Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Aug 15, 2020; 12(8): 918-930
Published online Aug 15, 2020. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v12.i8.918
Published online Aug 15, 2020. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v12.i8.918
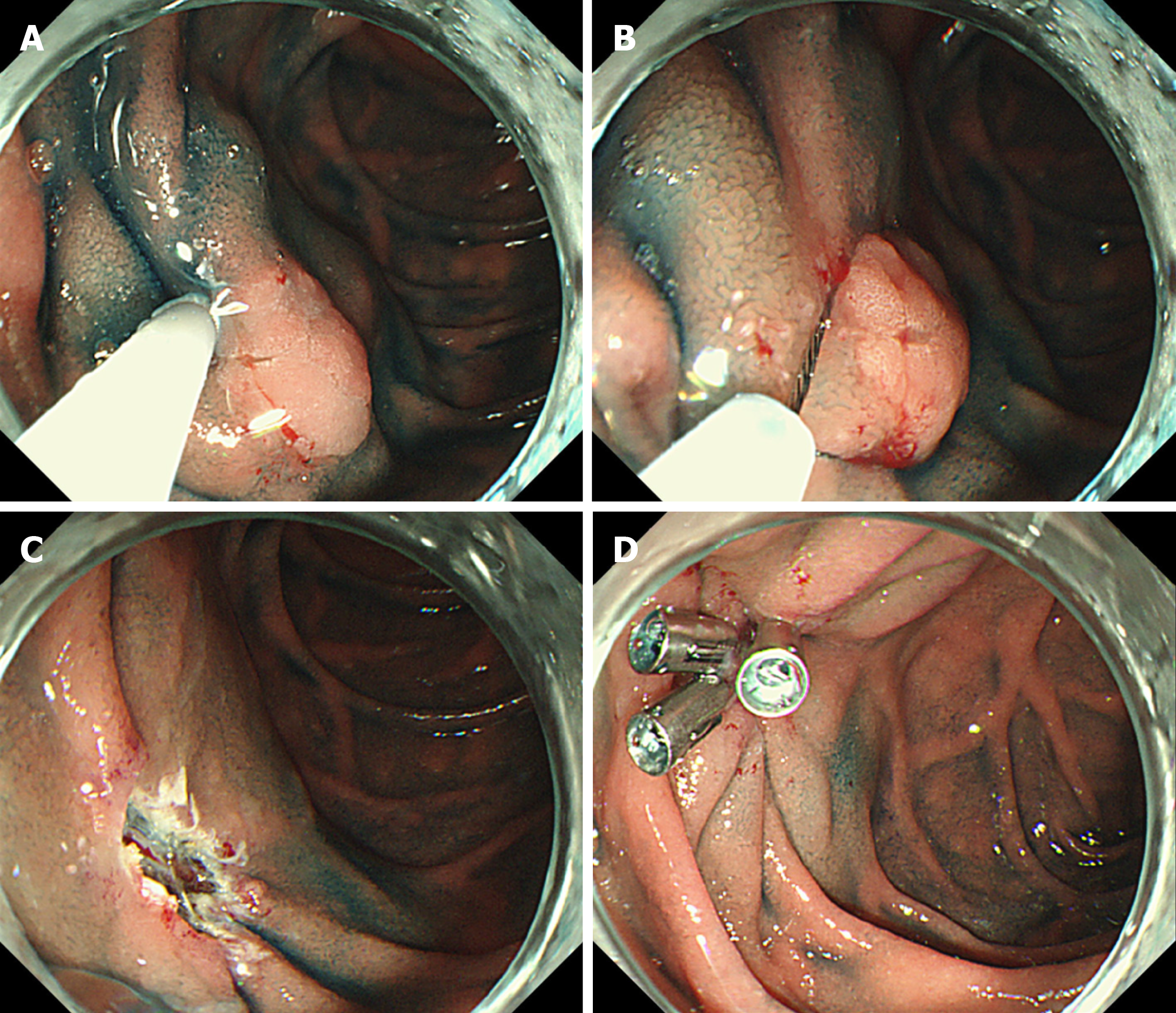
Figure 1 Procedure for endoscopic mucosal resection.
A: Injection into the submucosal layer; B: Snaring of the lesion; C: Mucosal defect after endoscopic submucosal dissection; and D: Clip closure of mucosal defect.
