Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Nov 15, 2024; 16(11): 4338-4353
Published online Nov 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i11.4338
Published online Nov 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i11.4338
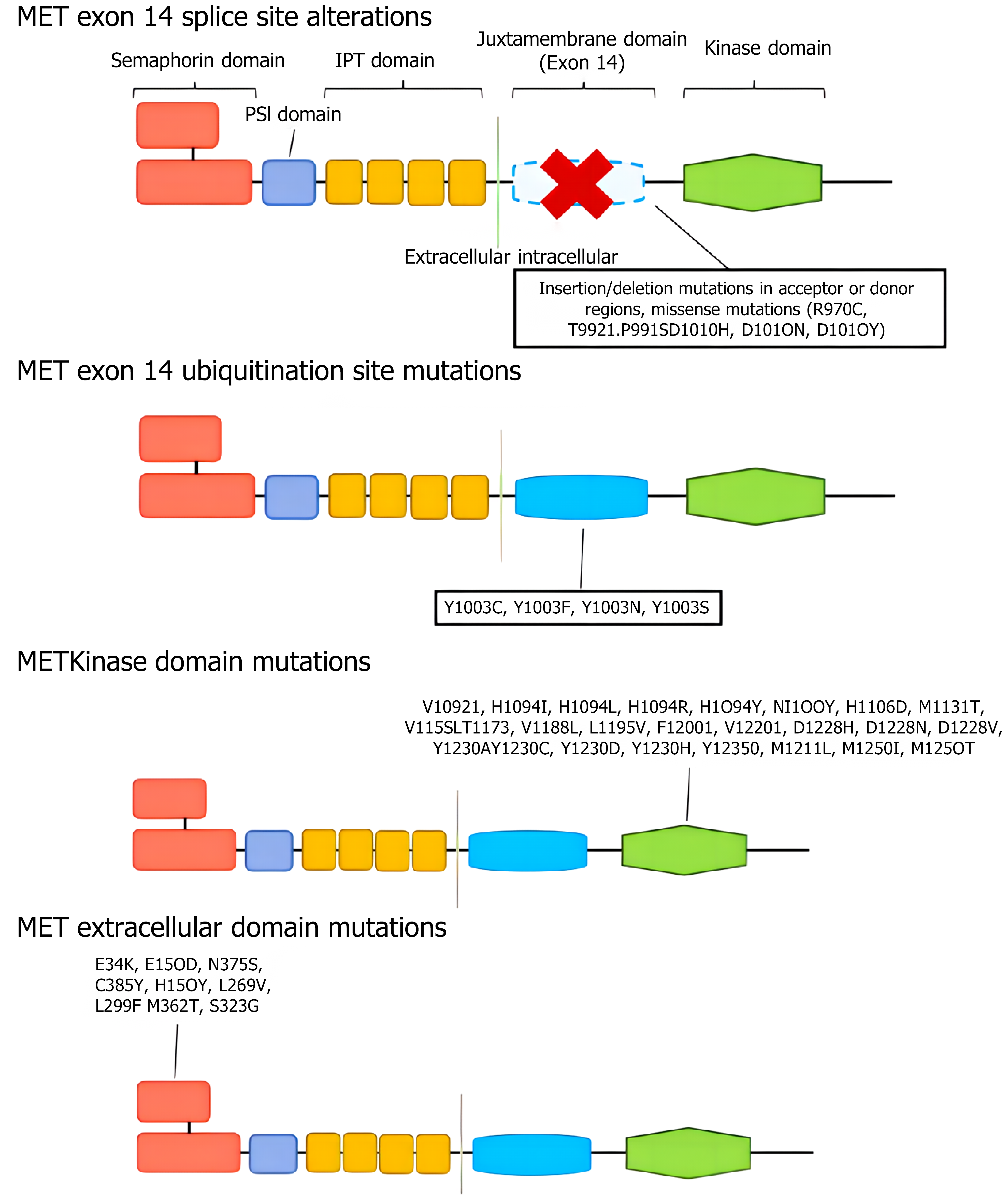
Figure 1 MET mutations.
