Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Apr 15, 2025; 17(4): 102619
Published online Apr 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i4.102619
Published online Apr 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i4.102619
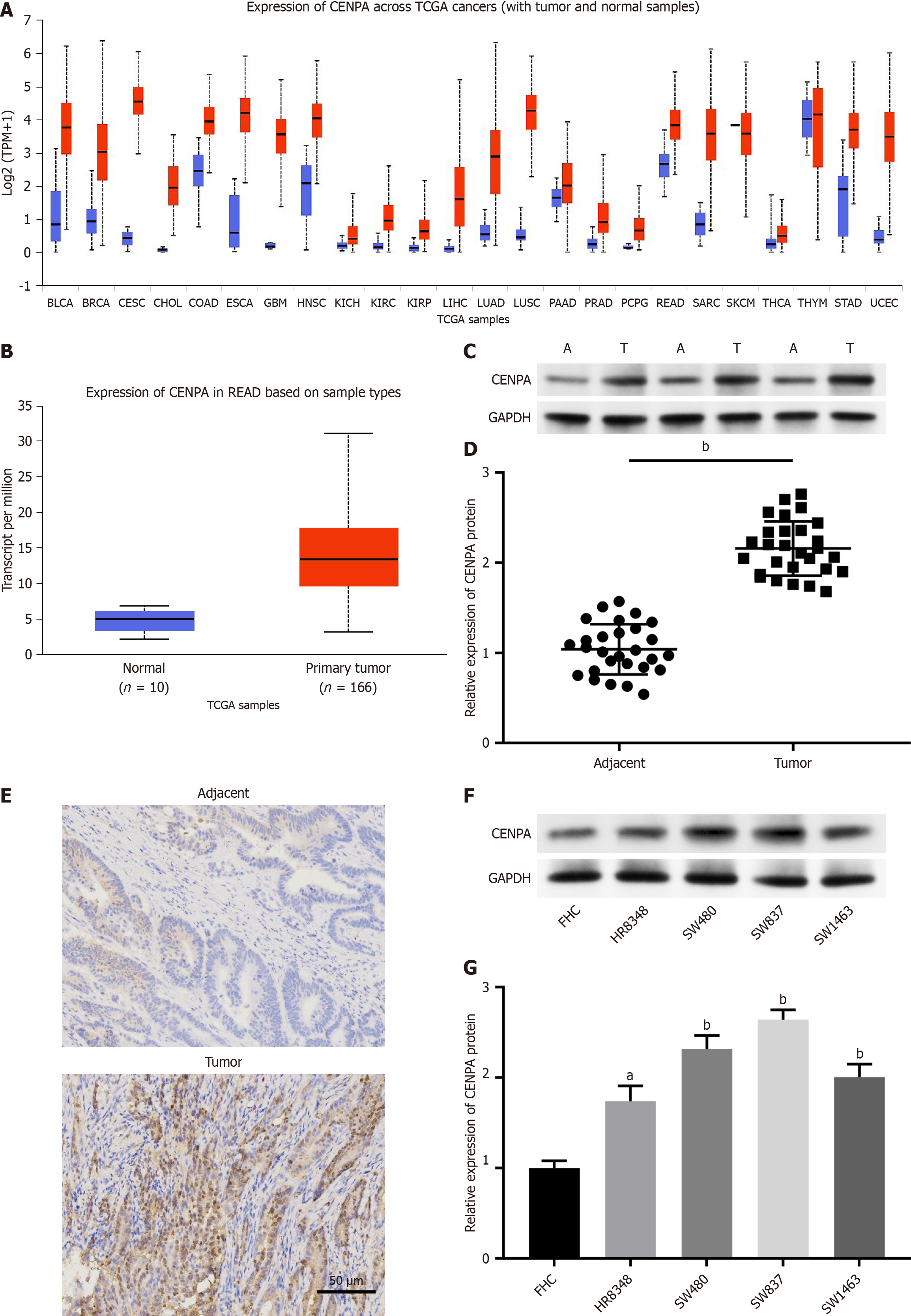
Figure 1 Centromere protein A is upregulated in rectal cancer.
A: Centromere protein A (CENPA) expression in various cancer types in the UALCAN database (http://ualcan.path.uab.edu/index.html); B: Relative CENPA expression in rectal cancer tissues and normal tissues shown in UALCAN database; C and D: Relative CENPA protein level in rectal cancer tissues and adjacent tissues (n = 28 per group) was examined using Western blot analysis; E: Immunohistochemistry assay was used to examine CENPA protein levels in collected tissues; F and G: Relative expression of CENPA in SW480, HR8348, SW837, and SW1463 cells measured through Western blot analysis. Data are presented as mean ± SE. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; A: Adjacent; T: Tumor; CENPA: Centromere protein A.
