Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Sep 15, 2019; 11(9): 750-760
Published online Sep 15, 2019. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v11.i9.750
Published online Sep 15, 2019. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v11.i9.750
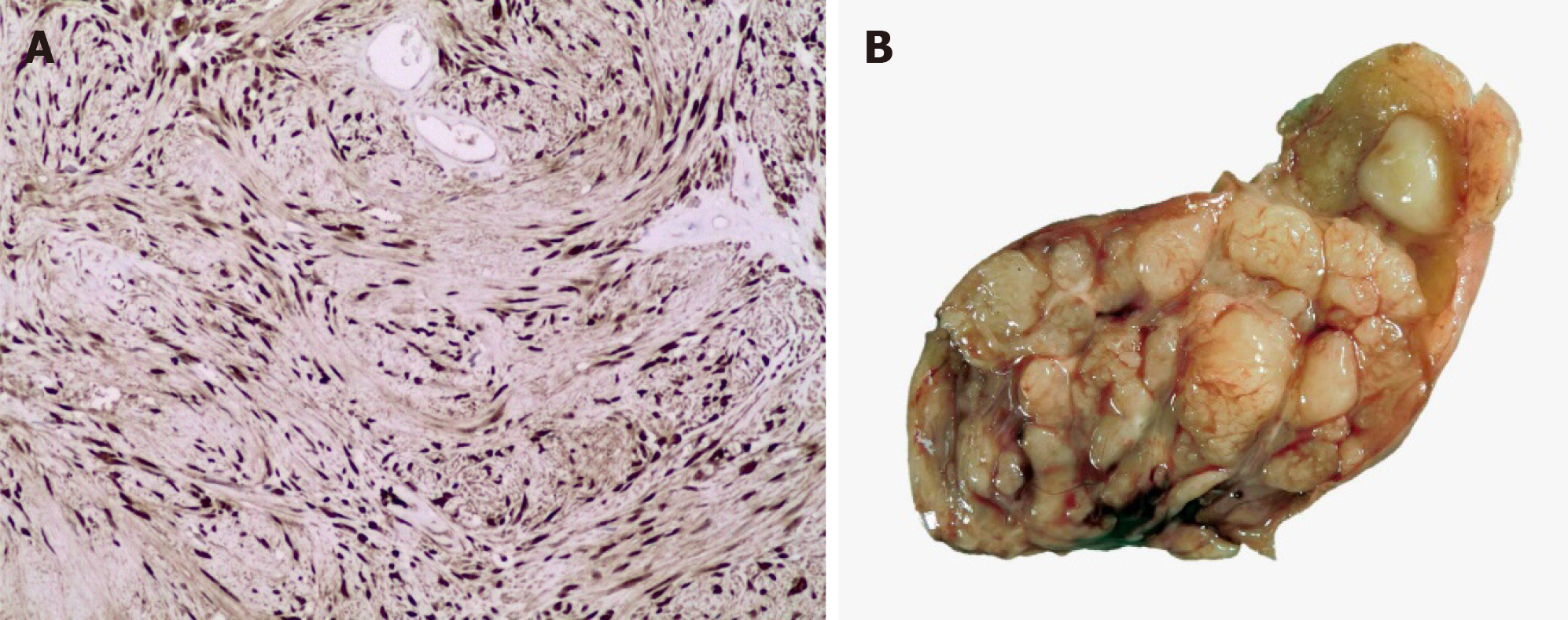
Figure 1 Immunohistochemistry and macroscopic images.
A: The immunohistochemistry was diffusely positive for S100 (in the nucleus and cytoplasm) in the proliferative cells; which confirms its histomorphogenesis of the cells of schwann. This image corresponds to the esophagic schwannoma resected at our institute; B: Macroscopic image of the esophageal schwannoma.
