Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Apr 15, 2025; 17(4): 103591
Published online Apr 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i4.103591
Published online Apr 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i4.103591
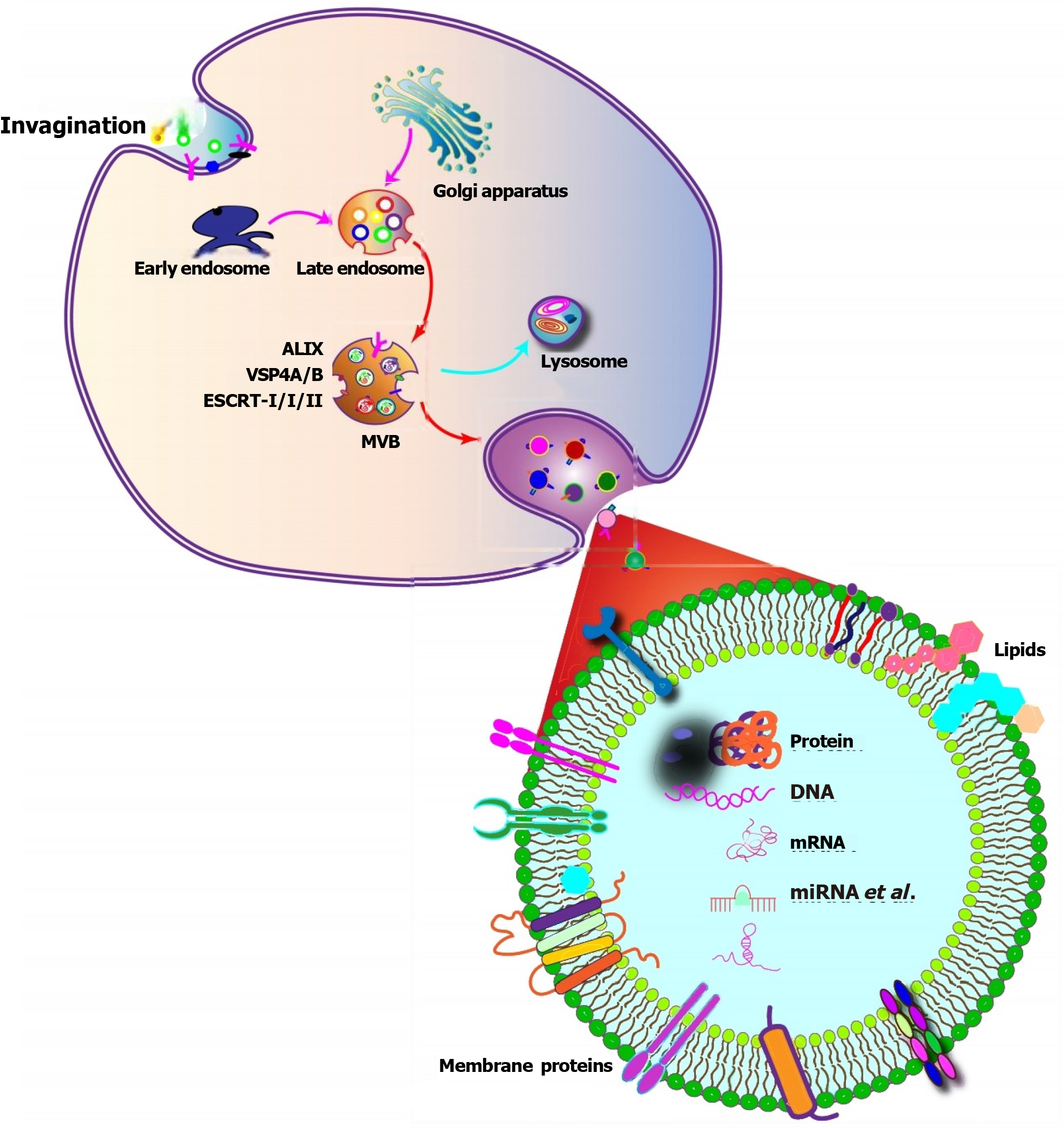
Figure 1 General illustration of exosome biogenesis and structural components.
Membrane outgrowth from the endosomal system produces early endosomes and subsequently multivesicular bodies of intraluminal vesicles. Once formed, multivesicular body fuse with the plasma membrane and release intraluminal vesicle contents. The endosomal sorting complex machinery pathway, Alix and tetraspanin are involved in the transport and biogenesis of exosomes. ESCRT: Endosomal sorting complex required for transport; MVB: Multivesicular body; miRNA: MicroRNA.