Figure 2 Effects of Centromere protein A overexpression and knockdown on the proliferation, invasion, apoptosis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of rectal cancer cells.
A and B: Centromere protein A protein expression in SW837 and SW480 cells was measured using Western blot analysis; C and D: SW837 and SW480 cell proliferation were examined using Cell Counting kit-8 assay; E-G: Cell invasion measured by Transwell assay (E) and quantitative analysis in SW837 (F) and SW480 (G) cells; H-K: Cell apoptosis of SW837 (H and I) and SW480 (J and K) cells examined using flow cytometry; L-O: E-cadherin, N-cadherin and vimentin levels in SW837 (L and M) and SW480 (N and O) cells were measured using Western blot analysis. Data are presented as mean ± SE. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; CENPA: Centromere protein A; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; MGMT: O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase; sh-CENPA: Short hairpin RNAs targeting Centromere protein A; sh-MGMT: Short hairpin RNAs targeting O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase; sh-PTPN4: Short hairpin RNAs targeting protein tyrosine phosphatase nonreceptor type 4.
Figure 3 Centromere protein A promoted DNA methyltransferase 1-mediated O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase methylation.
A: Schematic diagram for screening interacting proteins of centromere protein A (CENPA); B: DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) has correlation with CENPA in rectal cancer as shown by the Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis (GEPIA) database; C: Interaction between CENPA and DNMT1 verified using co-immunoprecipitation assay; D: CpG islands within the