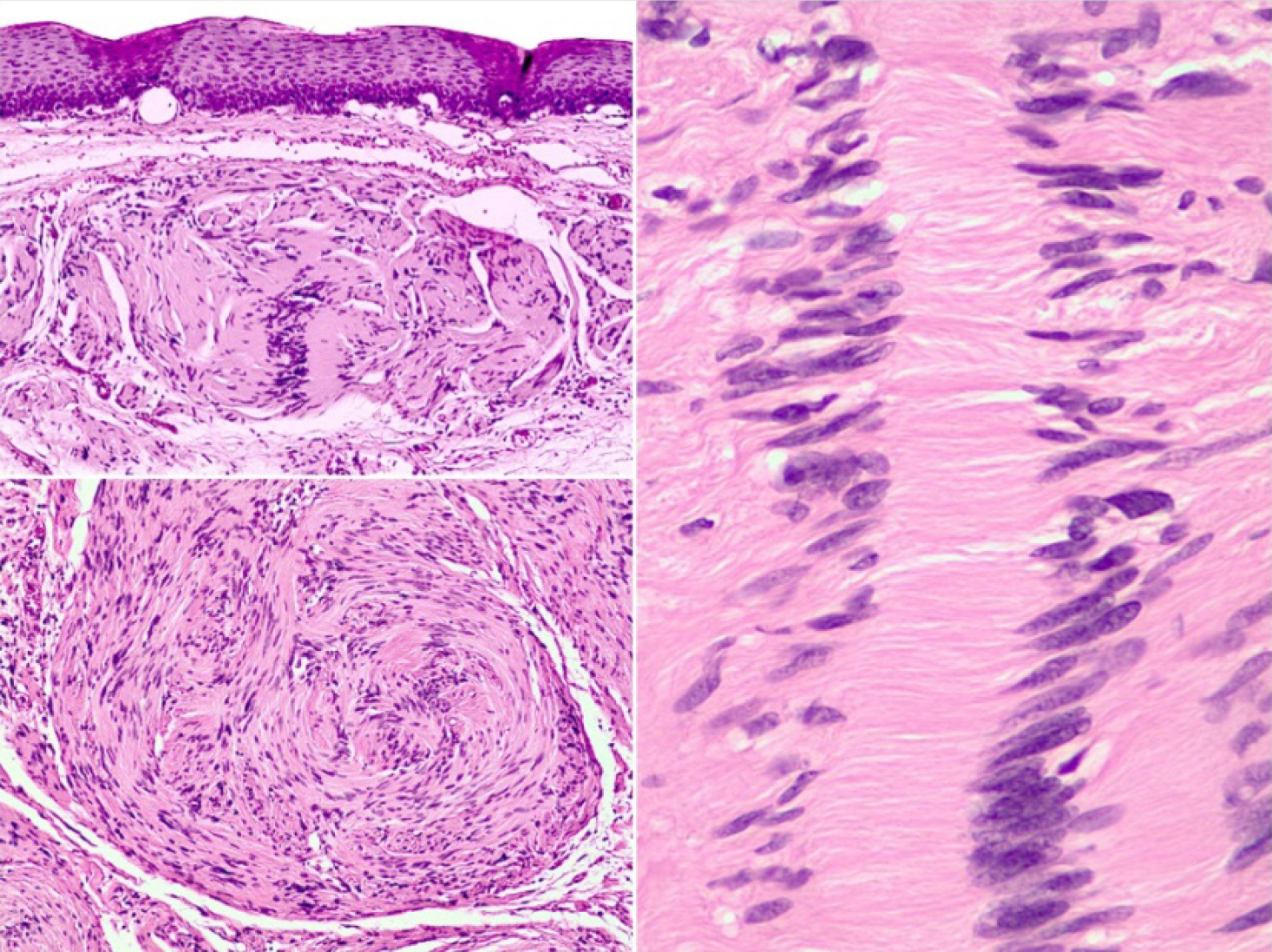
Figure 2 Nulcear palisading around fibrillary process (verocay bodies) is often seen in cellular areas.
This image corresponds to the esophagic schwannoma resected at our institute.
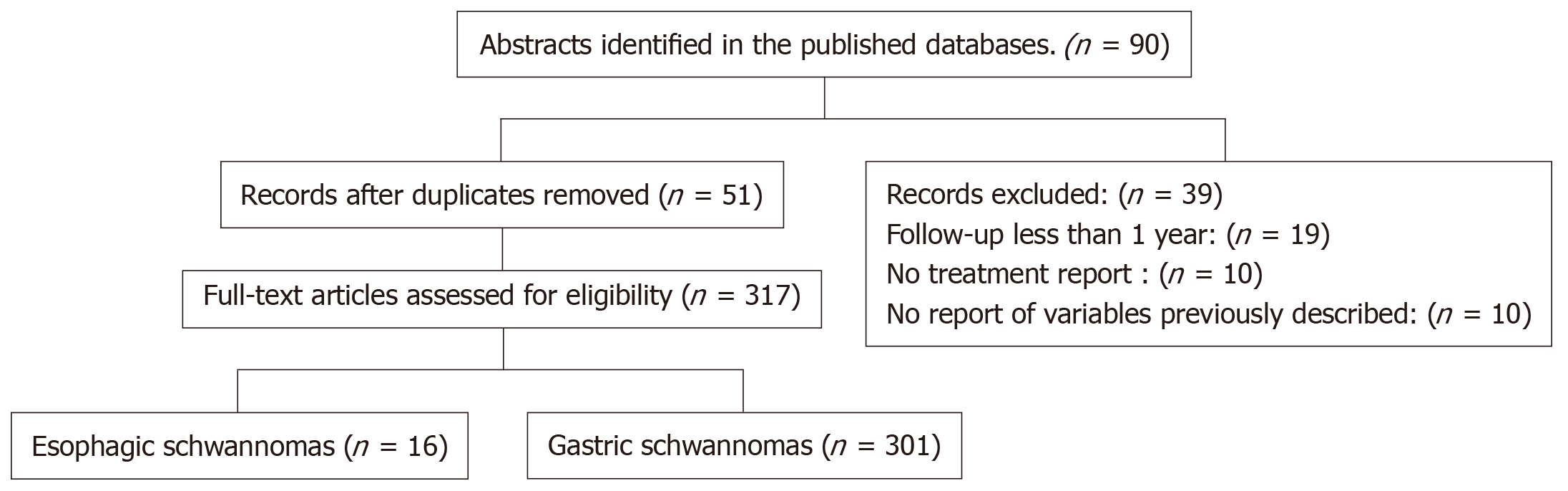
Figure 3 Flowchart.
