Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Mar 15, 2016; 8(3): 305-313
Published online Mar 15, 2016. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v8.i3.305
Published online Mar 15, 2016. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v8.i3.305
Figure 1 The experimental protocol.
VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.
Figure 2 Administration of N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine induced macroscopic changes: Gastritis, atrophic gastritis, dysplasia and gastric tumor in rats (A) and respective microscopic changes were observed by hematoxylin and eosin staining (B).
Figure 3 Expression of p-signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 and vascular endothelial growth factor in the model groups.
A: The expression of p-signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) measured by immunohistochemistry. From a normal sample to samples with tumor induced by the administration of N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine, the expression of p-STAT3 was more obvious; B: Similar results for the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor were observed.
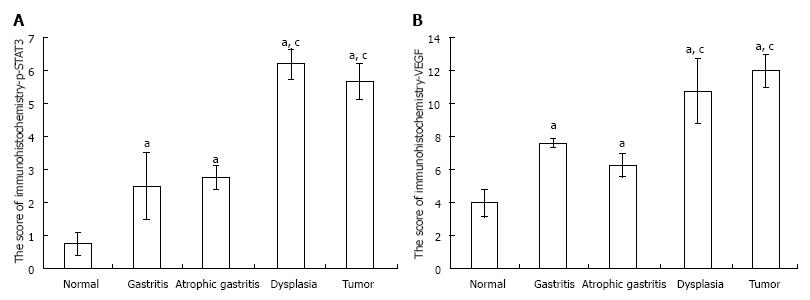
Figure 4 Immunohistochemical score of p-signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 and vascular endothelial growth factor.
A: The immunohistochemical score of p-signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) was significantly increased by N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine during the progression from gastritis to gastric tumor. The p-STAT3 score in precancerous lesions and tumor samples was significantly higher than that in the normal sample; and the p-STATS score in dysplasia samples was significantly higher than that in gastritis and atrophic gastritis, which was comparable to that in tumor samples; B: Similar results were observed for the vascular endothelial growth factor score (aP < 0.05 vs normal group; cP < 0.05 vs gastritis or atrophic gastritis).
Figure 5 Protein expression of p-signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 and vascular endothelial growth factor.
A: The protein expression of p-signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT3) in dysplasia and tumor samples was more obvious than that in the other samples; B: The protein expression of p-STAT3 in dysplasia and tumor samples was significantly higher than that in gastritis and atrophic gastritis samples, but the difference between the dysplasia and tumor samples was not significant. The same results were observed for gastritis and atrophic gastritis samples; C: Consistent results were found for the protein expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in samples (aP < 0.05 vs normal group; cP < 0.05 vs gastritis or atrophic gastritis).
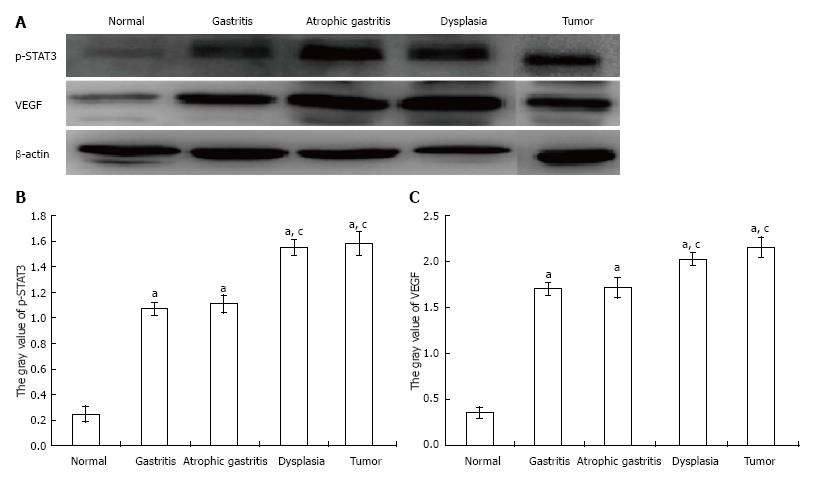
Figure 6 Protein expression of p-signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 and vascular endothelial growth factor.
A: The protein expression of p-signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT3) in dysplasia and tumor samples was more obvious than that in the other samples; B: The protein expression of p-STAT3 in dysplasia and tumor samples was significantly higher than that in gastritis and atrophic gastritis samples, but the difference between the dysplasia and tumor samples was not significant. The same results were observed for gastritis and atrophic gastritis samples; C: Consistent results were found for the protein expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in samples (aP < 0.05 vs normal group; cP < 0.05 vs gastritis or atrophic gastritis).
- Citation: Wang XY, Wang LL, Zheng X, Meng LN, Lyu B, Jin HF. Expression of p-STAT3 and vascular endothelial growth factor in MNNG-induced precancerous lesions and gastric tumors in rats. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2016; 8(3): 305-313
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v8/i3/305.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v8.i3.305