Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Oct 15, 2020; 12(10): 1091-1103
Published online Oct 15, 2020. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v12.i10.1091
Published online Oct 15, 2020. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v12.i10.1091
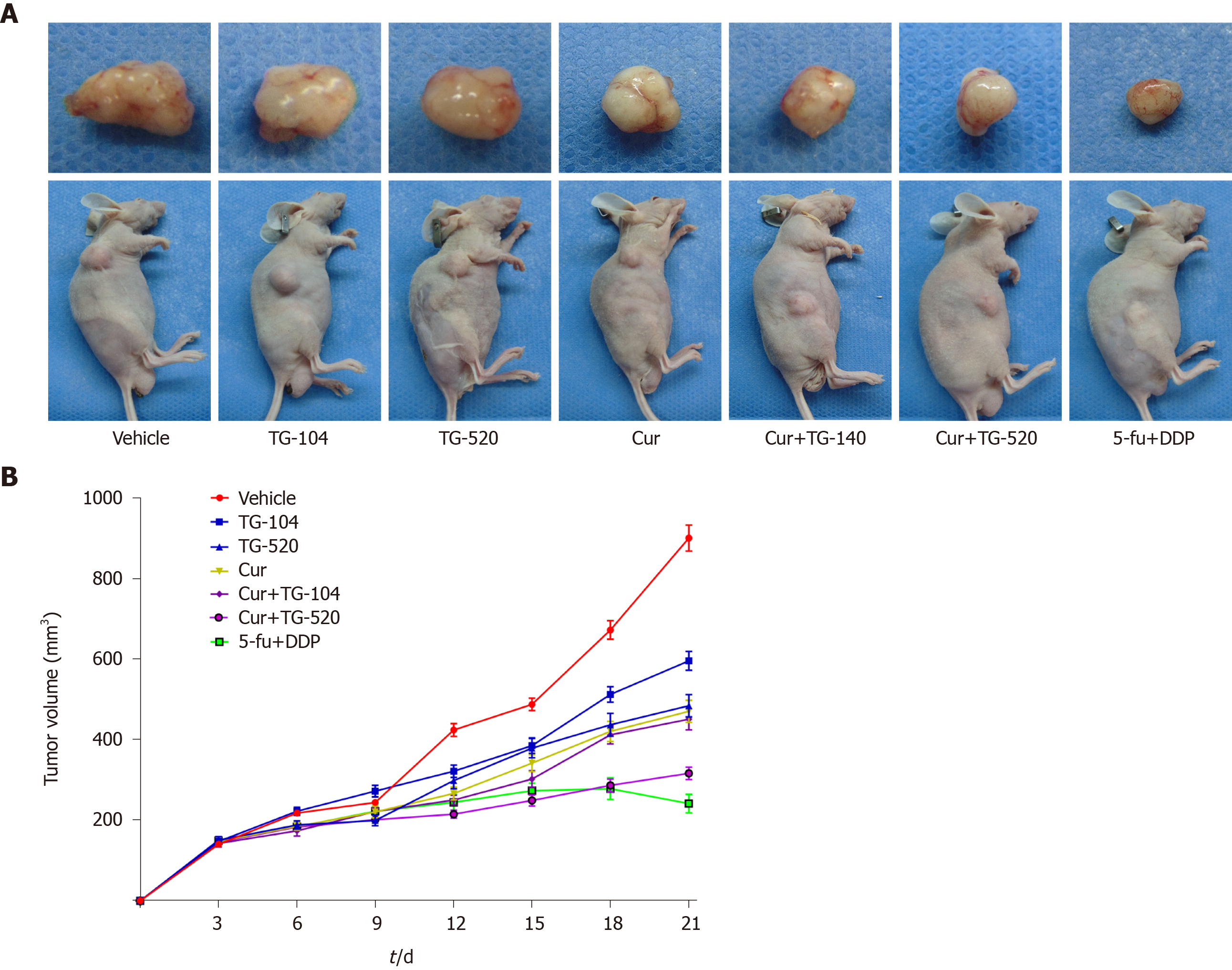
Figure 1 Curcumin and total ginsenosides inhibit liver cancer growth.
A: Representative photographs of subcutaneous liver cancer following treatment with curcumin (200 mg/kg per day), total ginsenosides (104 mg/kg per day or 520 mg/kg per day), or the combination of the two for 21 d; B: The tumor volume of mice was measured. Data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01 between two groups using least significant difference or Dunnett’s T3 method. Cur: Curcumin; TG: Total ginsenosides; 5-Fu: 5-fluorouracil; DDP: Cisplatin.