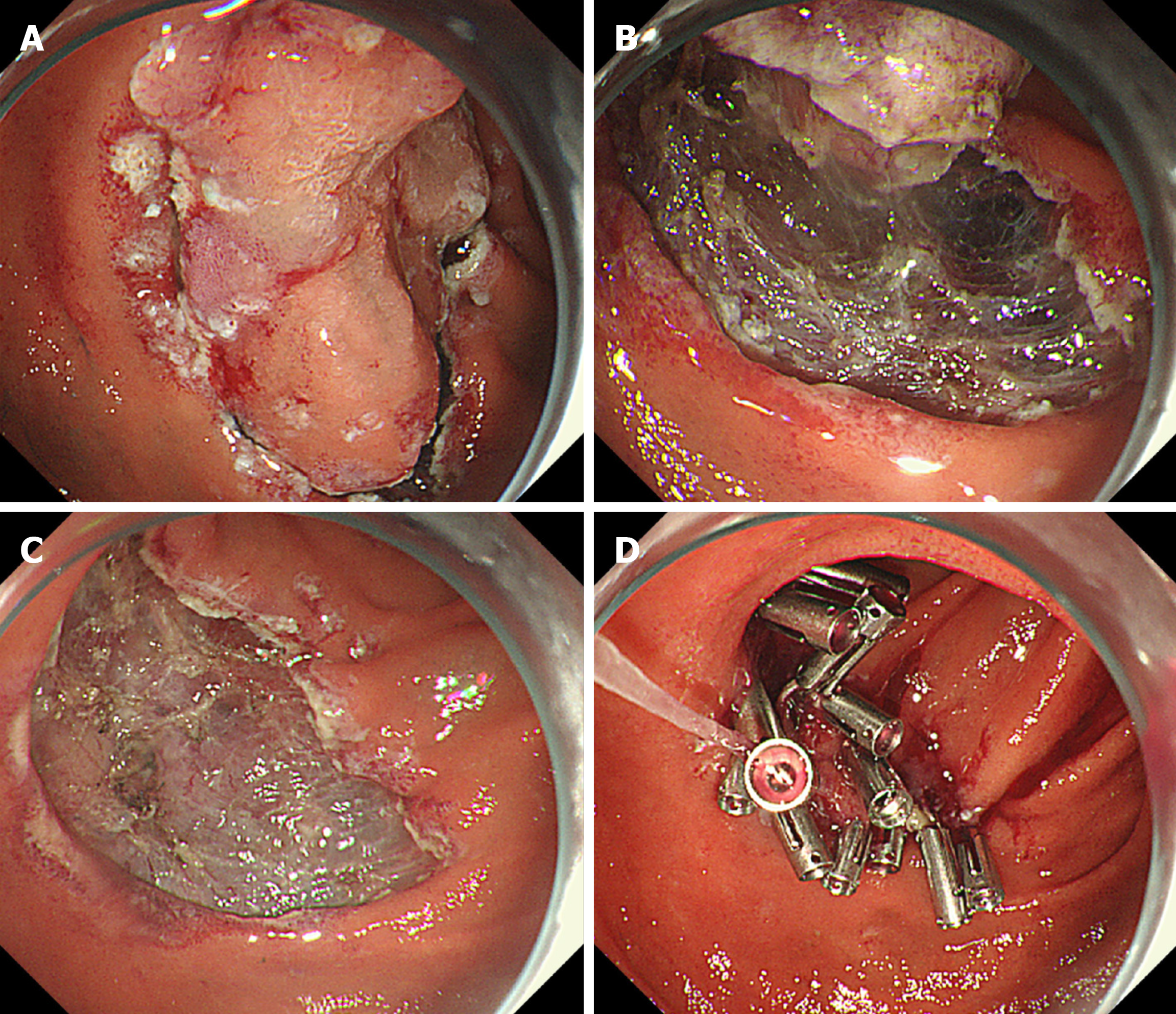
Figure 2 Procedure for endoscopic submucosal dissection.
A: Circumferential mucosal incision; B: Dissection of the submucosal layer; C: Mucosal defect after endoscopic submucosal dissection; D: Clip closure of mucosal defect.
