Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Aug 15, 2020; 12(8): 931-941
Published online Aug 15, 2020. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v12.i8.931
Published online Aug 15, 2020. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v12.i8.931
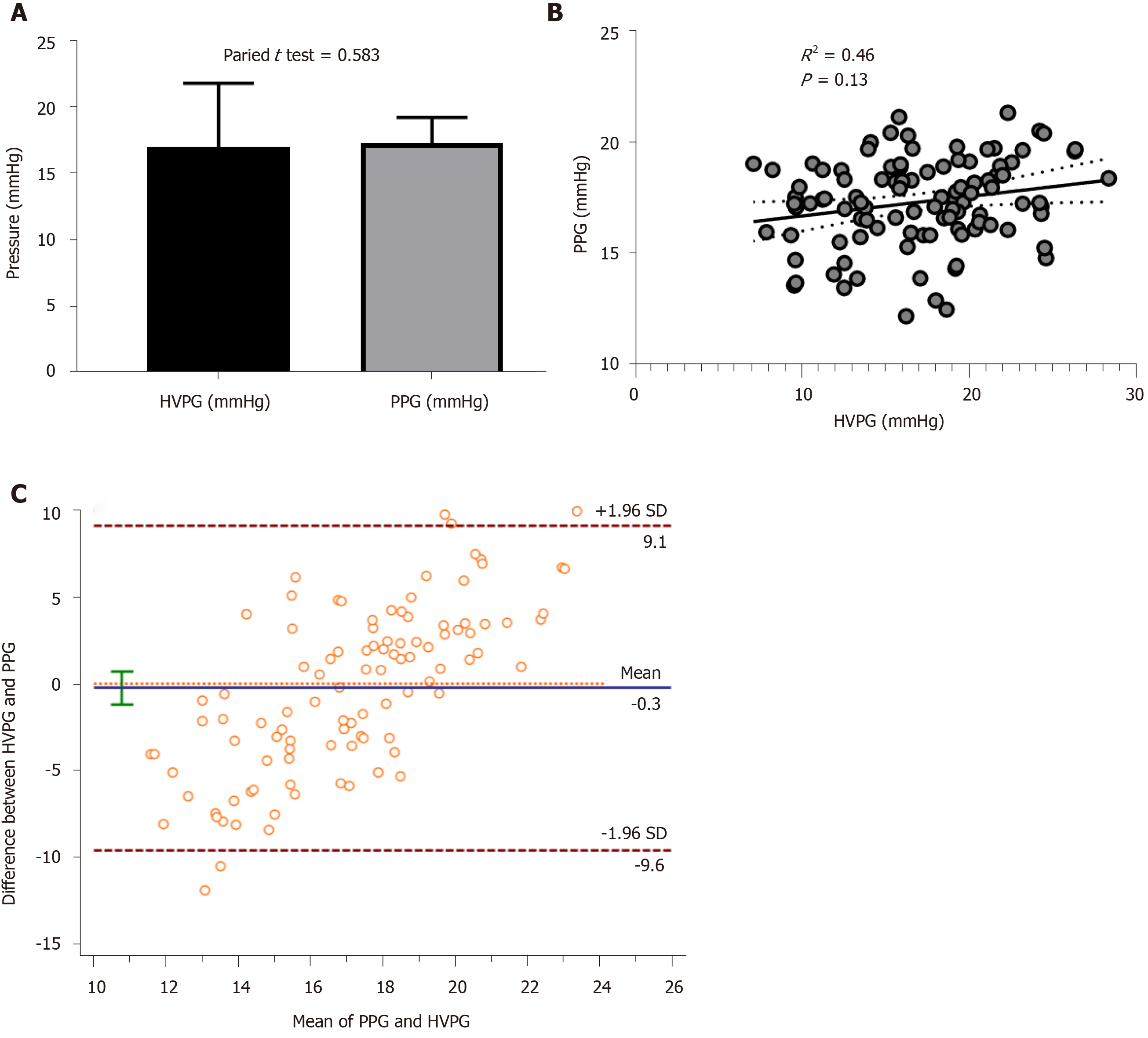
Figure 1 Correlation between portal pressure gradient and hepatic venous pressure gradient in the overall group.
A: Paired t-test showed that there was no significant difference between hepatic venous pressure gradient (HVPG) and portal pressure gradient (PPG); B: Scatterplot shows agreement between PPG and HVPG; C: Bland-Altman plot shows the difference between PPG and HVPG.
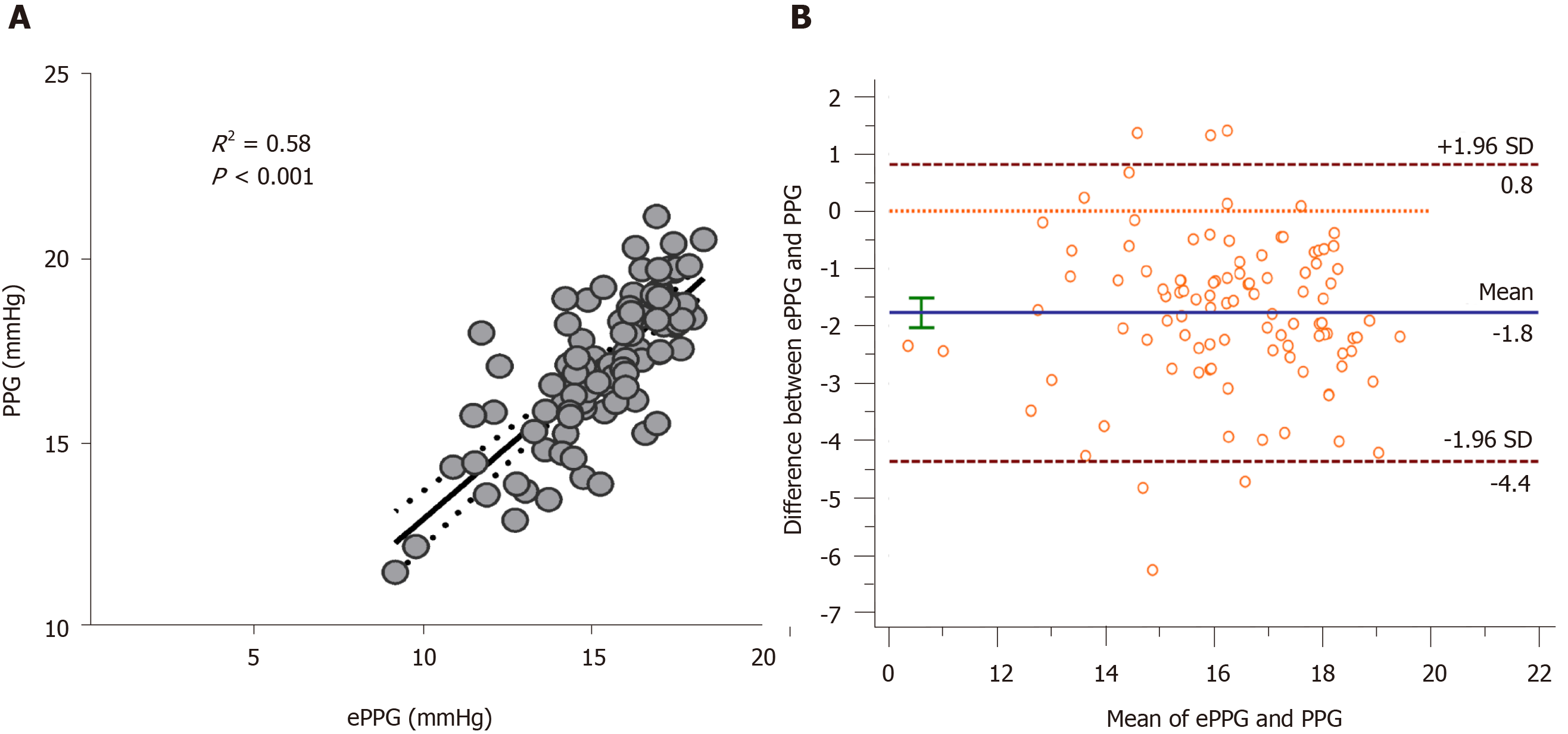
Figure 2 Correlation between portal pressure gradient and estimated portal pressure gradient in the overall group.
A: Scatterplot shows agreement between portal pressure gradient (PPG) and estimated PPG (ePPG); B: Bland-Altman plot shows the difference between PPG and ePPG.