methyltransferase (MGMT) promoter region; E: DNMT1 enrichment of the MGMT promoter region examined through chromatin immunoprecipitation assay; F: Methylation-specific PCR was used to examine MGMT methylation level in SW837 cells; G: MGMT mRNA levels were measured using RT-qPCR; H: MGMT protein levels were measured using Western blot analysis. Data are presented as mean ± SE. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; U: Unmethylated; M: Methylated; CENPA: Centromere protein A; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; DNMT1: DNA methyltransferase 1; MGMT: O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase; sh-CENPA: Short hairpin RNAs targeting Centromere protein A.
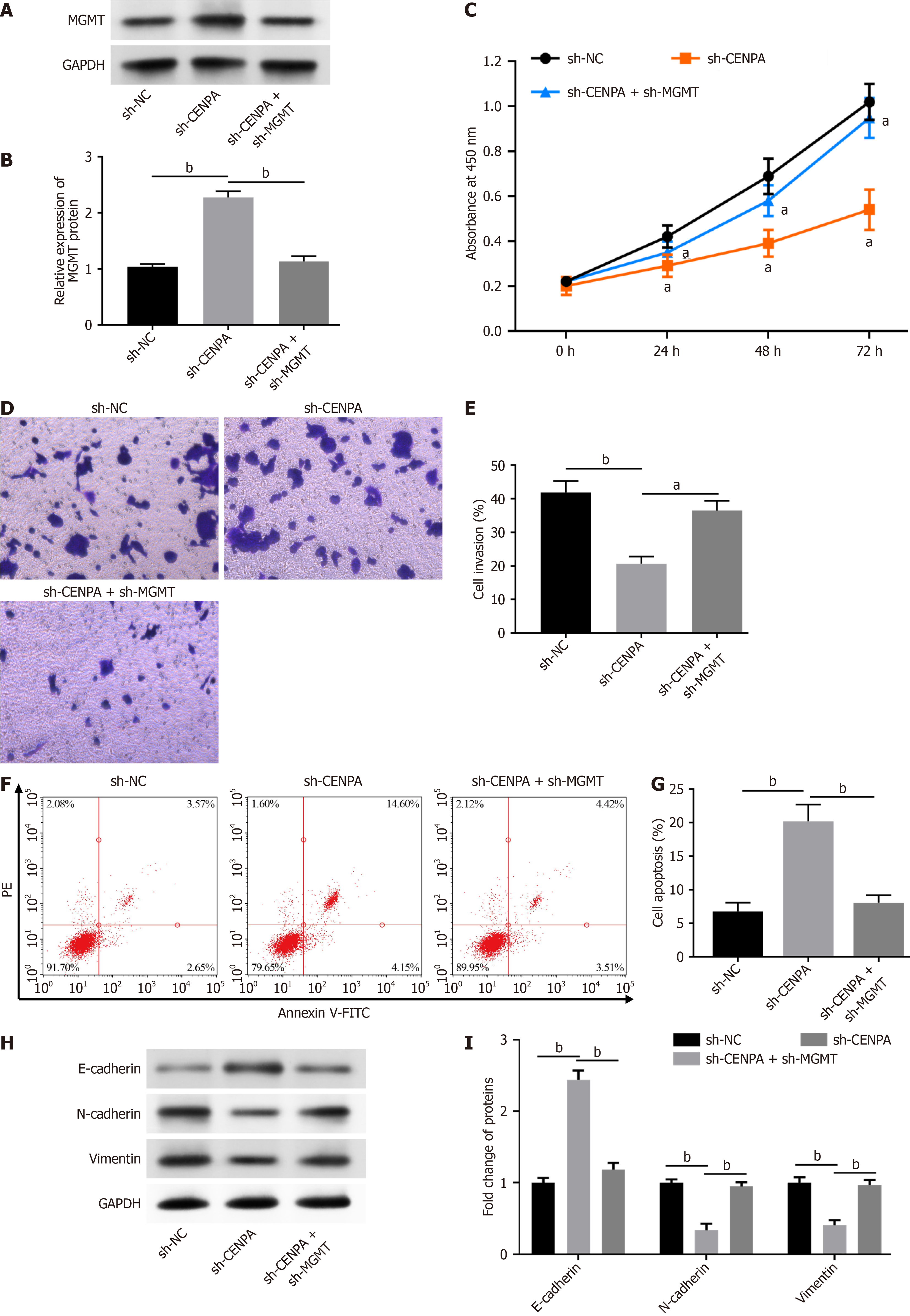
Figure 4 O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase knockdown abolished the effects of centromere protein A knockdown on rectal cancer cell progression.
A and B: O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase protein levels in SW837 cells were measured by Western blot analysis; C: SW837 cell proliferation was detected using Cell Counting kit-8 assay; D and E: Transwell assay used to detect SW837 cell invasion; F and G: SW837 cell apoptosis examined using flow cytometry; H and I: E-cadherin, N-cadherin and vimentin levels in SW837 cells were examined via Western blot analysis. Data are presented as mean ± SE. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; CENPA: Centromere protein A; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; DNMT1: DNA methyltransferase 1; MGMT: O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase; sh-CENPA: Short hairpin RNAs targeting Centromere protein A; sh-MGMT: Short hairpin RNAs targeting O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase.
