Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jun 15, 2024; 16(6): 2769-2780
Published online Jun 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i6.2769
Published online Jun 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i6.2769
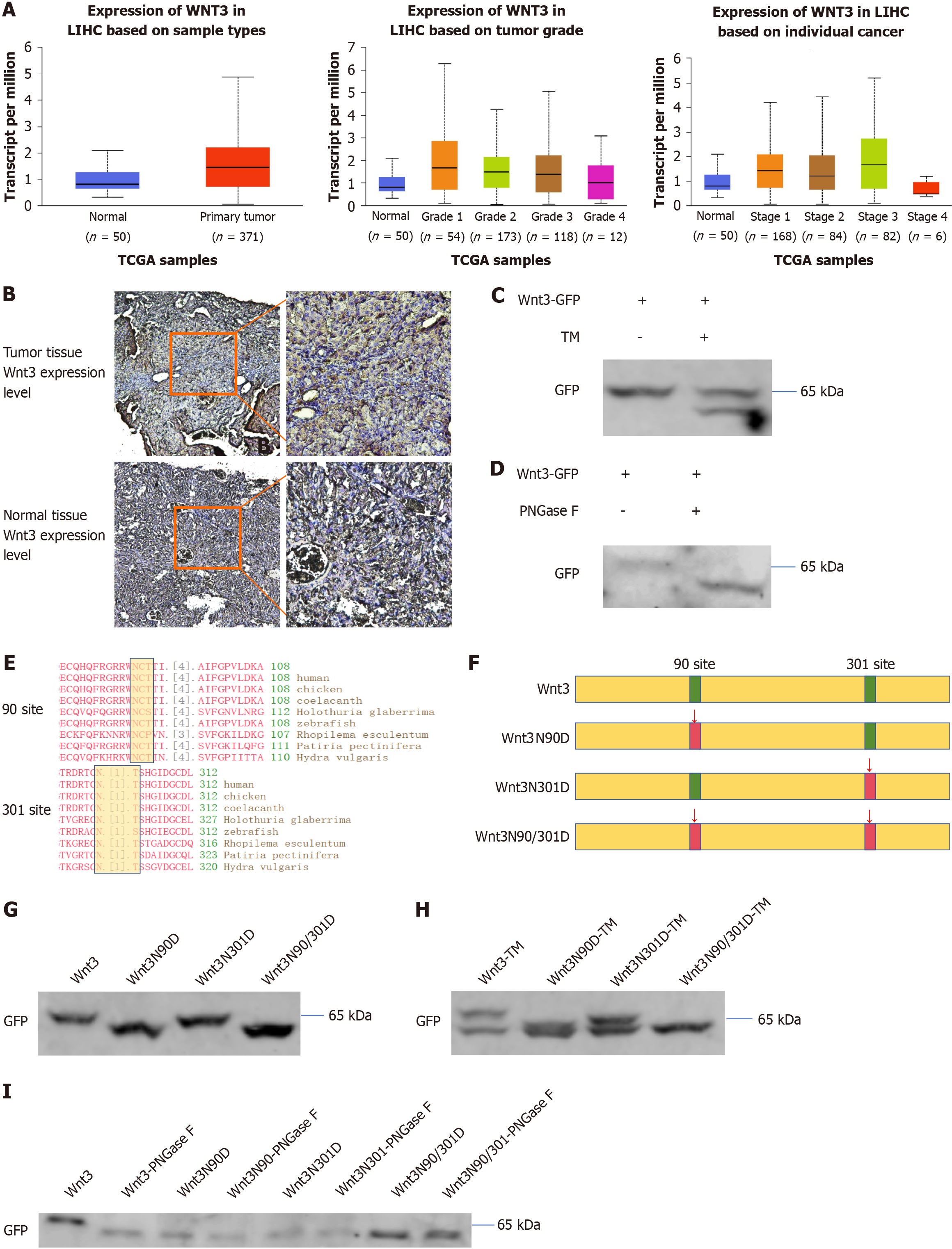
Figure 1 Wnt3 is upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and modified by N-glycosylation at residues 90 and 301.