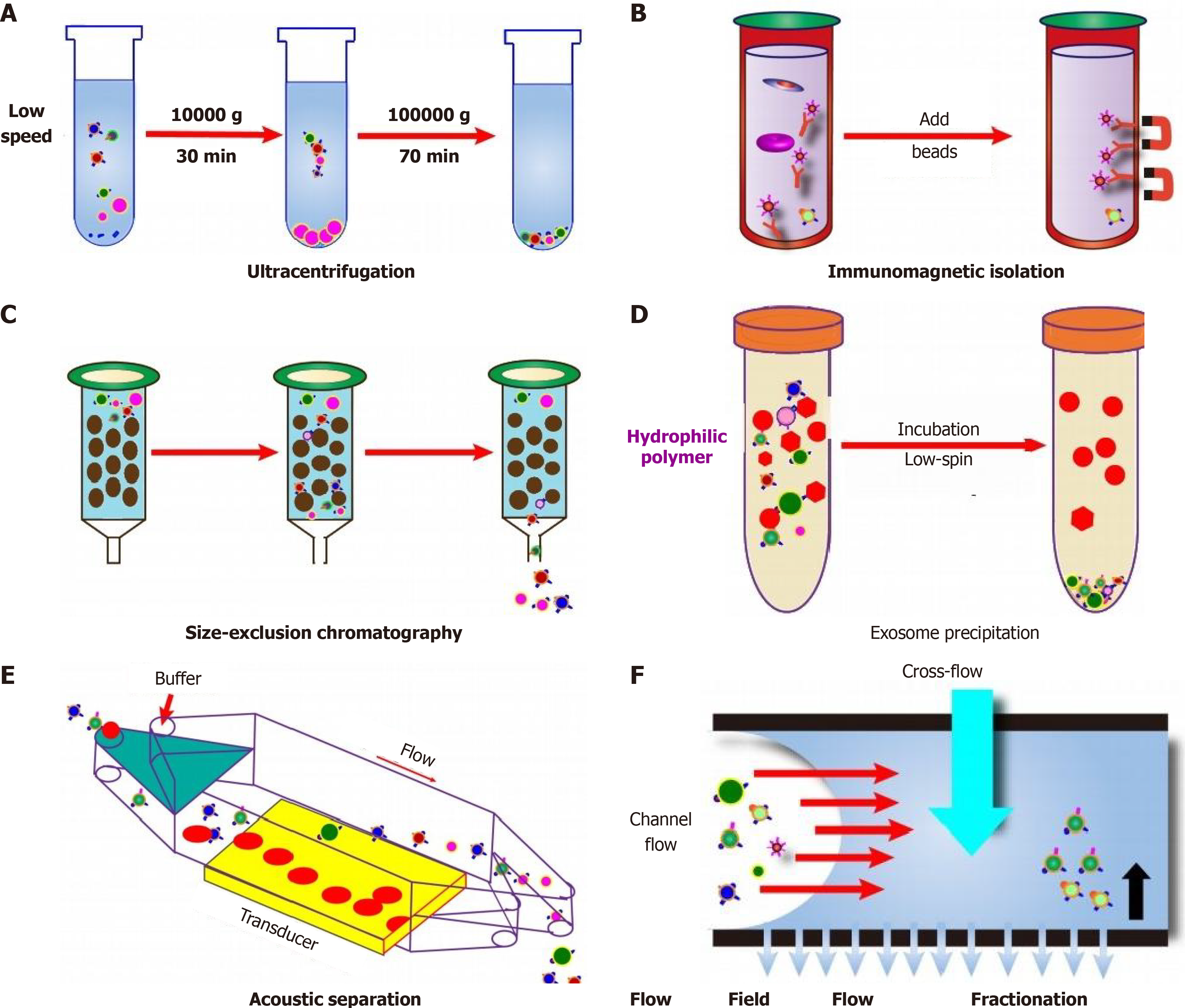
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of extracellular vesicles isolation methods and principles.
A: Ultracentrifugation is used to separate extracellular vesicles based on the precipitation subjected to their size/density; B: Using immunoaffinity magnetic beads are added to the exosome mixture and the beads with captured extracellular vesicles are separated by magnets; C: Particles of different sizes are compressed through the porous matrix and pass through the column at different speeds; D: Addition of a precipitation reagent induces that exosomes can be separated by centrifugation at a lower speed; E and F: Acoustic-based microfluidic device (E) and flow field flow fractionation (F) take advantage of the unique biophysical properties of exosomes that is capable of high-throughput separation of exosome based on field microfluidic devices use external forces (e.g., surface acoustic waves) or physical barriers to completely separate exosomes along the flow direction. Large particles are deflected to one side, while smaller exosomes are deflected to the other side.