MET mutations include point mutations, insertion mutations, amplification and other types. Common mutation sites are mainly concentrated in tyrosine kinase domains (such as Exon 14 hops) and extracellular domains, which lead to abnormal activation of MET signaling pathway.
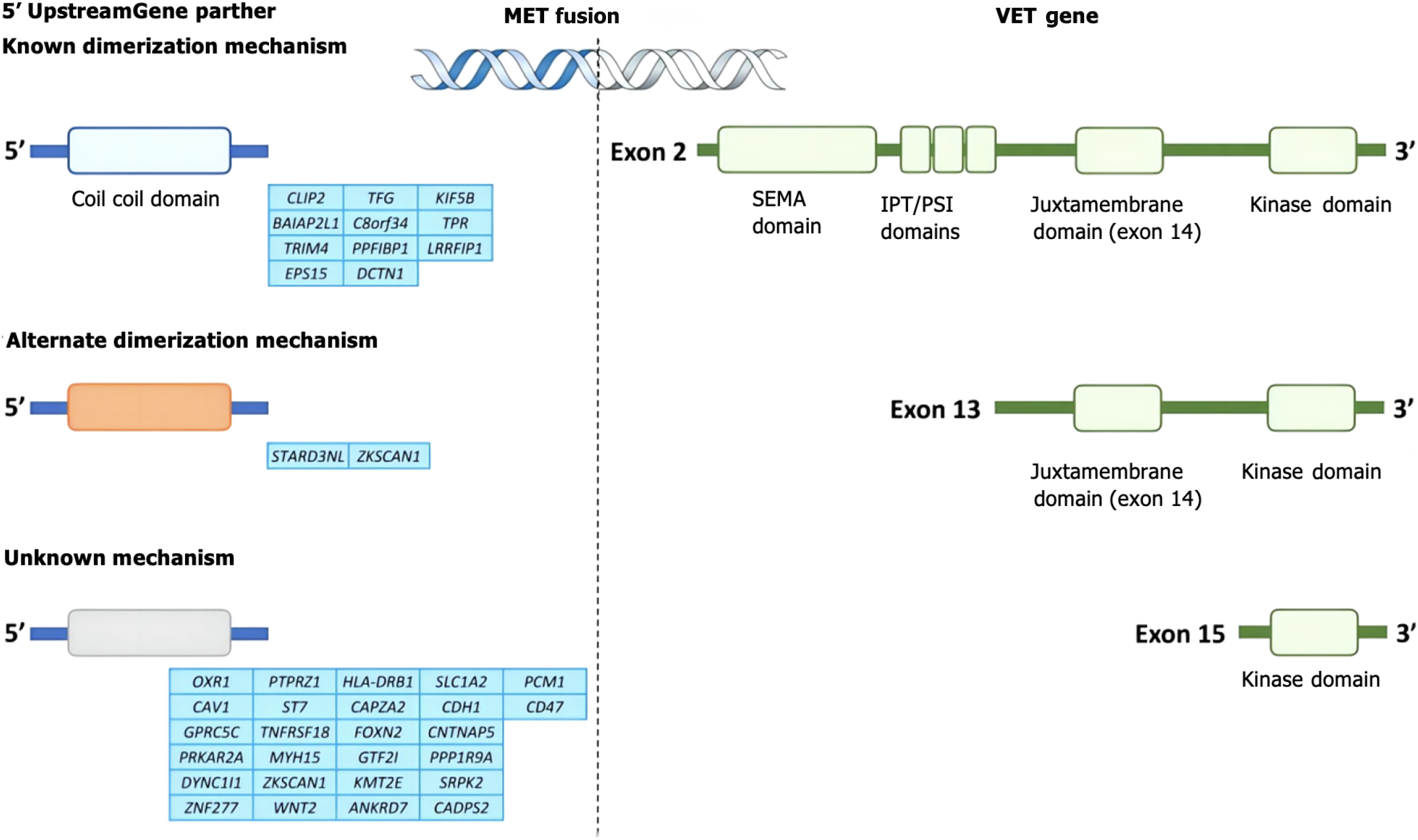
Figure 2 MET fusion.