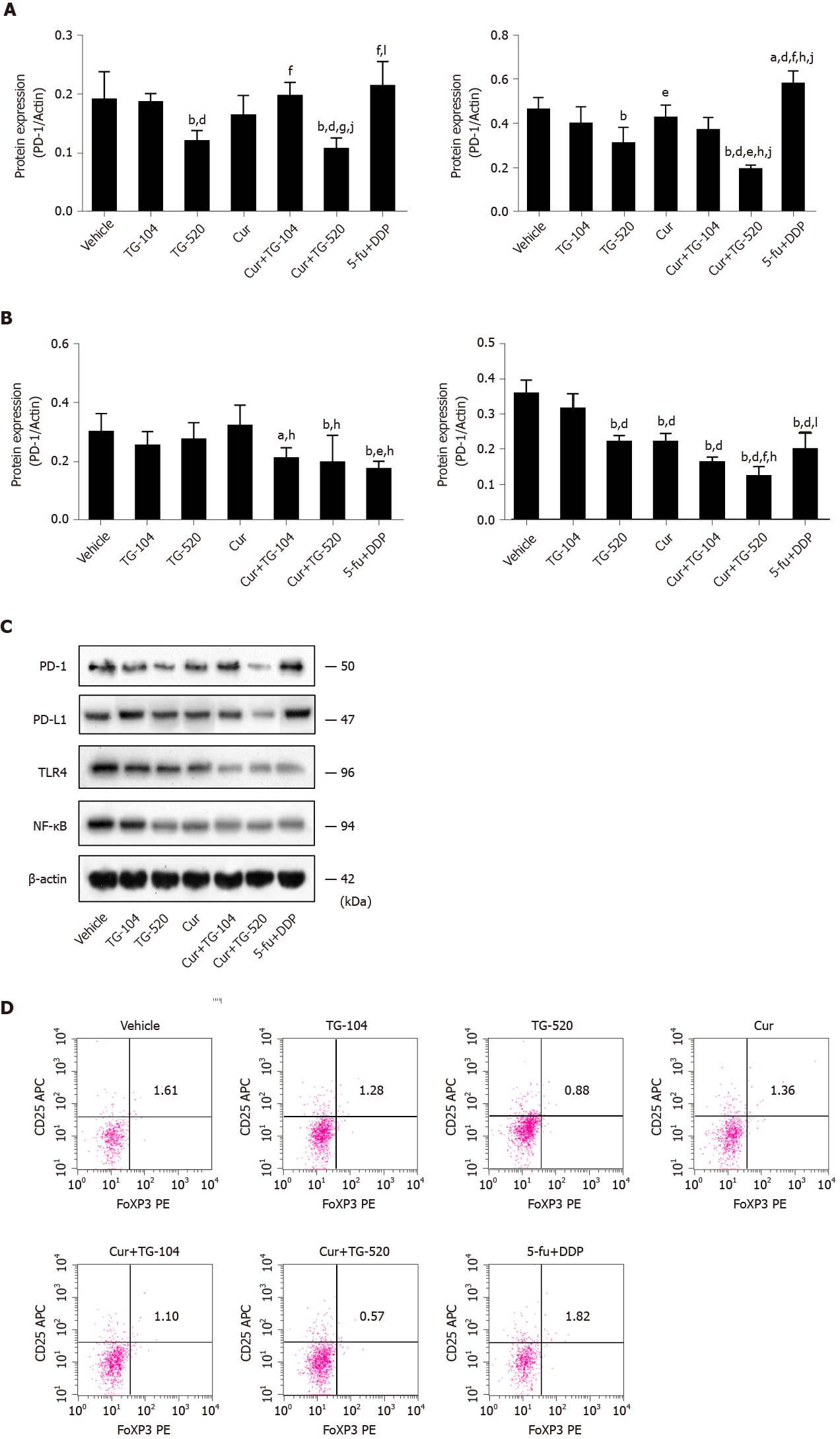
Figure 2 Curcumin and total ginsenosides inhibit the activation of programmed cell death 1/ programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 and Tregs.
A subcutaneous liver cancer mouse model was treated with curcumin (Cur), total ginsenosides (TG), or a combination of the two for 21 d, and tumor tissues were harvested as indicated. A-C: The protein levels of programmed cell death 1, programmed cell death 1 ligand 1, Toll like receptor 4, and nuclear factor-κB were evaluated by Western blot analysis. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase was used as the loading control; D: CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs were evaluated by flow cytometry. Results show the proportion of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs in HepG2 subcutaneous tumor tissues of BALB/c mice. Data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean, and were compared between two groups using least significant difference or Dunnett’s T3 method. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01 vs vehicle group; cP < 0.05 and dP < 0.01 vs TG-104 group; eP < 0.05 and fP < 0.01 vs TG-520 group; gP < 0.05 and hP < 0.01 vs Cur group; iP < 0.05 and jP < 0.01 vs Cur + TG-104 group; kP < 0.05 and lP < 0.01 vs Cur + TG-520 group. Cur: Curcumin; TG: Total ginsenosides; PD-1: Programmed cell death 1; PD-L1: Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1; Tregs: CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells; TLR4: Toll like receptor 4; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB; DDP: Cisplatin; 5-Fu: 5-fluorouracil.
