Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Apr 15, 2020; 12(4): 365-382
Published online Apr 15, 2020. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v12.i4.365
Published online Apr 15, 2020. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v12.i4.365
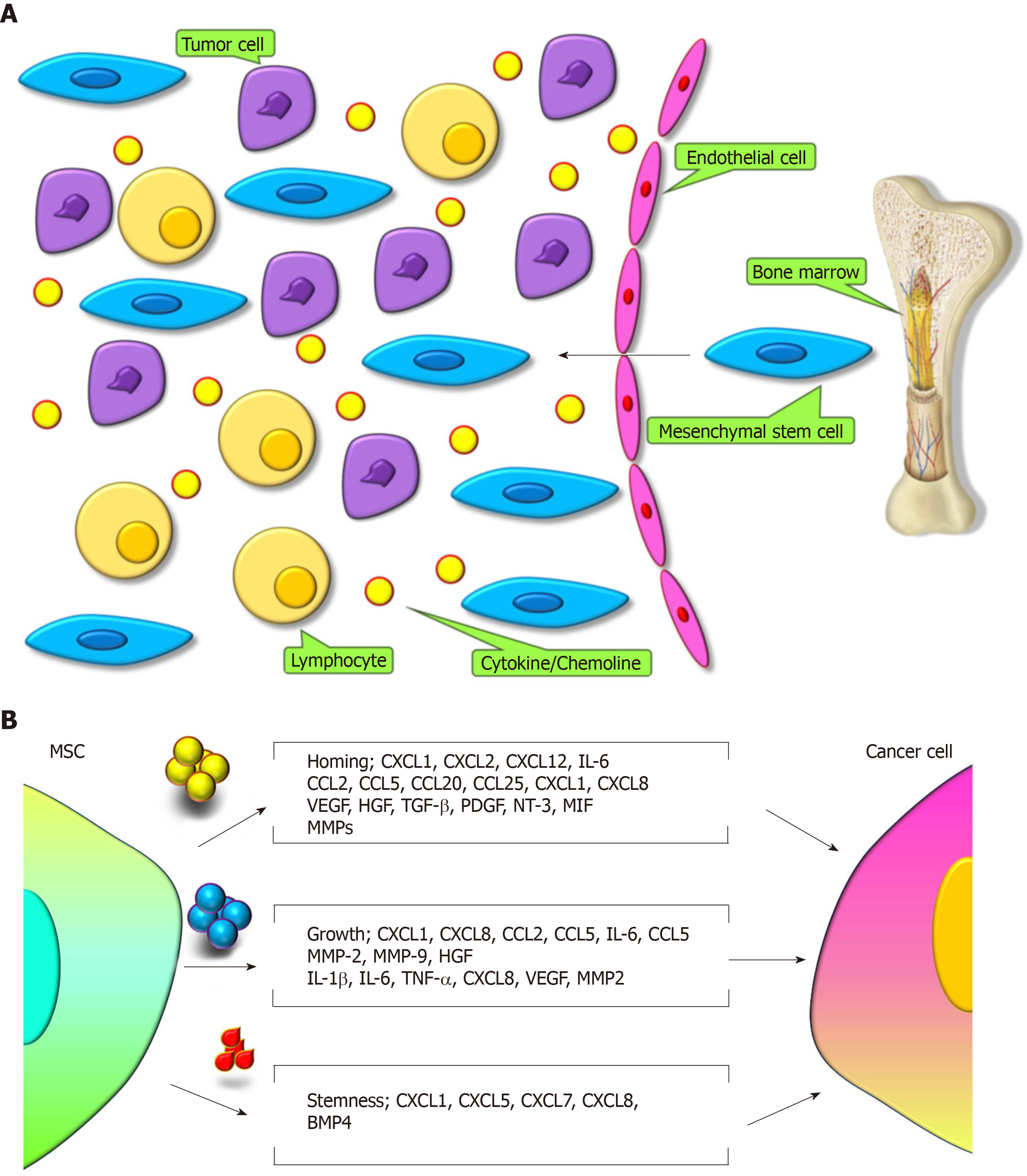
Figure 1 Interactions between mesenchymal stem cells and cancer cells[27].
A: Tumor microenvironment release certain molecules to recruit mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) to tumor. B: MSCs secret different molecules in distinct microenvironment to interact with tumor cells for homing, growth, and stemness of tumors. MSC: Mesenchymal stem cell.
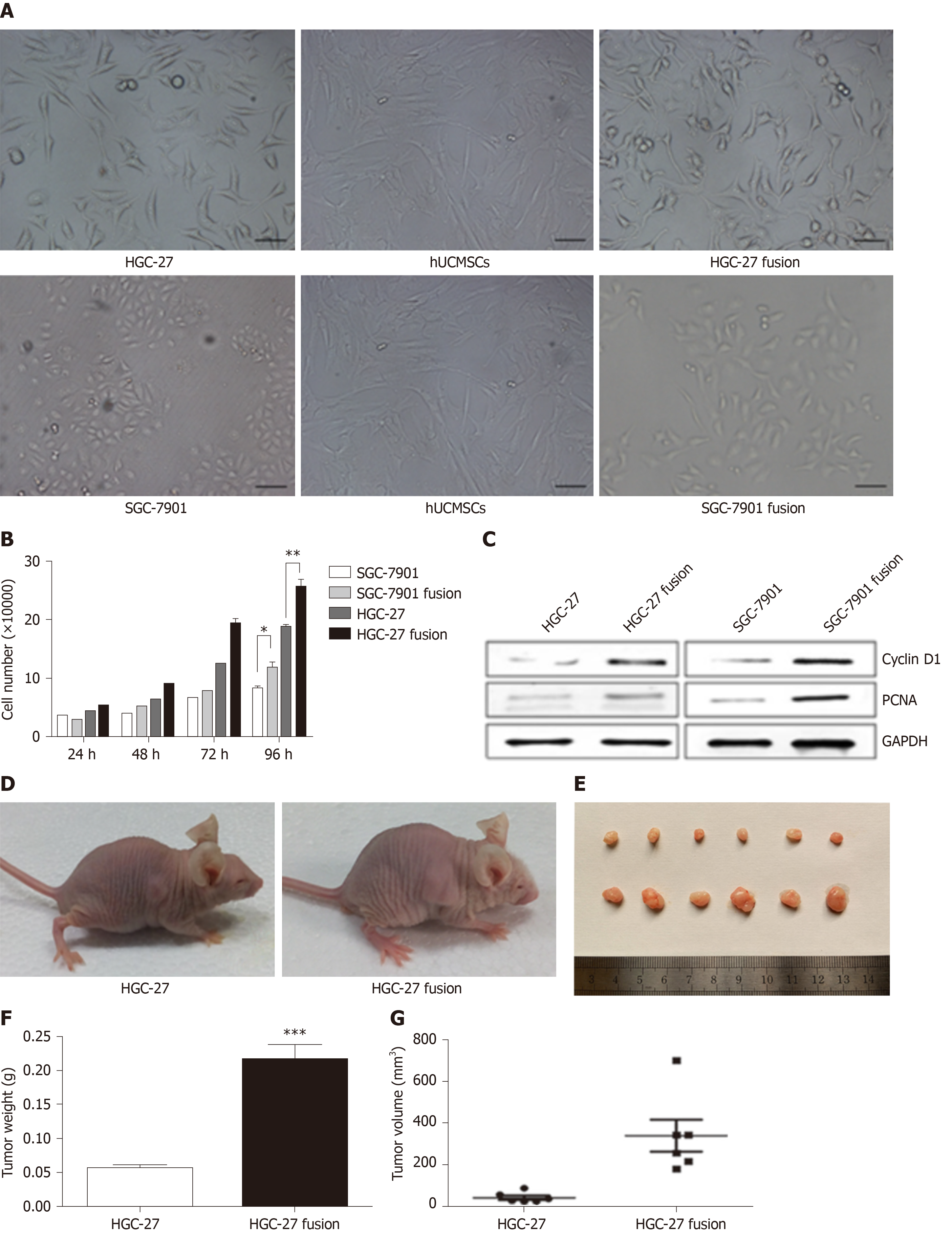
Figure 2 The effects of hybrids (HGC-27 or SGC-7901 fused with mesenchymal stem cells) on gastric cancer[60].
A: The morphology of the two gastric cancer cell lines, hUCMSCs, HGC-27 fusion, and SGC-7901 fusion; B: The growth of the parental and hybrid cells was determined by cell counting assay; C: The expression of PCNA and CyclinD1 proteins in different groups; D: Representative images of the gastric tumor bearing mice; E: The images of the tumor tissues; F: Tumor weight; and G: Tumor volume. hUCMSCs: Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells; PCNA: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen.
