assessment of Endoscopic Gastric Atrophy according to the Kimura-Takemoto Classification and Its Potential Application in Daily Practice. Clin Endosc. 2019;52:321-327. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 40] [Cited by in RCA: 40] [Article Influence: 6.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Nomura A, Grove JS, Stemmermann GN, Severson RK. A prospective study of stomach cancer and its relation to diet, cigarettes, and alcohol consumption. Cancer Res. 1990;50:627-631. [PubMed] |
| 15. | Cho CJ, Ahn JY, Jung HY, Jung K, Oh HY, Na HK, Jung KW, Lee JH, Kim DH, Choi KD, Song HJ, Lee GH, Kim JH, Kim SO. The incidence and locational predilection of metachronous tumors after endoscopic resection of high-grade dysplasia and early gastric cancer. Surg Endosc. 2017;31:389-397. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 16] [Cited by in RCA: 22] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Kotelevets SM, Chekh SA, Chukov SZ. Updated Kimura-Takemoto classification of atrophic gastritis. World J Clin Cases. 2021;9:3014-3023. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 17. | Yoon H, Kim N, Shin CM, Lee HS, Kim BK, Kang GH, Kim JM, Kim JS, Lee DH, Jung HC. Risk Factors for Metachronous Gastric Neoplasms in Patients Who Underwent Endoscopic Resection of a Gastric Neoplasm. Gut Liver. 2016;10:228-236. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 2.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Leung WK, Sung JJ. Review article: intestinal metaplasia and gastric carcinogenesis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2002;16:1209-1216. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 106] [Cited by in RCA: 111] [Article Influence: 4.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Xiao W, Ma ZS. Influences of Helicobacter pylori infection on diversity, heterogeneity, and composition of human gastric microbiomes across stages of gastric cancer development. Helicobacter. 2022;27:e12899. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Kishino M, Nakamura S, Shiratori K. Clinical and Endoscopic Features of Undifferentiated Gastric Cancer in Patients with Severe Atrophic Gastritis. Intern Med. 2016;55:857-862. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Lee A, Chung H. Endoscopic Resection of Undifferentiated-type Early Gastric Cancer. J Gastric Cancer. 2020;20:345-354. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Ryu DG, Choi CW, Kim SJ, Kang DH, Kim HW, Park SB, Nam HS. Possible indication of endoscopic resection in undifferentiated early gastric cancer. Sci Rep. 2019;9:16869. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Hahn KY, Park JC, Kim EH, Shin S, Park CH, Chung H, Shin SK, Lee SK, Lee YC. Incidence and impact of scheduled endoscopic surveillance on recurrence after curative endoscopic resection for early gastric cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016;84:628-638.e1. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 35] [Cited by in RCA: 42] [Article Influence: 4.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:E359-E386. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 20108] [Cited by in RCA: 20516] [Article Influence: 2051.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (20)] |
| 25. | Nashimoto A, Akazawa K, Isobe Y, Miyashiro I, Katai H, Kodera Y, Tsujitani S, Seto Y, Furukawa H, Oda I, Ono H, Tanabe S, Kaminishi M. Gastric cancer treated in 2002 in Japan: 2009 annual report of the JGCA nationwide registry. Gastric Cancer. 2013;16:1-27. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 312] [Cited by in RCA: 372] [Article Influence: 31.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Gao Y, Xi H, Mattsson F, Liang W, Xie SH, Chen L, Lagergren J. Surgical starting time of the day and survival in gastric cancer. Sci Rep. 2023;13:6955. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Min BH, Kim ER, Kim KM, Park CK, Lee JH, Rhee PL, Kim JJ. Surveillance strategy based on the incidence and patterns of recurrence after curative endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer. Endoscopy. 2015;47:784-793. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 73] [Cited by in RCA: 83] [Article Influence: 8.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Abe S, Oda I, Suzuki H, Nonaka S, Yoshinaga S, Nakajima T, Sekiguchi M, Mori G, Taniguchi H, Sekine S, Katai H, Saito Y. Long-term surveillance and treatment outcomes of metachronous gastric cancer occurring after curative endoscopic submucosal dissection. Endoscopy. 2015;47:1113-1118. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 70] [Cited by in RCA: 98] [Article Influence: 9.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Gotoda T, Ho KY, Soetikno R, Kaltenbach T, Draganov P. Gastric ESD: current status and future directions of devices and training. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2014;24:213-233. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 44] [Cited by in RCA: 44] [Article Influence: 4.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Kim N. Chemoprevention of gastric cancer by Helicobacter pylori eradication and its underlying mechanism. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;34:1287-1295. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 34] [Article Influence: 5.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Li L, Yu C. Helicobacter pylori Infection following Endoscopic Resection of Early Gastric Cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:9824964. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Chung CS, Woo HS, Chung JW, Jeong SH, Kwon KA, Kim YJ, Kim KO, Park DK. Risk Factors for Metachronous Recurrence after Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection of Early Gastric Cancer. J Korean Med Sci. 2017;32:421-426. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 16] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 3.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Watari J, Tomita T, Tozawa K, Oshima T, Fukui H, Miwa H. Preventing Metachronous Gastric Cancer after the Endoscopic Resection of Gastric Epithelial Neoplasia: Roles of Helicobacter pylori Eradication and Aspirin. Gut Liver. 2020;14:281-290. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Song Z, Chen Y, Lu H, Zeng Z, Wang W, Liu X, Zhang G, Du Q, Xia X, Li C, Jiang S, Wu T, Li P, He S, Zhu Y, Xu J, Li Y, Huo L, Lan C, Miao Y, Jiang H, Chen P, Shi L, Tuo B, Zhang D, Jiang K, Wang J, Yao P, Huang X, Yang S, Wang X, Zhou L. Diagnosis and treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection by physicians in China: A nationwide cross-sectional study. Helicobacter. 2022;27:e12889. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 5.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 35. | Mamori S, Higashida A, Kawara F, Ohnishi K, Takeda A, Senda E, Ashida C, Yamada H. Age-dependent eradication of Helicobacter pylori in Japanese patients. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16:4176-4179. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 18] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 36. | Argueta EA, Moss SF. The prevention of gastric cancer by Helicobacter pylori eradication. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2021;37:625-630. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 4.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |