Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Feb 15, 2021; 13(2): 147-156
Published online Feb 15, 2021. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v13.i2.147
Published online Feb 15, 2021. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v13.i2.147
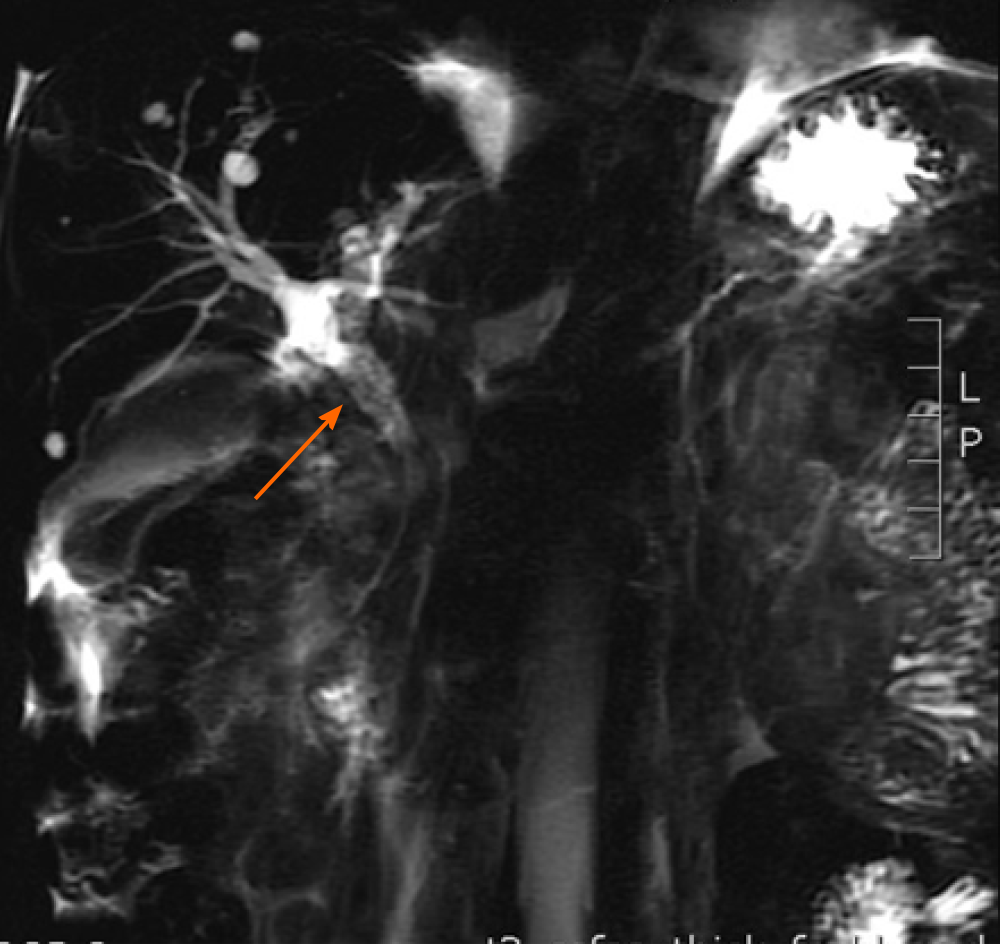
Figure 1 Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography.
Findings of dilatation of the common bile duct, stenosis of the distal common bile duct, and density shadow of soft tissue are indicated by an arrow.
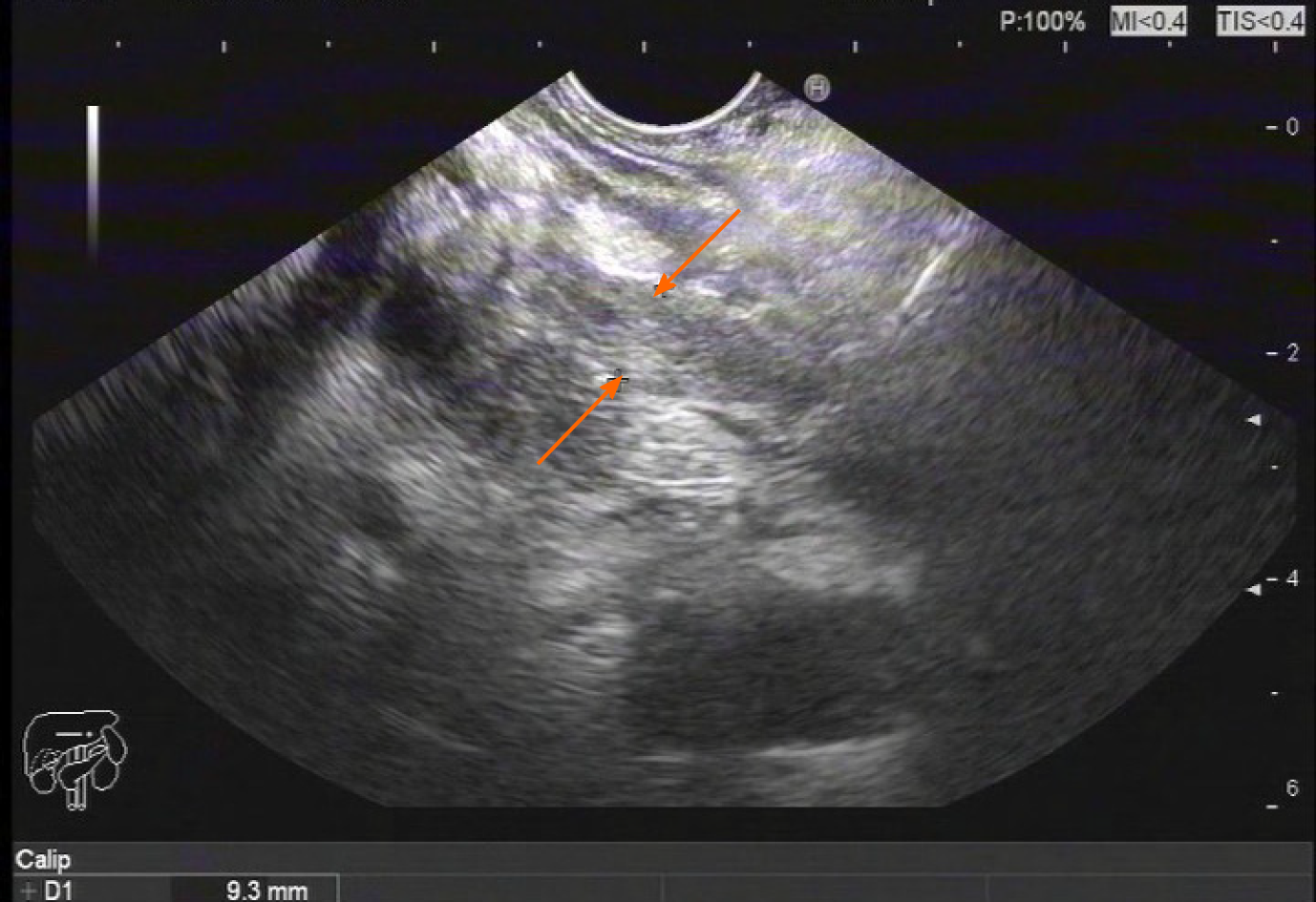
Figure 2 Endoscopy findings.
Ultrasound gastroscopy revealed widening of the bile duct wall (arrows).