MET fusion refers to the gene fusion between MET gene and other genes. Common fusion partner genes include TPR, KIF5B, etc. Fusion mutations usually occur in the tyrosine kinase domain of MET, resulting in its continuous activation.
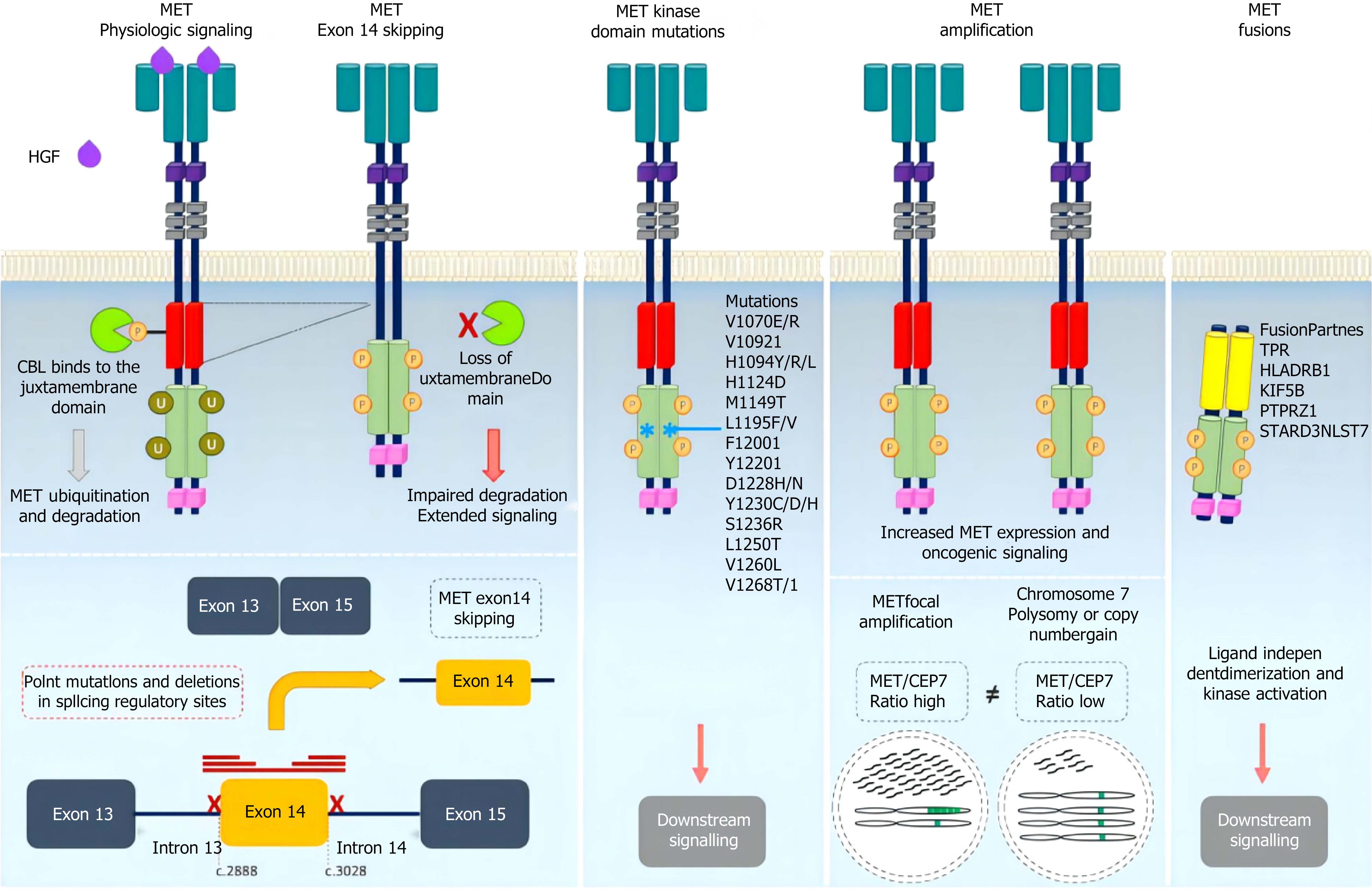
Figure 3 Mechanisms of MET oncogenic activation.