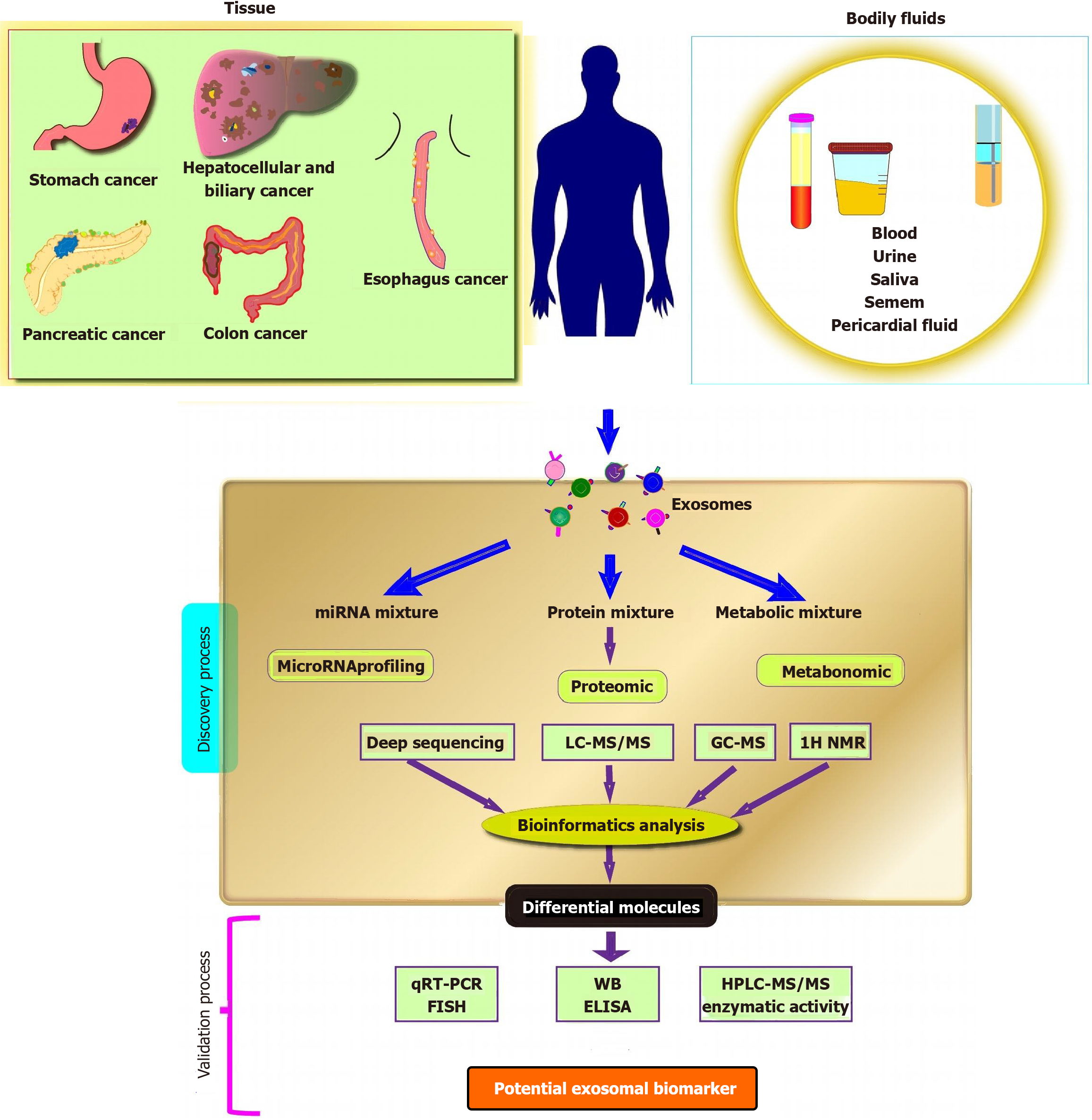
Figure 3 Clinical application of exosomal biomarkers for gastrointestinal diagnostic.
Biopsies of exosomes include tumor tissue, blood, urine, saliva and feces. These sources contain cancer-derived exosome-encapsulated microRNAs, proteins and metabolic molecules. Treatment efficacy is monitored in real time by detecting and quantifying these molecular targets in association with tumor stage. miRNA: MicroRNA; LC-MS/MS: Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry; GC-MS: Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry; qRT-PCR: Quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction; FISH: Fluorescence in situ hybridization; WB: Western blot; ELISA: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; HPLC-MS/MS: High performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.