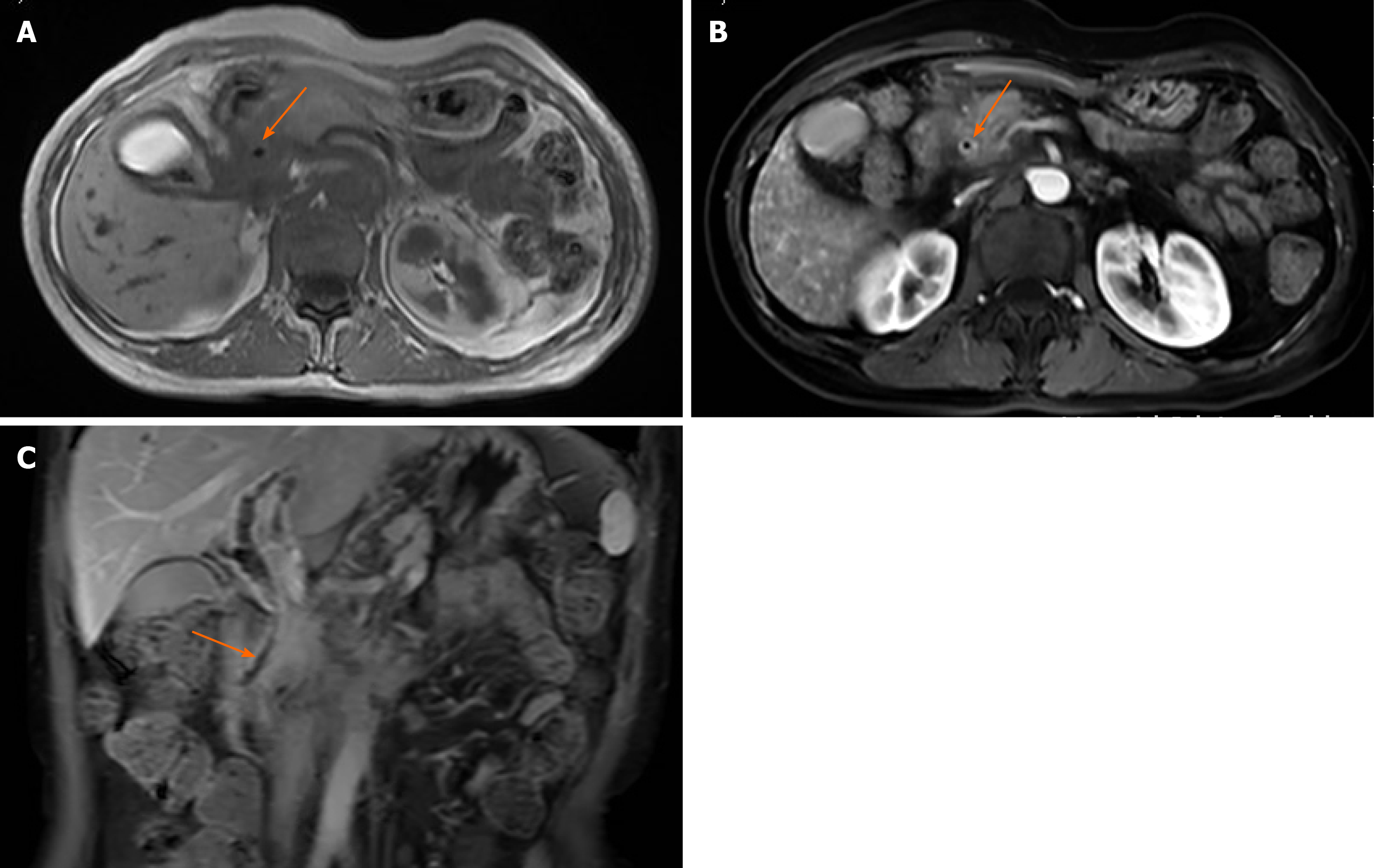
Figure 3 Magnetic resonance imaging of the abdomen.
A and B: The wall of the common bile duct was thickened (arrows) and became obviously enhanced with contrast agent; C: Local nodular thickening was seen in the lower segment of the common bile duct (arrow).