The mechanism of MET carcinogenic activation mainly includes gene mutation, gene amplification and fusion, etc. Through abnormal activation of MET receptor tyrosine kinase, downstream signaling pathways such as RAS/mitogen-activated protein kinase, phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B and Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription are triggered to promote cell proliferation, migration and anti-apoptosis. HGF: Hepatocyte growth factor.
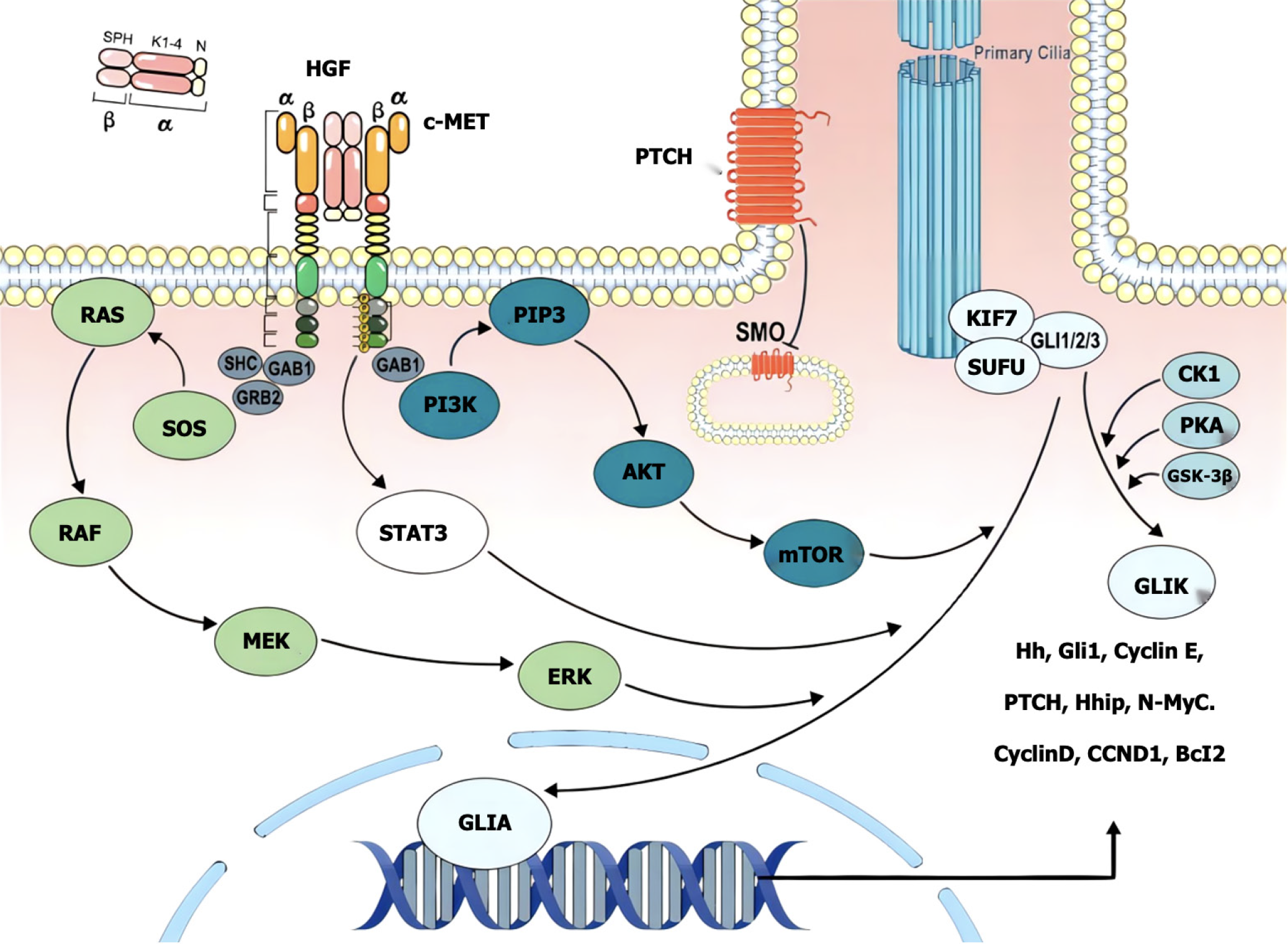
Figure 4 The hepatocyte growth factor/c-Met axis activates the Hedgehog pathway through downstream signaling.
The hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)/c-Met axis activates the Hedgehog pathway through its downstream signaling pathway. After binding to the c-Met receptor, hepatocyte growth factor