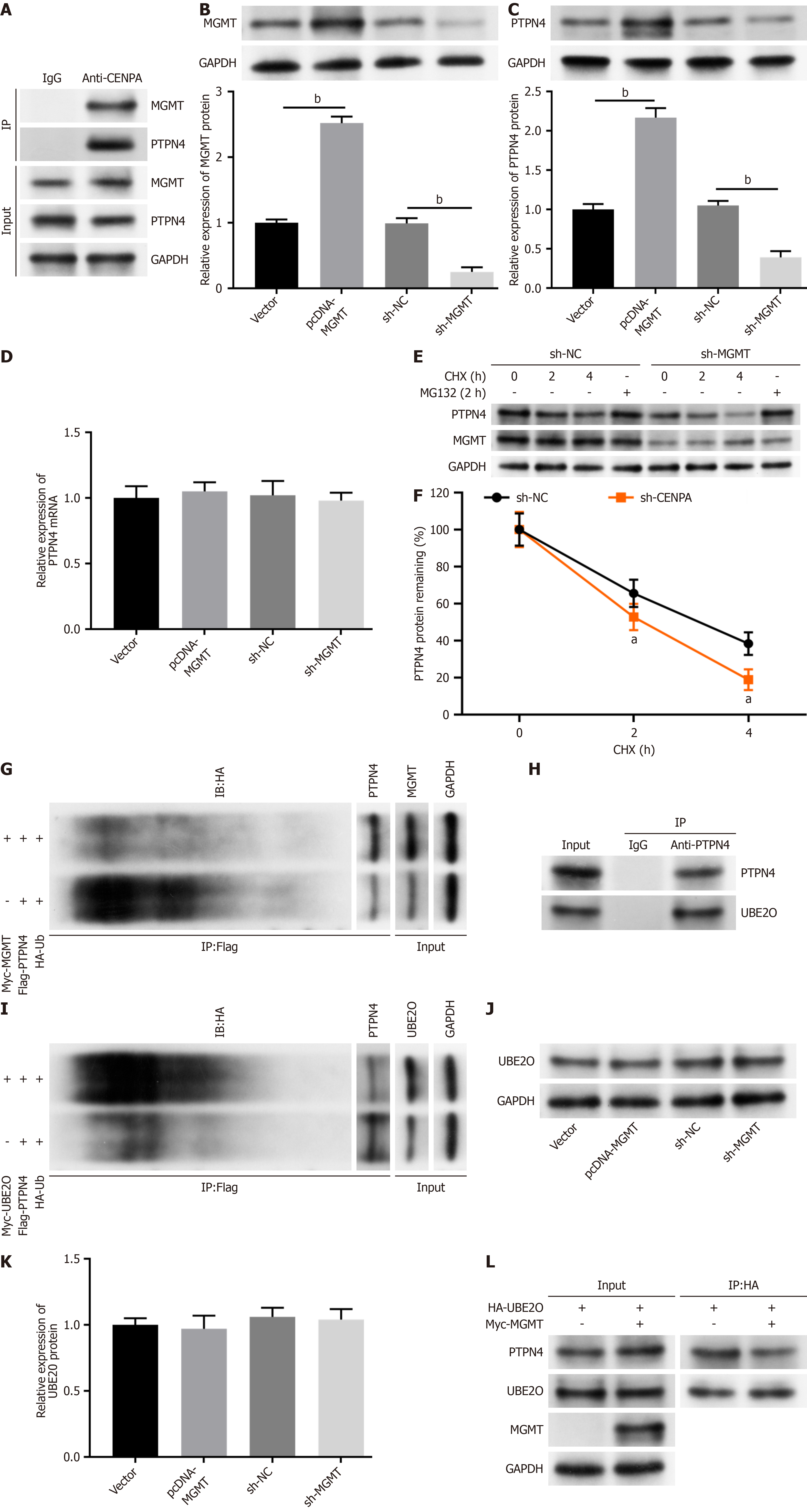
Figure 5 O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase interacted with protein tyrosine phosphatase nonreceptor type 4 and increased phosphatase nonreceptor type 4 protein stability.
A: Co-immunoprecipitation assay showing the interaction of O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase with phosphatase nonreceptor type 4 (PTPN4); B and C: Western blot assay was used to examine methyltransferase (MGMT) and PTPN4 protein levels; D: PTPN4 mRNA expression was assessed with quantitative reverse transcription PCR; E and F: PTPN4 protein stability was evaluated after treatment with cycloheximide and MG132 for indicated times; G: PTPN4 protein ubiquitination were detected after MGMT overexpression; H: Co-immunoprecipitation assay showing the interaction of ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2O (UBE2O) with PTPN4; I: PTPN4 protein ubiquitination were detected after UBE2O overexpression; J and K: Western blot assay was used to measure UBE2O protein levels after MGMT overexpression and knockdown; L: MGMT reduced the interaction between UBE2O and PTPN4. Data are presented as mean ± SE. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; CENPA: Centromere protein A; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; MGMT: O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase; PTPN4: Protein tyrosine phosphatase nonreceptor type 4; sh-CENPA: Short hairpin RNAs targeting Centromere protein A; sh-MGMT: Short hairpin RNAs targeting O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase; sh-PTPN4: Short hairpin RNAs targeting protein tyrosine phosphatase nonreceptor type 4; UBE2O: Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2O.