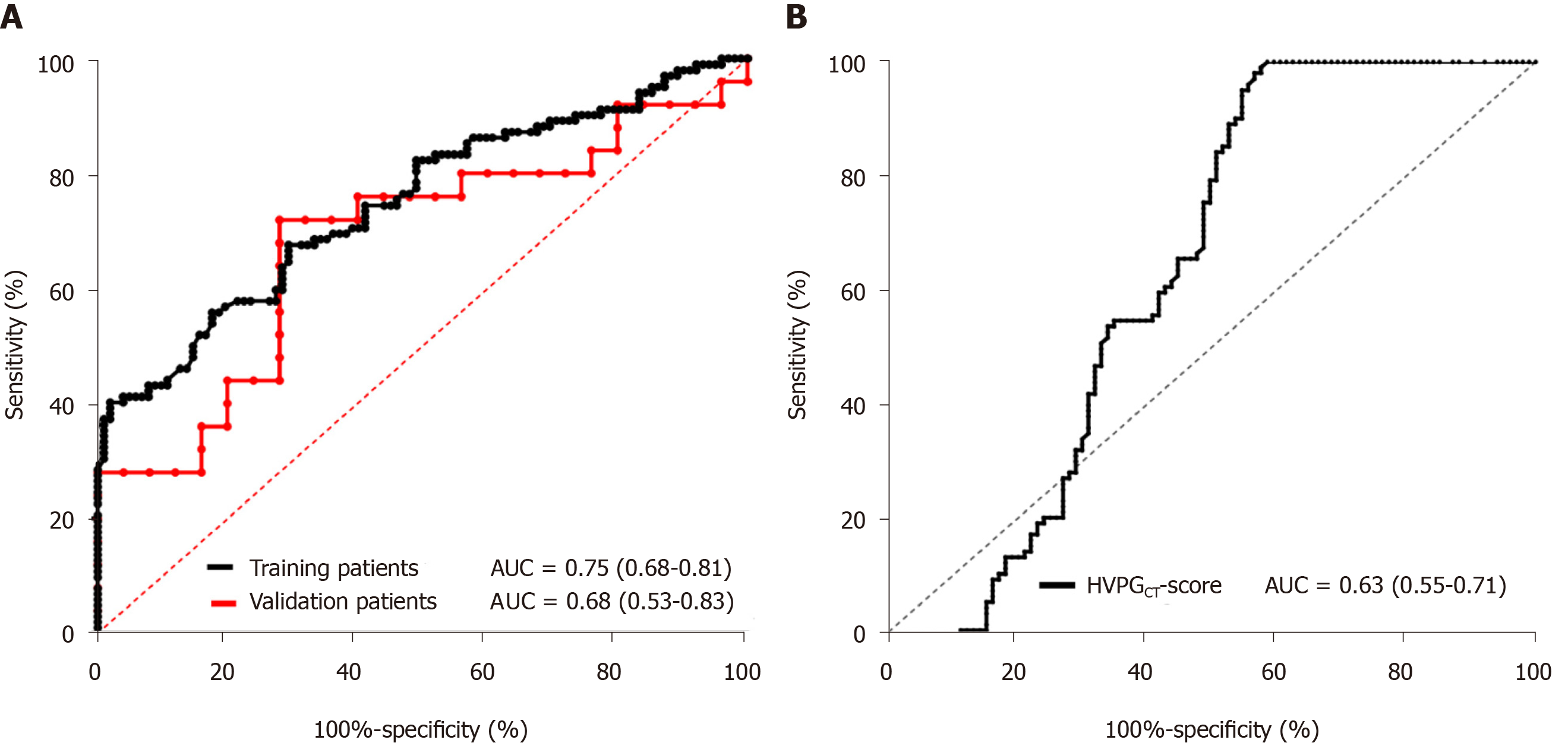
Figure 3 Diagnostic performance of estimated portal pressure gradient for portal pressure gradient.
A: Receiver operating characteristic curves of estimated portal pressure gradient (PPG) for predicting PPG in the training and validation cohorts (n = 102 and n = 20, respectively); B: Receiver operating characteristic curves of the HVPGCT score. AUC: Area under curve; HVPGCT score: CT-based portal pressure score.
- Citation: Zhang Y, Wang Z, Yue ZD, Zhao HW, Wang L, Fan ZH, Wu YF, He FL, Liu FQ. Accurate ultrasonography-based portal pressure assessment in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2020; 12(8): 931-941
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v12/i8/931.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v12.i8.931