activates the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and protein kinase B signaling pathways, further promoting the activation of GLI transcription factors, and thereby initiating the transcription activity of the Hedgehog pathway. HGF: Hepatocyte growth factor; Hh: Hedgehog; SPH: Secreted protein, acidic and rich in cysteine; MEK: Mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; SHC: Src homology 2 domain containing; GAB: Grb2-associated binder; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; KIF7: Kinesin family member 7; GLI: GLI family zinc finger transcription factor; PKA: Protein kinase A; GSK-3β: Glycogen synthase kinase 3 β; AKT: Protein kinase B; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; GLIA: Glioma-associated oncogene homolog; Bcl: B-cell lymphoma; CCND: Cyclin D.
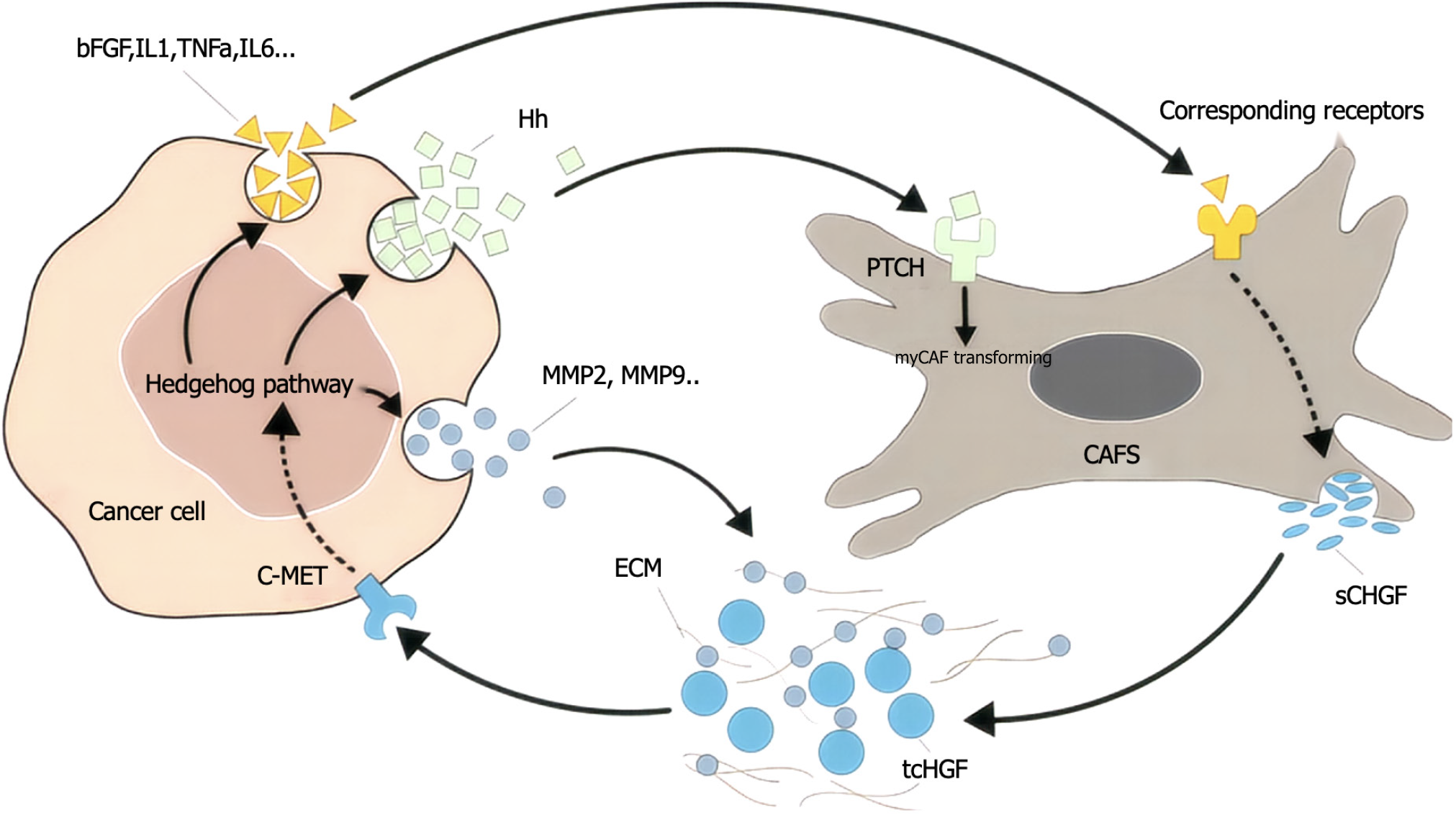
Figure 5 Hepatocyte growth factor and Hedgehog loops between cancer cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts.
Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and Hedgehog (Hh) pathways form a feedback loop between cancer cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts. Cancer-associated fibroblasts secrete hepatocyte growth factor, activate c-Met receptors in cancer cells, trigger downstream signaling pathways, and thus enhance the proliferation, migration, and invasion of cancer cells. bFGF: Basic fibroblast growth factor; IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; Hh: Hedgehog; MMP: Matrix metalloproteinase; ECM: Extracellular matrix; tcHGF: Truncated hepatocyte growth factor; CAFS: Cancer-associated fibroblasts; sCHGF: Soluble hepatocyte growth factor.