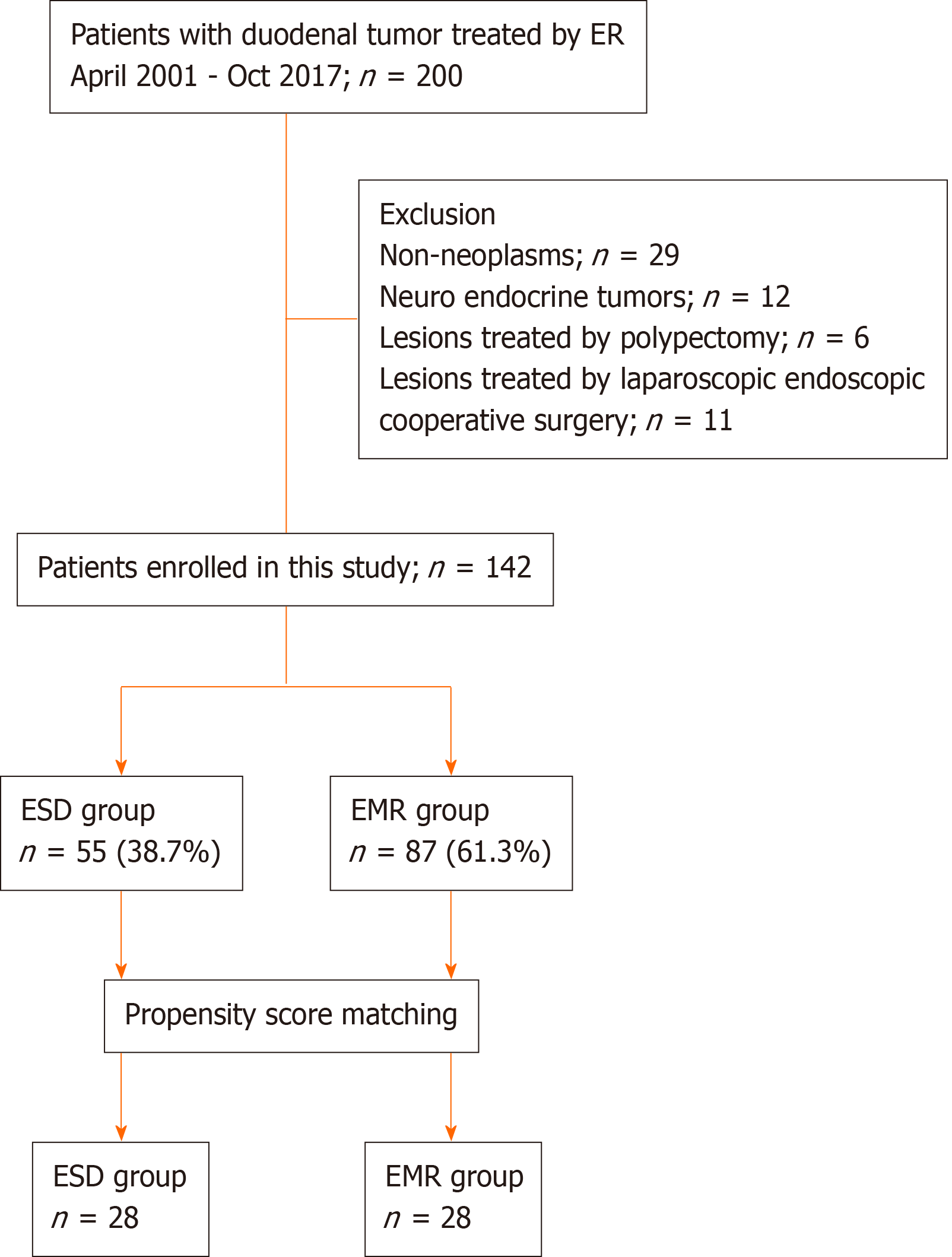
Figure 3 Flowchart showing patient enrollment in the current study.
ESD: Endoscopic submucosal dissection; EMR: Endoscopic mucosal resection.
- Citation: Esaki M, Haraguchi K, Akahoshi K, Tomoeda N, Aso A, Itaba S, Ogino H, Kitagawa Y, Fujii H, Nakamura K, Kubokawa M, Harada N, Minoda Y, Suzuki S, Ihara E, Ogawa Y. Endoscopic mucosal resection vs endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial non-ampullary duodenal tumors. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2020; 12(8): 918-930
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v12/i8/918.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v12.i8.918