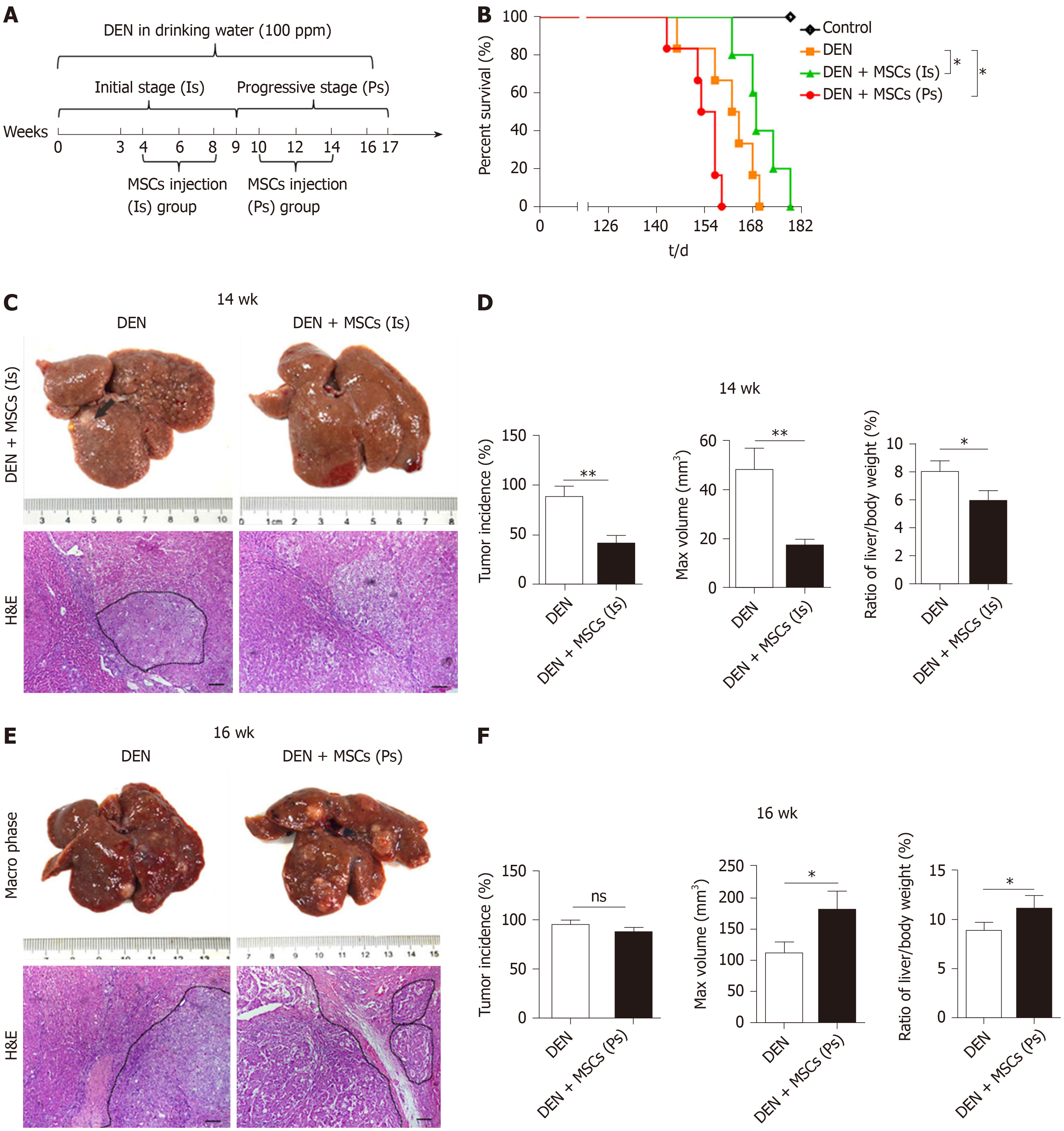
Figure 3 The effects of mesenchymal stem cells on liver cancer in different stages[80].
A: The experimental protocol. Rats were administrated N-diethylnitrosamine (DEN) in drinking water for 14 wk. DEN + mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) (Is) group was transplanted MSCs (1 × 106) by intravenous injection at 4th, 6th, 8th week, and DEN + MSC (Ps) group was transplanted MSCs (1 × 106) as the same method at the 10th, 12th, 14th week, respectively. B: The rat percent survival in different groups. C: The macro phase and H&E images of liver in DEN and DEN + MSCs (Is) groups at 14 wk after DEN treatment. D: Tumor incidence, tumor max volume, and ratio of liver/body weight in DEN and DEN+MSCs (Is) groups at 14th week. E: The macro phase and H&E images of liver in DEN and DEN + MSCs (Ps) groups at 16 weeks after DEN treatment. F: Tumor incidence, tumor max volume, and ratio of liver/body weight in DEN and DEN + MSCs (Ps) groups at 16th week. DEN: N-diethylnitrosamine; MSCs: Mesenchymal stem cells; Is: Initial stage; Ps: Progressive stage; H&E: Hematoxylin-eosin.