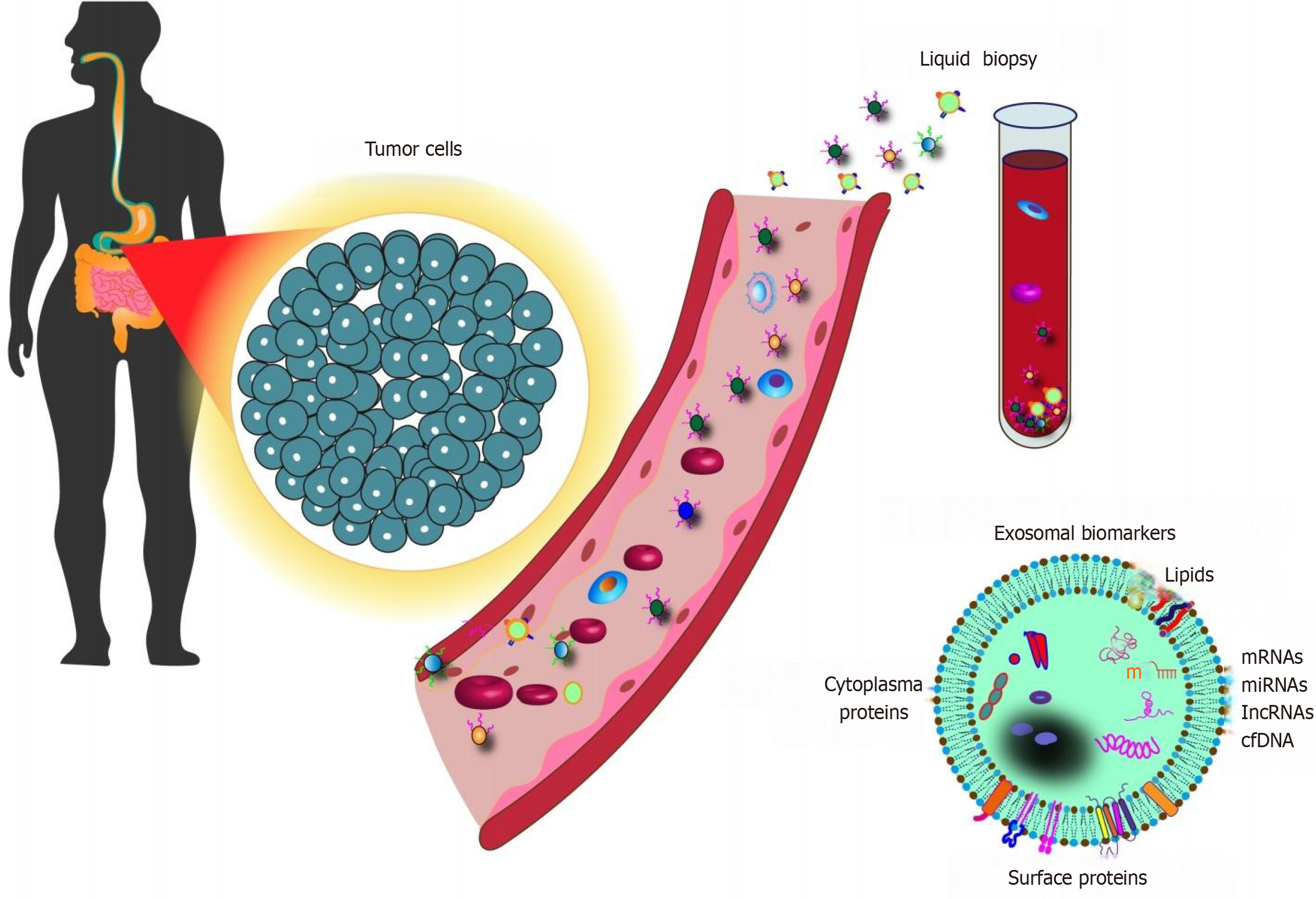
Figure 4 Graphic abstract.
Application of exosomal biomarkers as liquid biopsy in clinical diagnosis of gastrointestinal cancers. miRNA: MicroRNA; lncRNA: Long noncoding RNA; cfDNA: Cell-free DNA.
- Citation: Zhang Y, Yue NN, Chen LY, Tian CM, Yao J, Wang LS, Liang YJ, Wei DR, Ma HL, Li DF. Exosomal biomarkers: A novel frontier in the diagnosis of gastrointestinal cancers. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(4): 103591
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i4/103591.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i4.103591