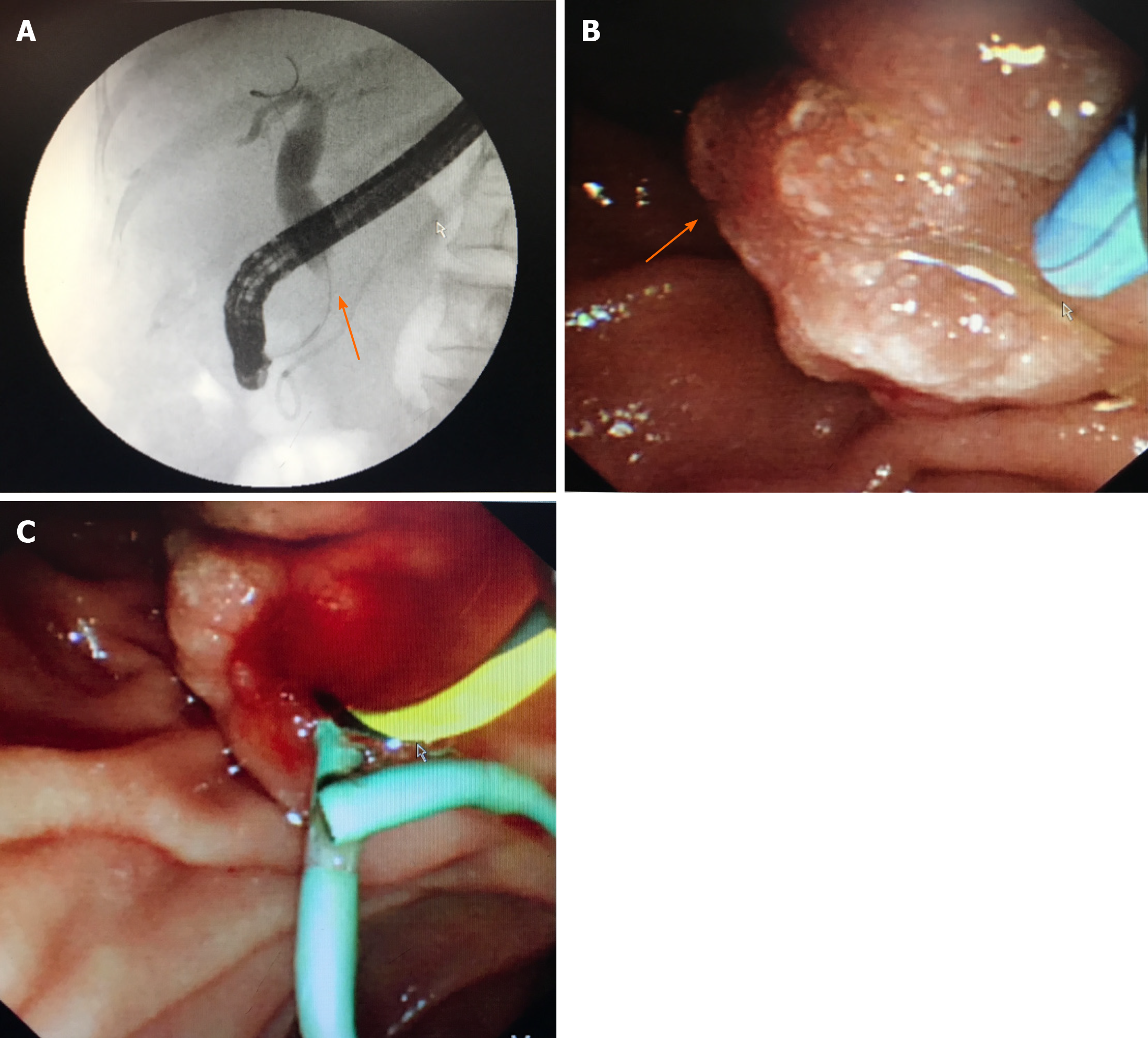
Figure 4 Endoscopy findings.
A: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography showed dilatation of the common bile duct and stenosis of the distal common bile duct (arrow); B: Edema of the ampulla; C: Implanted plastic stent.