A: According to the TCGA database query, the expression level of Wnt3 increased during the early stage of hepatocellular carcinoma; B: DEN and TAA were used to induce primary liver cancer in C3H mice, and normal mouse liver tissue was used as a control. The expression of Wnt3 in the two tissues was detected by immunohistochemical staining; C and H: Wnt3-GFP was transfected into PLC/PRF/5 cells for 36 h, which were then treated with TM for 24 h at a working concentration of 2.5 μg/mL; D and I: PLC/PRF/5 cells were transfected with Wnt3-GFP for 48 h, after which the cells were collected. Wnt3 was purified with a GFP tag, and the purified protein was treated according to the instructions of the PNGase F deglycosylation kit; E: Query of conserved areas of Wnt3 identified through the National Center for Biotechnology Information database; F: Schematic diagram showing the construction of site-directed Wnt3 mutants; G: Forty-eight hours after transfection, the cells were collected and subjected to Western blotting. LIHC: Liver hepatocellular carcinoma; GFP: Green fluorescent protein.
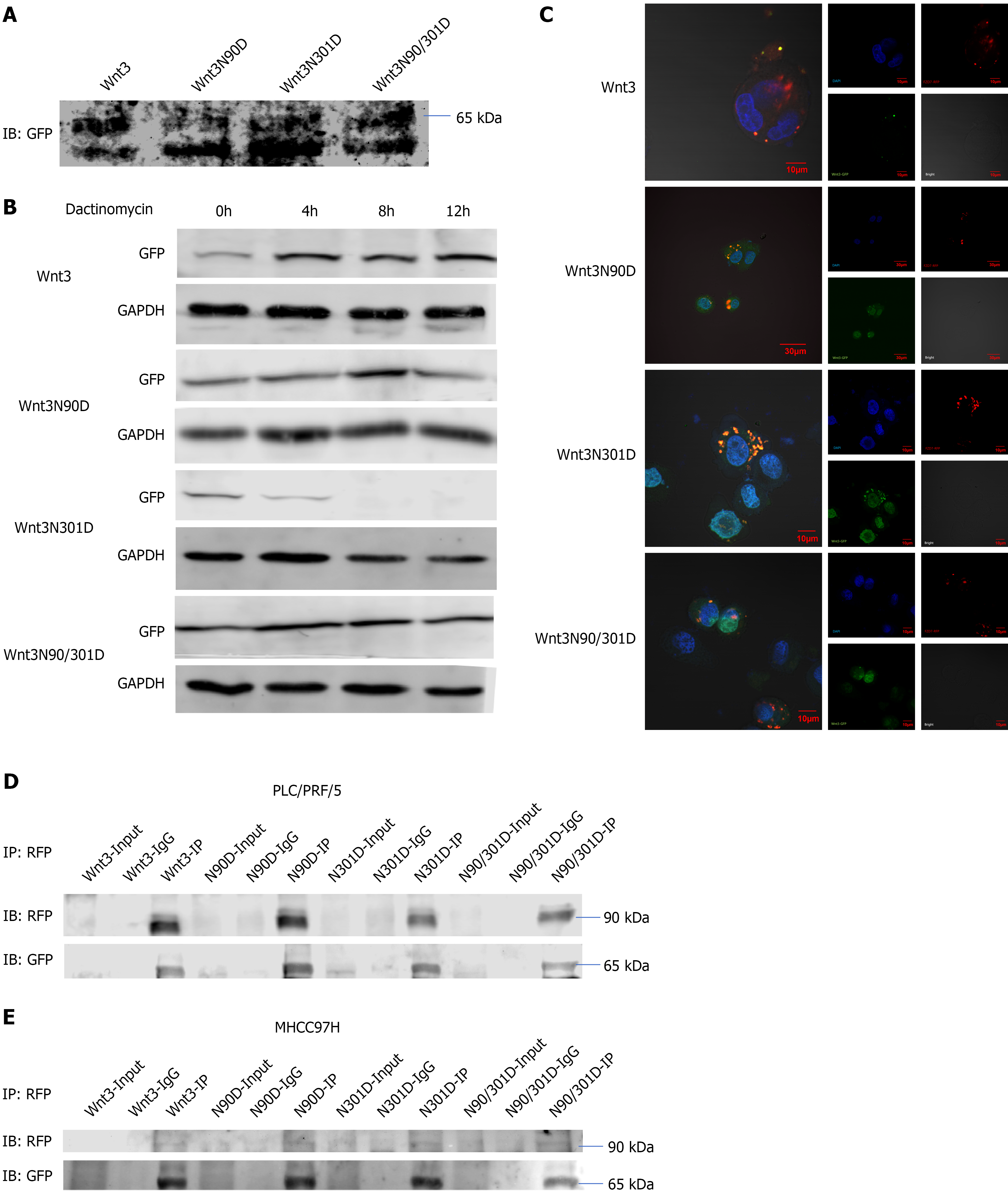
Figure 2 N-glycosylation affects the stability of Wnt3 and its ability to bind to the FZD7 receptor.
A: The medium was replaced with serum-free medium 36 h after the transfection of PLC/PRF/5 cells. Twenty-four hours later, the medium was collected, ultrafiltration tubes were used for concentration, and then the samples were prepared for detection; B: At 36 h after the transfection of PLC/PRF/5 cells, actinomycin D was added, and the working concentration was 20 μg/mL; C: Localization of Wnt3 and its N-glycosylation deletion mutants (green) and FZD7 (red) in PLC/PRF/5 cells. The nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue); D and E: In PLC/PRF/5 and MHCC97H cells, anti-RFP was used for pull-down, and anti-GFP was used for detection. GFP: Green fluorescent protein; RFP: Red fluorescent protein; IP: Immunoprecipitation; IB: Immunoblotting.
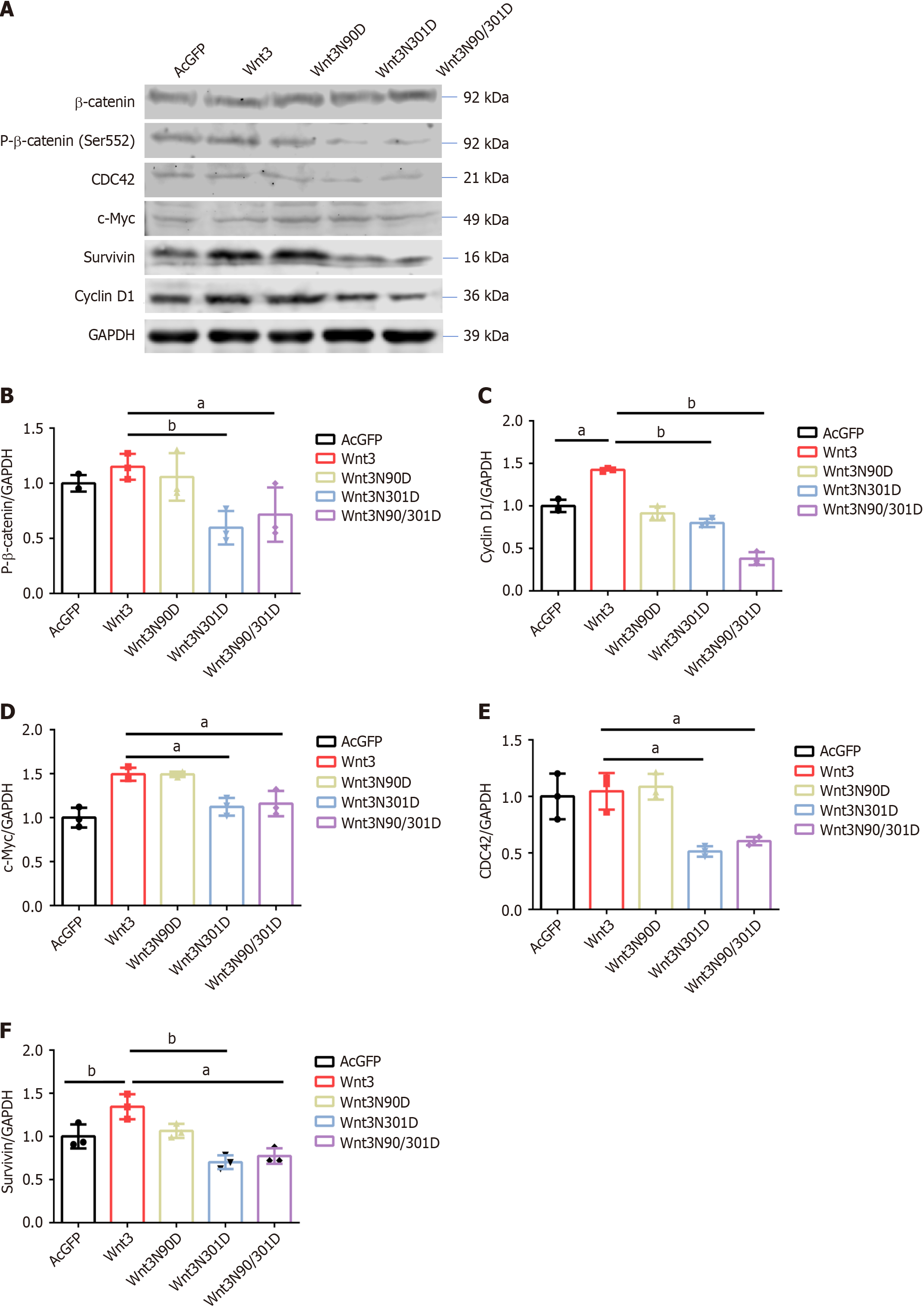
Figure 3 Site-directed mutations in Wnt3 affect signaling pathways downstream.
A: The effect of different Wnt3 N-glycosylation-deficient mutants on the expression of effector molecules in the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway was assessed by Western blot analysis; B: ImageJ software was used to detect the IntDen values, and the p-β-catenin/GAPDH values were compared between the groups; C: ImageJ software was used to detect the IntDen values, and the Cyclin D1/GAPDH values were compared between the groups; D: ImageJ software was used to detect the IntDen values, and the C-myc/GAPDH values were compared between the groups; E: ImageJ software was used to detect the IntDen values, and the CDC42/GAPDH values were compared between the groups; F: ImageJ software was used to detect the IntDen values, and the Survivin/GAPDH values were compared between the groups. The data are presented as the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. GFP: Green fluorescent protein.