Figure 4 Exosomes derived from human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibited the development of pancreatic cancer[83].
A: Images of the tumor bearing mice in different groups; B: Images of resected tumors; C: Tumor volume; and D: Tumor weight.
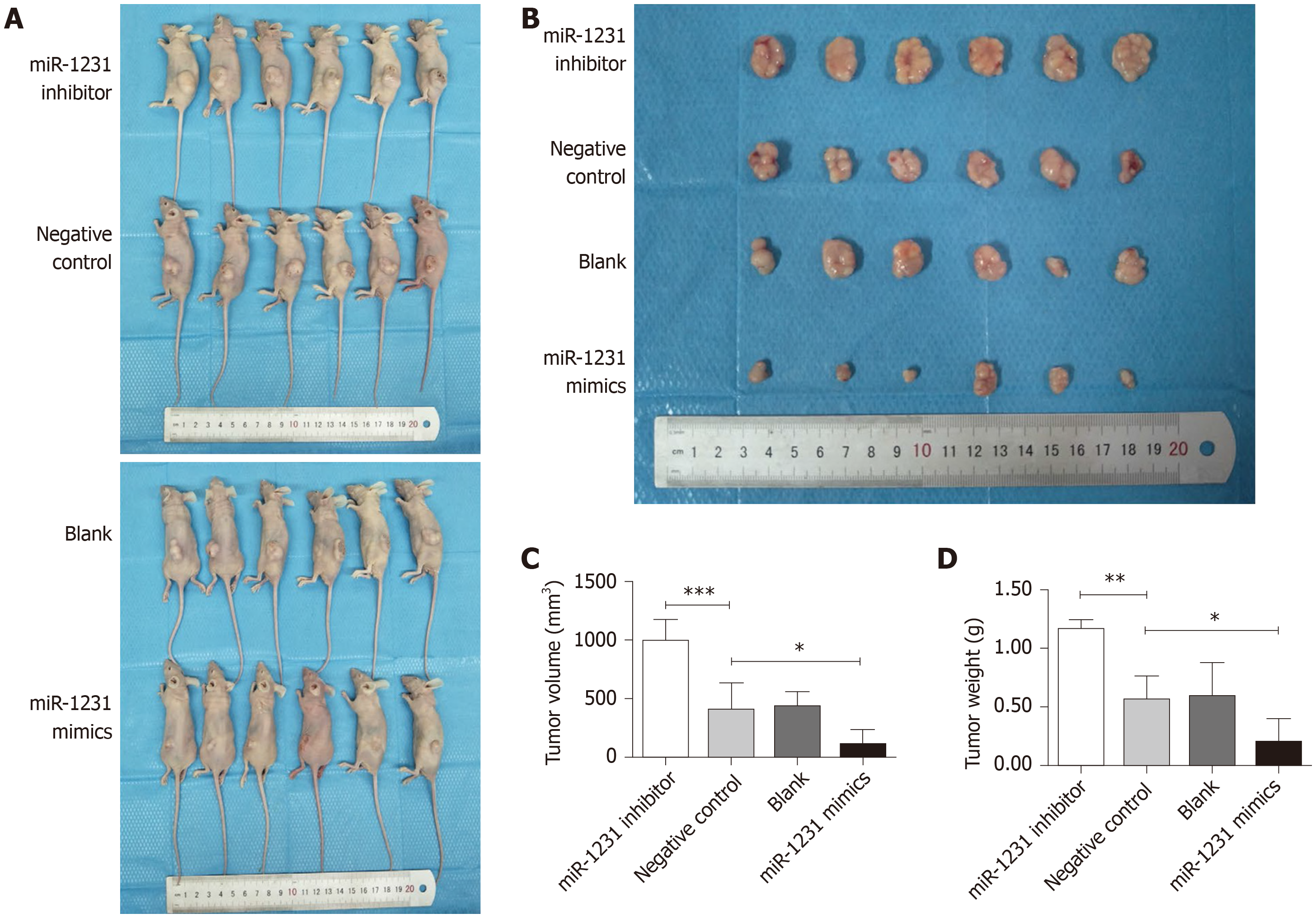
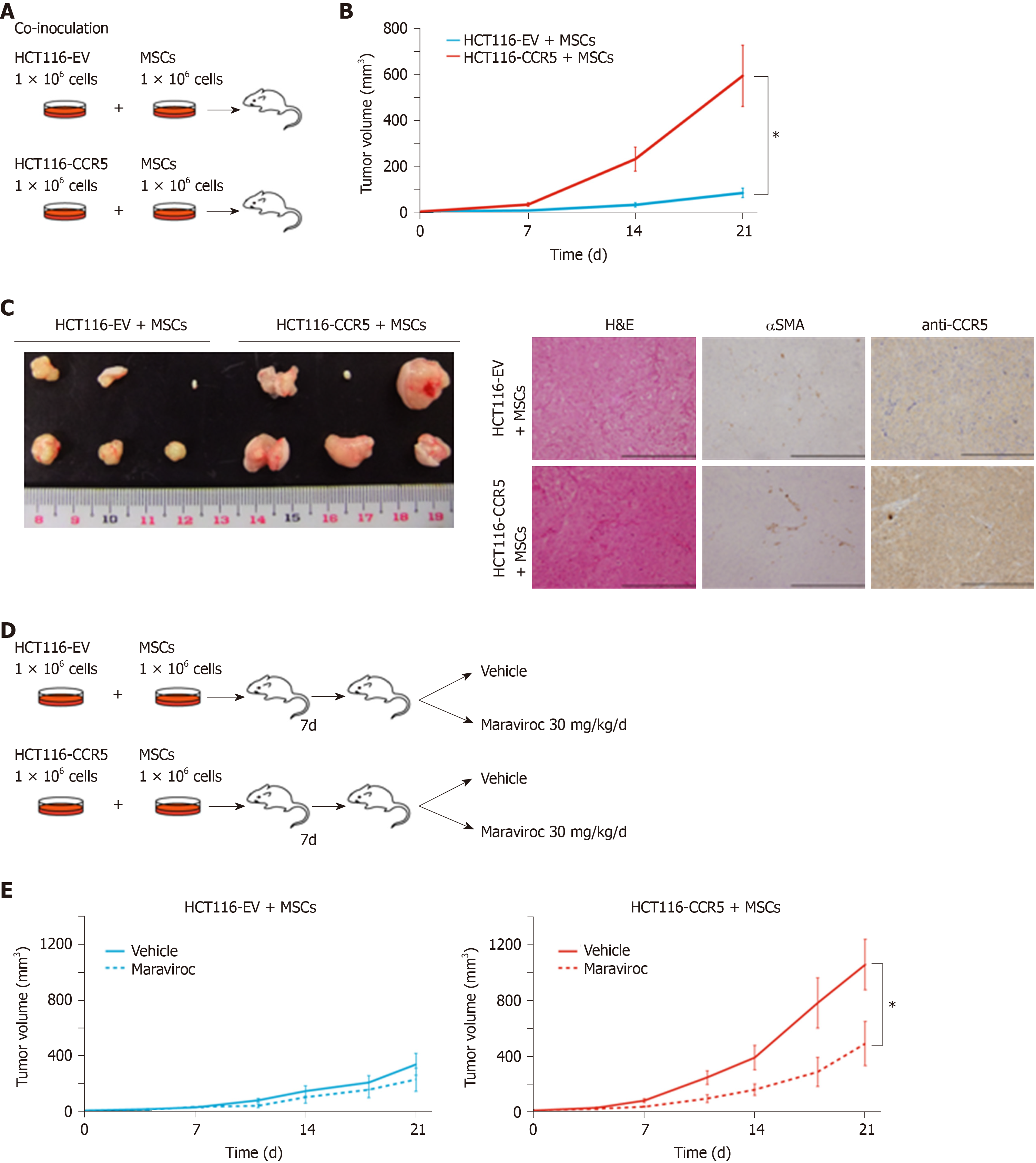
Figure 5 Mesenchymal stem cells promote colorectal cancer progression via CCR5[99].
A: Scheme of co-inoculation mice model. HCT116-EV, HCT116 cells transfected with empty vector; HCT116-CCR5, HCT116 cells transfected with CCR5. B: Tumor volume curves in HCT116-EV and HCT116-CCR5 co-cultured with MSCs. C: Representative images of tumors and histological findings in HCT116-EV + MSCs and HCT116-CCR5 + MSCs groups. D: Scheme of treatment procedure. E: Tumor volume curves in HCT116-EV + MSCs and HCT116-CCR5 + MSCs groups. Dotted lines show treatment group with maraviroc 30 mg/kg/d, and solid lines show control group with vehicles.
- Citation: Li JN, Li W, Cao LQ, Liu N, Zhang K. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of gastrointestinal malignancies. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2020; 12(4): 365-382
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v12/i4/365.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v12.i4.365