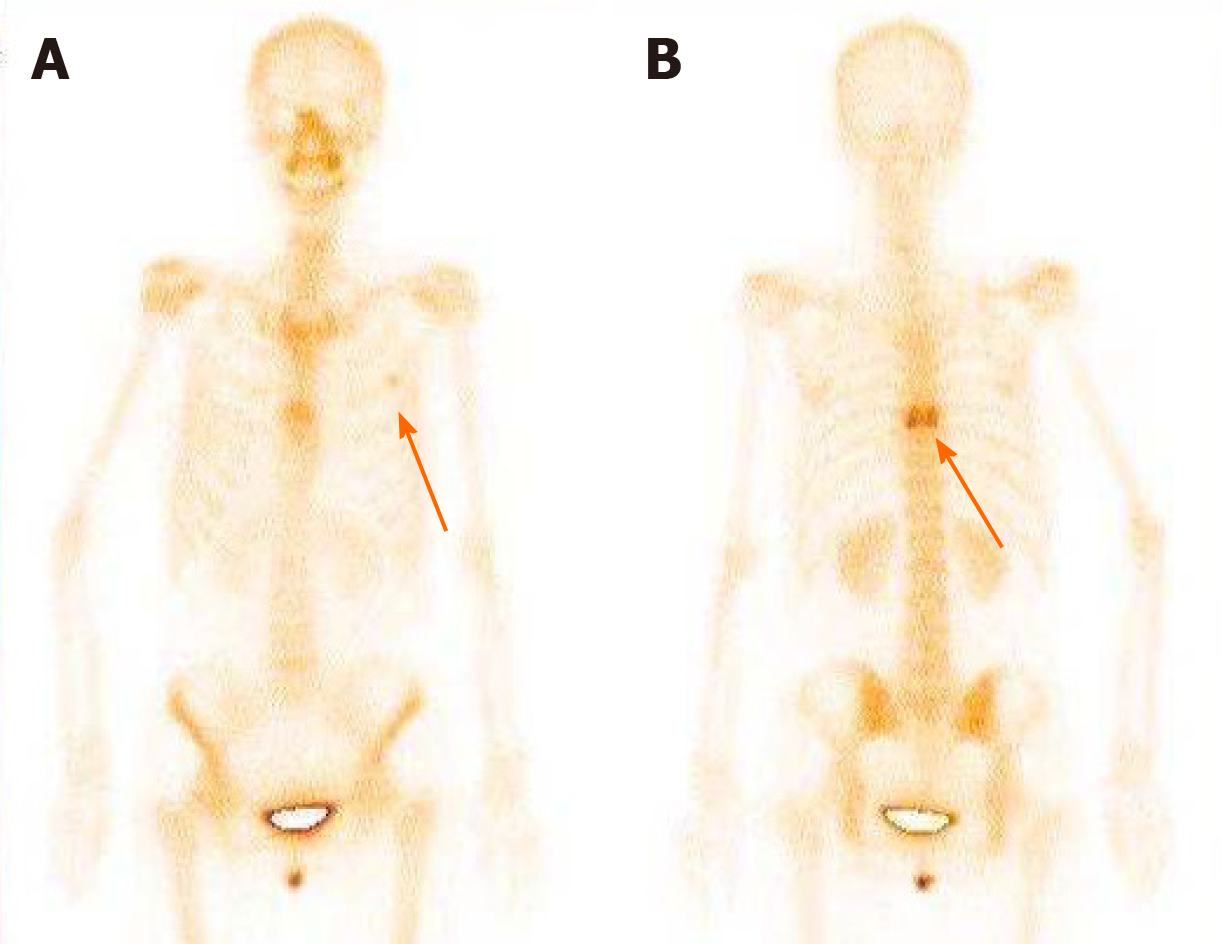
Figure 5 Bone scan findings.
A: Metastasized tumors in the left third rib; B: Metastasized tumors in the eighth vertebral body.