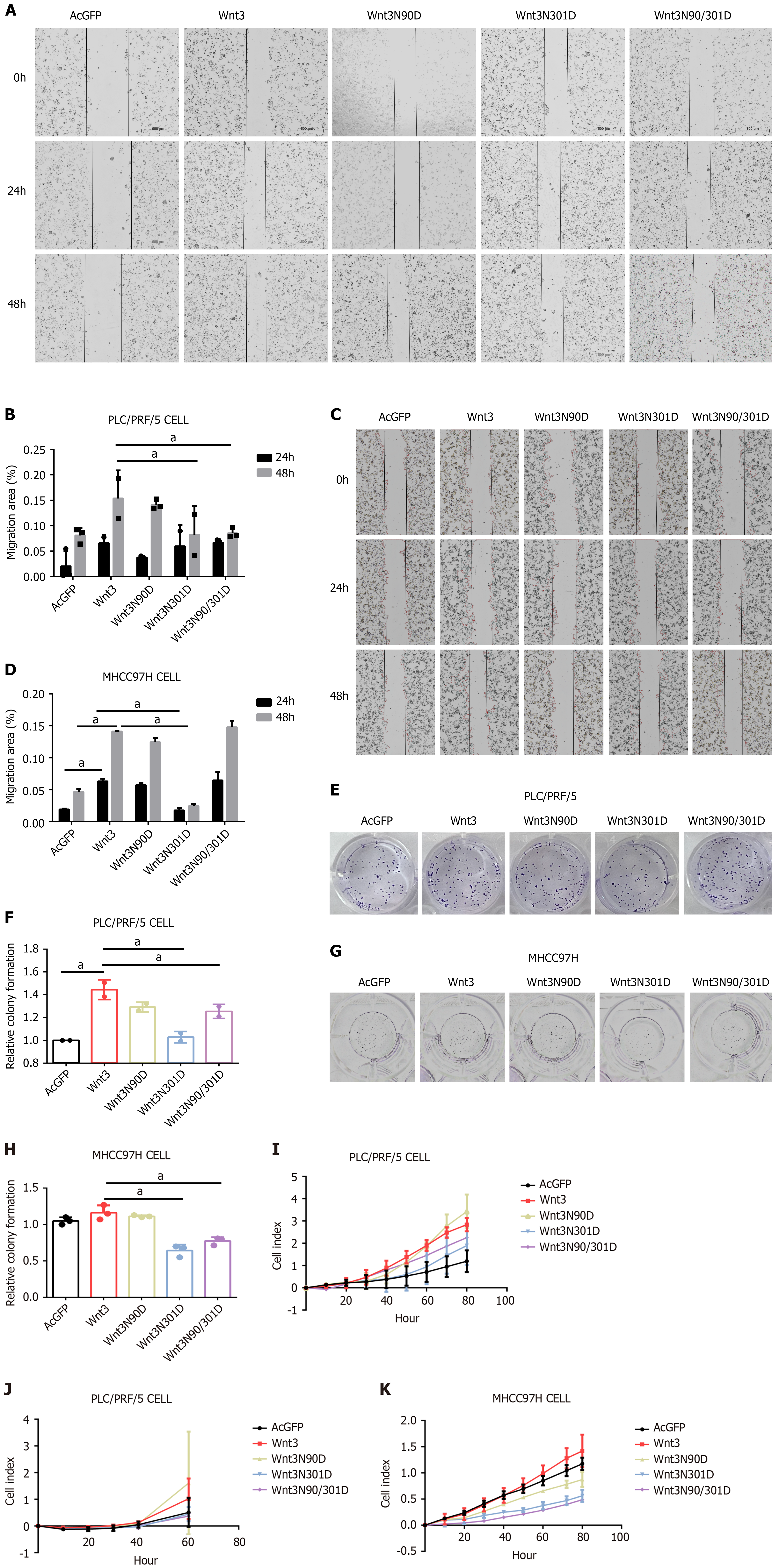
Figure 4 Loss of N-glycosylation from Wnt3 weakens cell proliferation, invasion, migration and colony formation.
A and B: Wound healing experiments were performed 36 h after PLC/PRF/5 cell transfection; C and D: At 36 h after transfection, the MHCC97H cells were subjected to wound healing experiments; E and F: At 36 h following the transfection of PLC/PRF/5 cells, after the cell count, 500 cells were removed for colony formation experiments; G and H: At 36 h after MHCC97H cell transfection, after the cell count, 500 cells were removed for colony formation experiments; I: Real-time cellular analysis (RTCA) was used to detect the proliferation of PLC/PRF/5 cells every 20 minutes for a total of 80 h; J: RTCA was used to detect the invasive ability of PLC/PRF/5 cells every 15 min for a total of 60 h; K: RTCA was used to detect the proliferation of MHCC97H cells every 20 min for a total of 80 h. aP < 0.01.
- Citation: Zhang XZ, Mo XC, Wang ZT, Sun R, Sun DQ. N-glycosylation of Wnt3 regulates the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by affecting Wnt/β-catenin signal pathway. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(6): 2769-2780
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i6/2769.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i6.2769