Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Sep 15, 2020; 12(9): 942-956
Published online Sep 15, 2020. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v12.i9.942
Published online Sep 15, 2020. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v12.i9.942
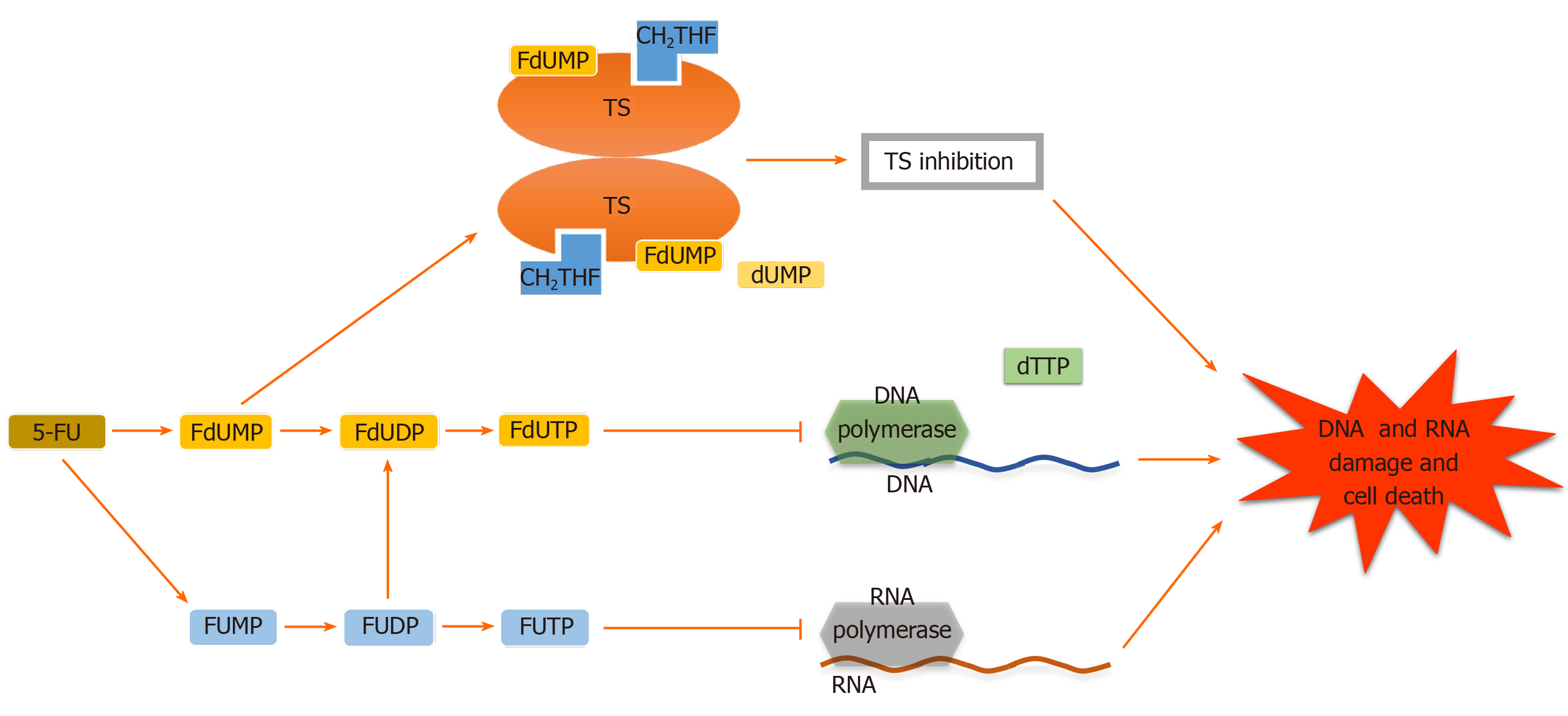
Figure 1 Different mechanisms of 5-fluorouracil action.
5-Fluorouracil (5_FU) and its derivative active metabolites exert their antitumor function at the levels of enzyme thymidylate synthase, DNA and RNA, leading to DNA and RNA damage and cell death. TS: Thymidylate synthase; FdUMP: Fluorodeoxyuridine’ monophosphate; FdUDP: Fluorodeoxyuridine diphosphate; FdUTP: Fluorodeoxyuridine triphosphate; FUMP: Fluorouridine monophosphate; FUDP: Fluorouridine diphosphate; FUTP: Fluorouridine triphosphate; CH2THF: 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate; dTTP: Deoxythymidine triphosphate; dUMP: Deoxyuridine monophosphate.
- Citation: Sabeti Aghabozorgi A, Moradi Sarabi M, Jafarzadeh-Esfehani R, Koochakkhani S, Hassanzadeh M, Kavousipour S, Eftekhar E. Molecular determinants of response to 5-fluorouracil-based chemotherapy in colorectal cancer: The undisputable role of micro-ribonucleic acids. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2020; 12(9): 942-956
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v12/i9/942.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v12.i9.942