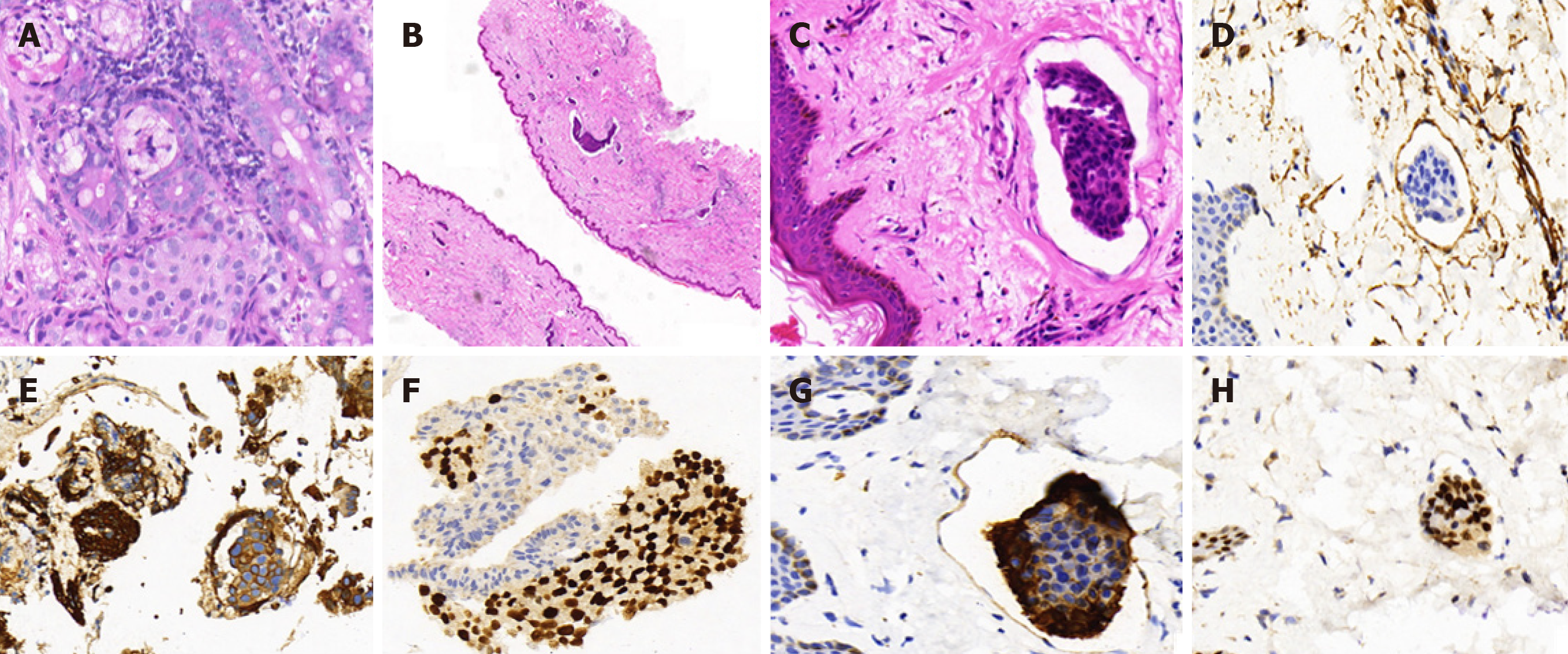
Figure 6 Histopathology of biopsies of the common bile duct and the skin of left neck and chest.
A: Cancer cells were found to have infiltrated the glandular duct of the common bile duct (CBD); B and C: Low-power magnifications (B: 2´, C: 40´) demonstrating cancer embolus in the vasculature of the skin; D: Positive immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining for CD34 in the cancer embolus areas; E and F: Strong positive IHC staining for cytokeratin (CK) 7 and trans-acting T-cell-specific transcription factor (GATA-3) in the CBD; G: Strong positive IHC staining for CK7 in the skin of left neck and chest; H: Strong positive IHC staining for GATA3 in the skin of left neck and chest.
- Citation: Tang J, Zhao GX, Deng SS, Xu M. Rare common bile duct metastasis of breast cancer: A case report and literature review . World J Gastrointest Oncol 2021; 13(2): 147-156
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v13/i2/147.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v13.i2.147