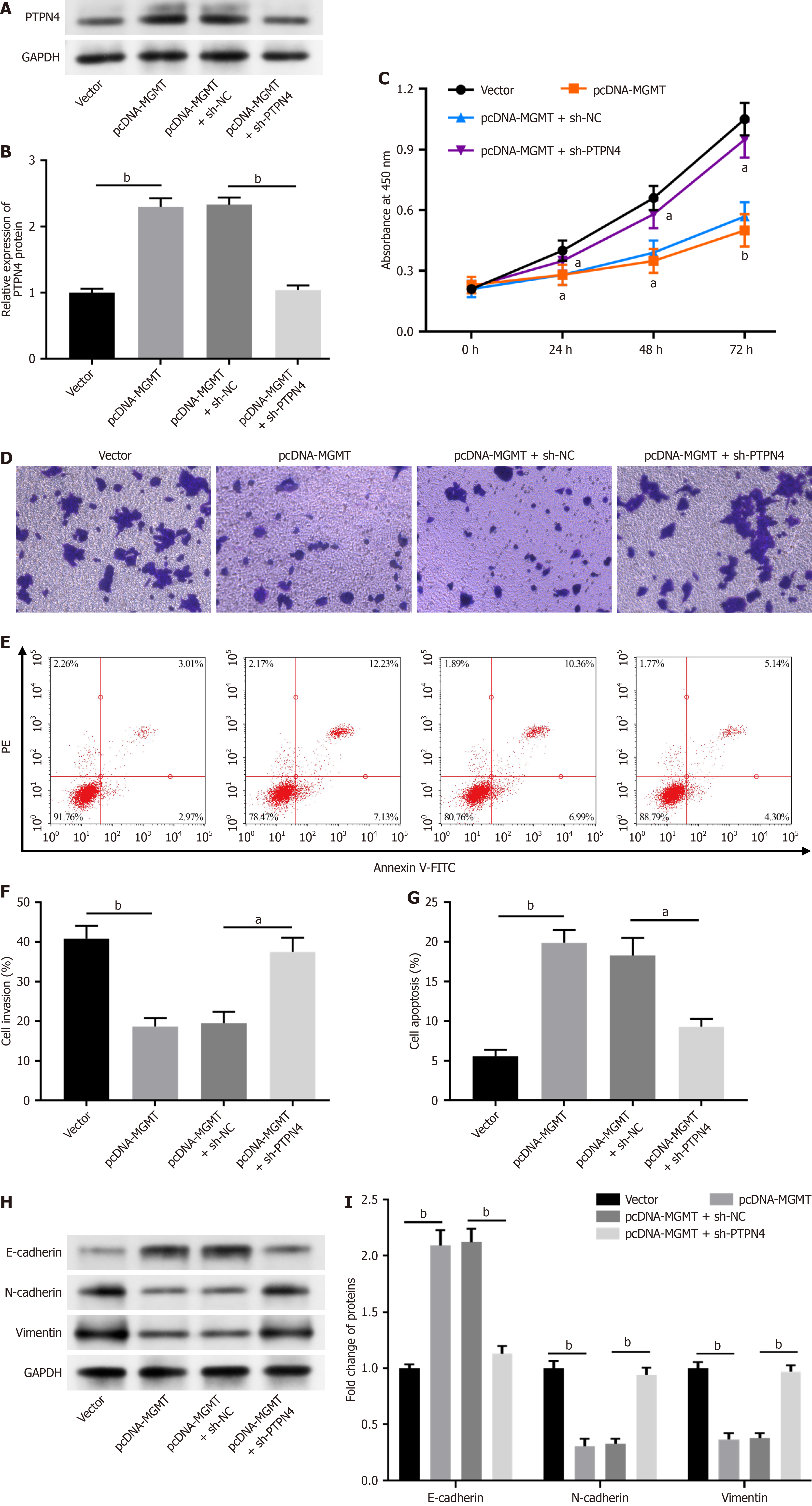
Figure 6 O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase inhibited rectal cancer progression by reducing protein tyrosine phosphatase nonreceptor type 4 expression.
A and B: Protein tyrosine phosphatase nonreceptor type 4 (PTPN4) protein levels in SW837 cells were assessed through Western blot analysis; C: SW837 cell proliferation detected using Cell Counting kit-8 assay; D and E: Transwell assay performed used to assess SW837 cell invasion; F and G: SW837 cell apoptosis was examined using flow cytometry; H and I: E-cadherin, N-cadherin and vimentin levels in SW837 cells were measured using Western blot analysis. Data are presented as mean ± SE. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; MGMT: O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase; PTPN4: Protein tyrosine phosphatase nonreceptor type 4; sh-MGMT: Short hairpin RNAs targeting O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase; sh-PTPN4: Short hairpin RNAs targeting protein tyrosine phosphatase nonreceptor type 4.
Figure 7 Centromere protein A knockdown inhibited rectal cancer tumor growth in xenograft mice.
A: Tumor images; B and C: Tumor volumes (B) and tumor weights (C) were recorded; D and E: CEPNA, O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase, and protein tyrosine phosphatase nonreceptor type 4 levels were detected using immunohistochemistry; F and G: The protein level of proliferation marker Ki67 protein was detected using immunohistochemistry. Data are presented as mean ± SE. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; CENPA: Centromere protein A; MGMT: O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase; PTPN4: Protein tyrosine phosphatase nonreceptor type 4; sh-CENPA: Short hairpin RNAs targeting Centromere protein A; sh-MGMT: Short hairpin RNAs targeting O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase; sh-PTPN4: Short hairpin RNAs targeting protein tyrosine phosphatase nonreceptor type 4.
- Citation: Xin MJ, Yuan Y. Centromere protein A knockdown inhibits rectal cancer through O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase/protein tyrosine phosphatase nonreceptor type 4 axis. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(4): 102619
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i4/102619.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i4.102619