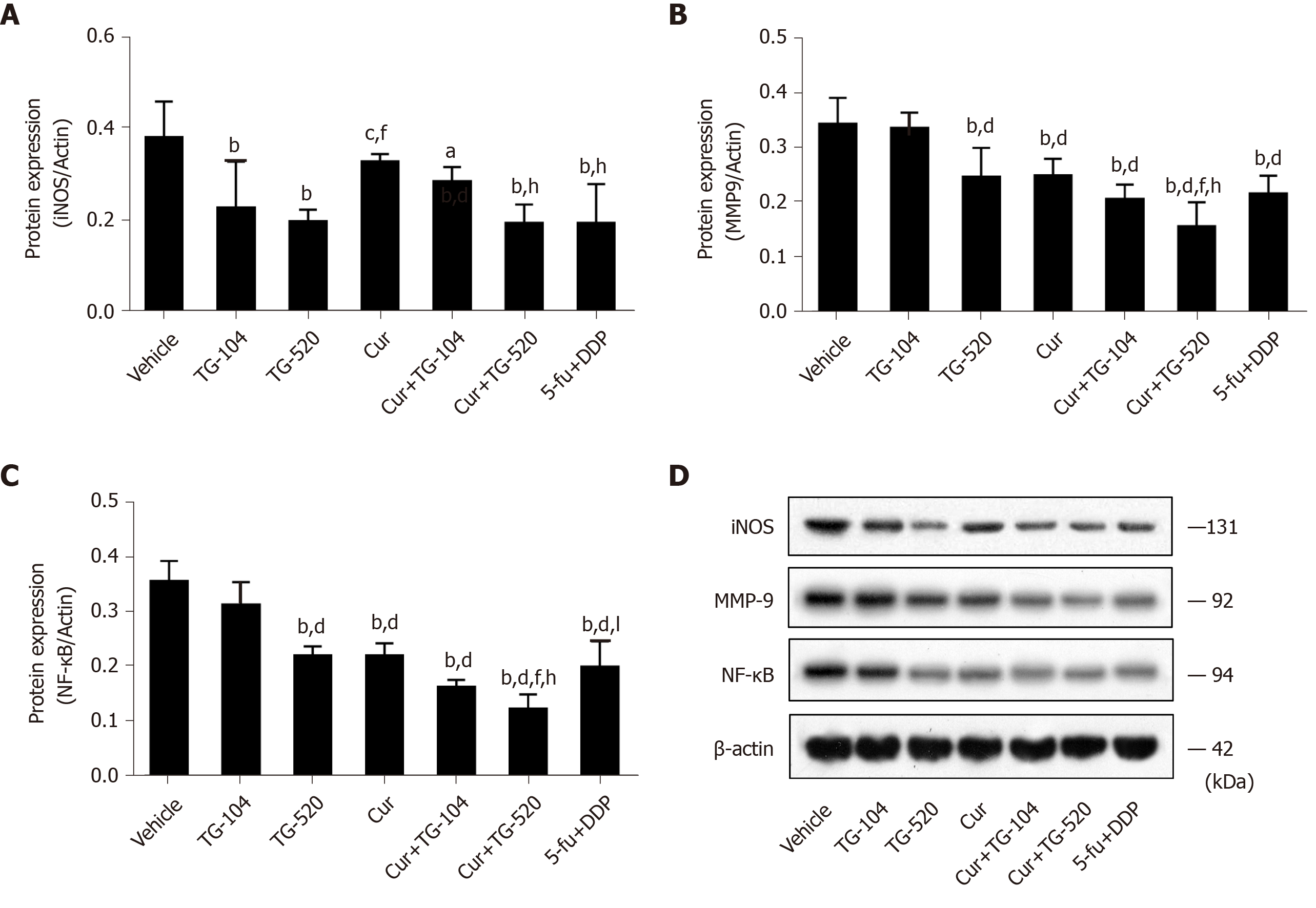
Figure 3 Curcumin and total ginsenosides inhibit the activation of matrix metalloproteinase 9 and nitric oxide synthase.
A-D: The protein levels of nitric oxide synthase, matrix metalloproteinase 9, and nuclear factor-κB were evaluated by Western blot analysis in tumor tissues from a subcutaneous liver cancer mouse model. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase was used as the loading control. Data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean, and were compared between two groups using least significant difference or Dunnett’s T3 method. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01 vs vehicle group; cP < 0.05 and dP < 0.01 vs TG-104 group; eP < 0.05 and fP < 0.01 vs TG-520 group; gP < 0.05 and hP < 0.01 vs Cur group; iP < 0.05 and jP < 0.01 vs Cur + TG-104 group; kP < 0.05 and lP < 0.01 vs Cur + TG-520 group. Cur: Curcumin; TG: Total ginsenosides; DDP: Cisplatin; 5-Fu: 5-fluorouracil; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB.
- Citation: Deng Z, Xu XY, Yunita F, Zhou Q, Wu YR, Hu YX, Wang ZQ, Tian XF. Synergistic anti-liver cancer effects of curcumin and total ginsenosides. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2020; 12(10): 1091-1103
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v12/i10/1091.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v12.i10.1091