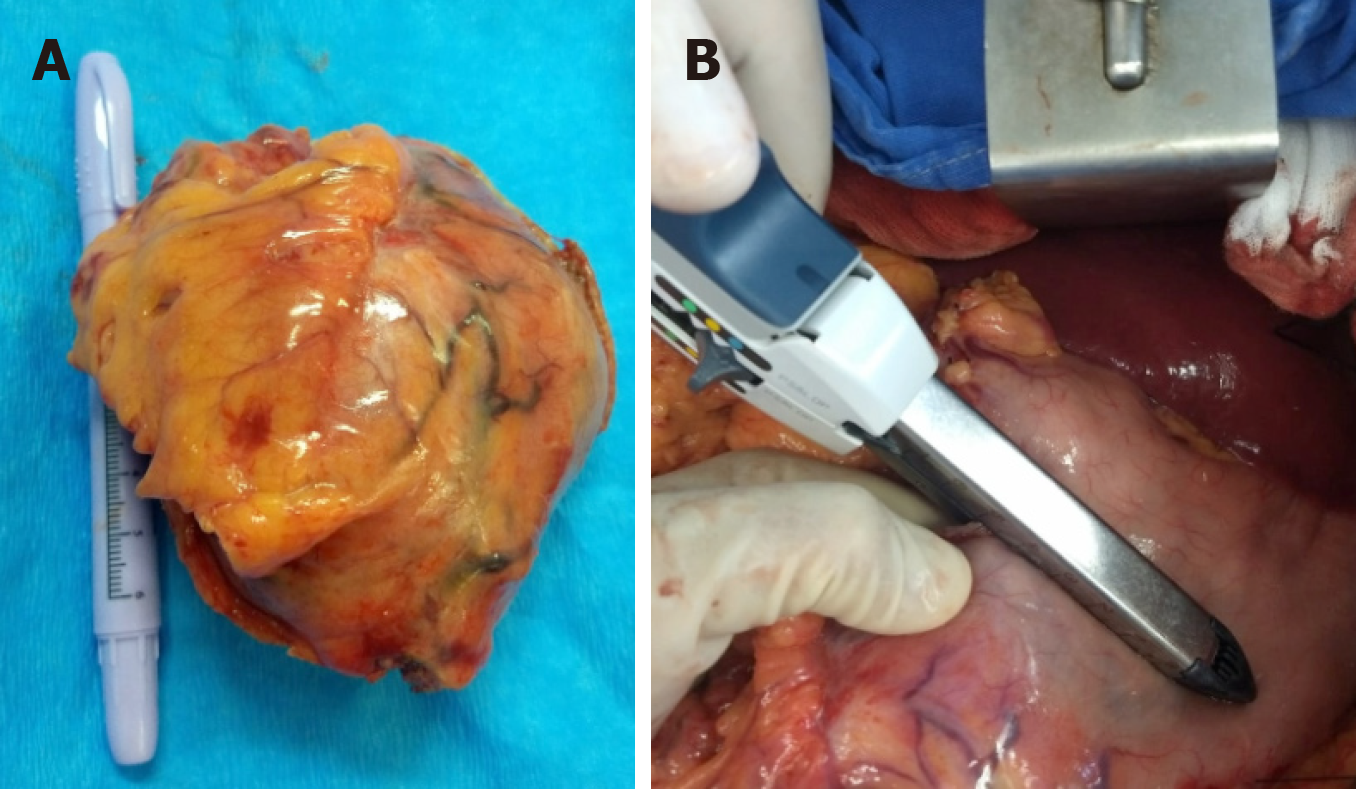
Figure 4 Resection of a gastric schwannoma.
A: Tumor of approximately 10 cm; B: Wedge resection by linear cutting stapler of the greater gastric curvature.
- Citation: Morales-Maza J, Pastor-Sifuentes FU, Sánchez-Morales GE, Ramos ESG, Santes O, Clemente-Gutiérrez U, Pimienta-Ibarra AS, Medina-Franco H. Clinical characteristics and surgical treatment of schwannomas of the esophagus and stomach: A case series and systematic review. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2019; 11(9): 750-760
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v11/i9/750.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v11.i9.750