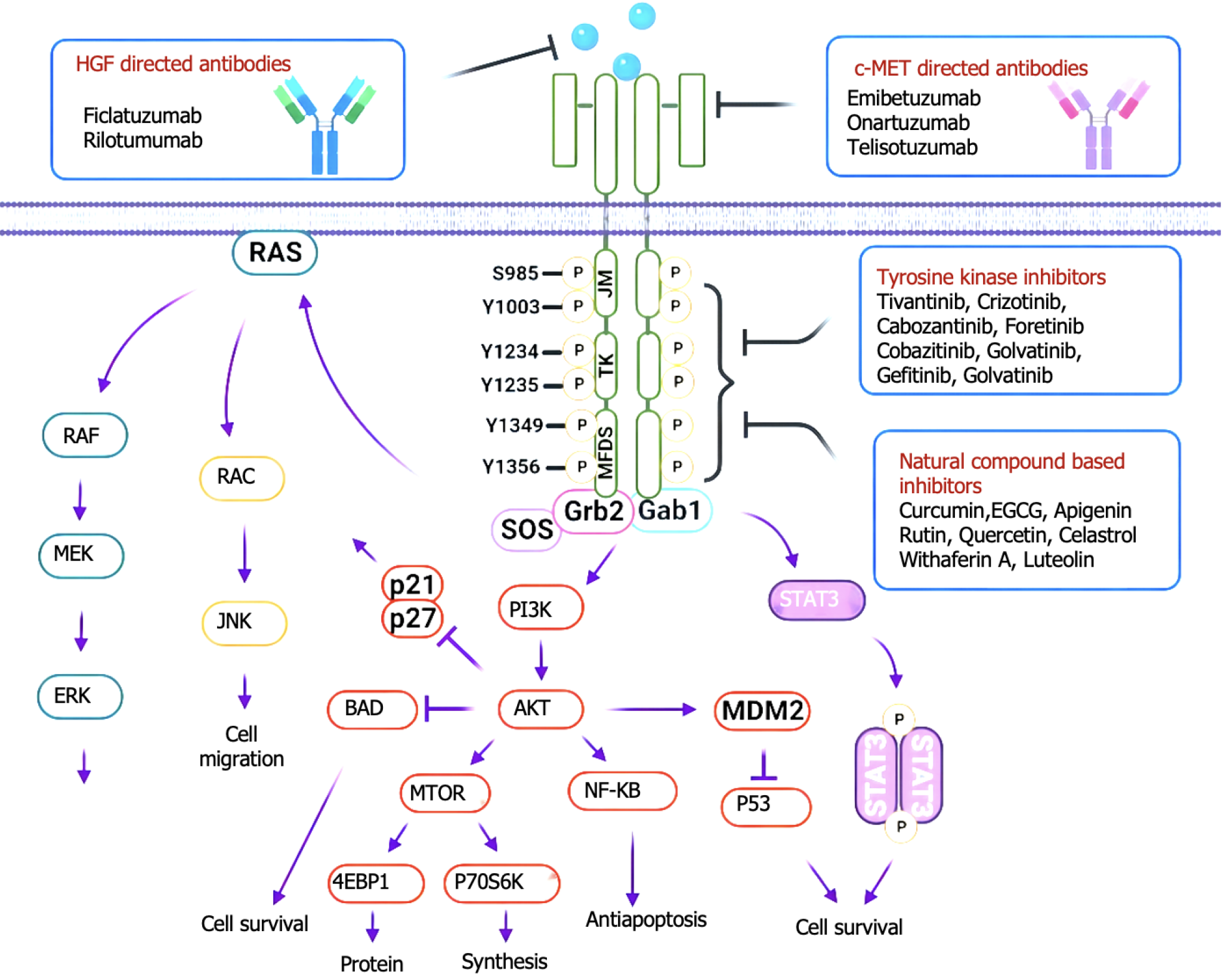
Figure 6 The c-MET pathway relays downstream signals to activate multiple oncogenic events to promote cell proliferation, migration, protein synthesis, and antiapoptosis.
The c-MET pathway transmits downstream signals by activating its receptor tyrosine kinase, triggering multiple carcinogenic events. This pathway activates signaling pathways such as RAS/mitogen-activated protein kinase, phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B, and promotes cell proliferation, migration, protein synthesis, and anti-apoptosis. HGF: Hepatocyte growth factor; MEK: Mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; RAC: Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate; JNK: Jun N-terminal kinase; BAD: Bcl-2-associated death promoter; mTOR: Mechanistic target of rapamycin; Grb2: Growth factor receptor-bound protein 2; Gab1: Grb2-associated binder 1; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; MDM2: Mouse double minute 2; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; AKT: Protein kinase B; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; EGCG: Epigallocatechin gallate.
- Citation: Zhang C, Dong HK, Gao JM, Zeng QQ, Qiu JT, Wang JJ. Advances in the diagnosis and treatment of MET-variant digestive tract tumors. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(11): 4338-4353
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i11/4338.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i11.4338