Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Oct 15, 2019; 11(10): 887-897
Published online Oct 15, 2019. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v11.i10.887
Published online Oct 15, 2019. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v11.i10.887
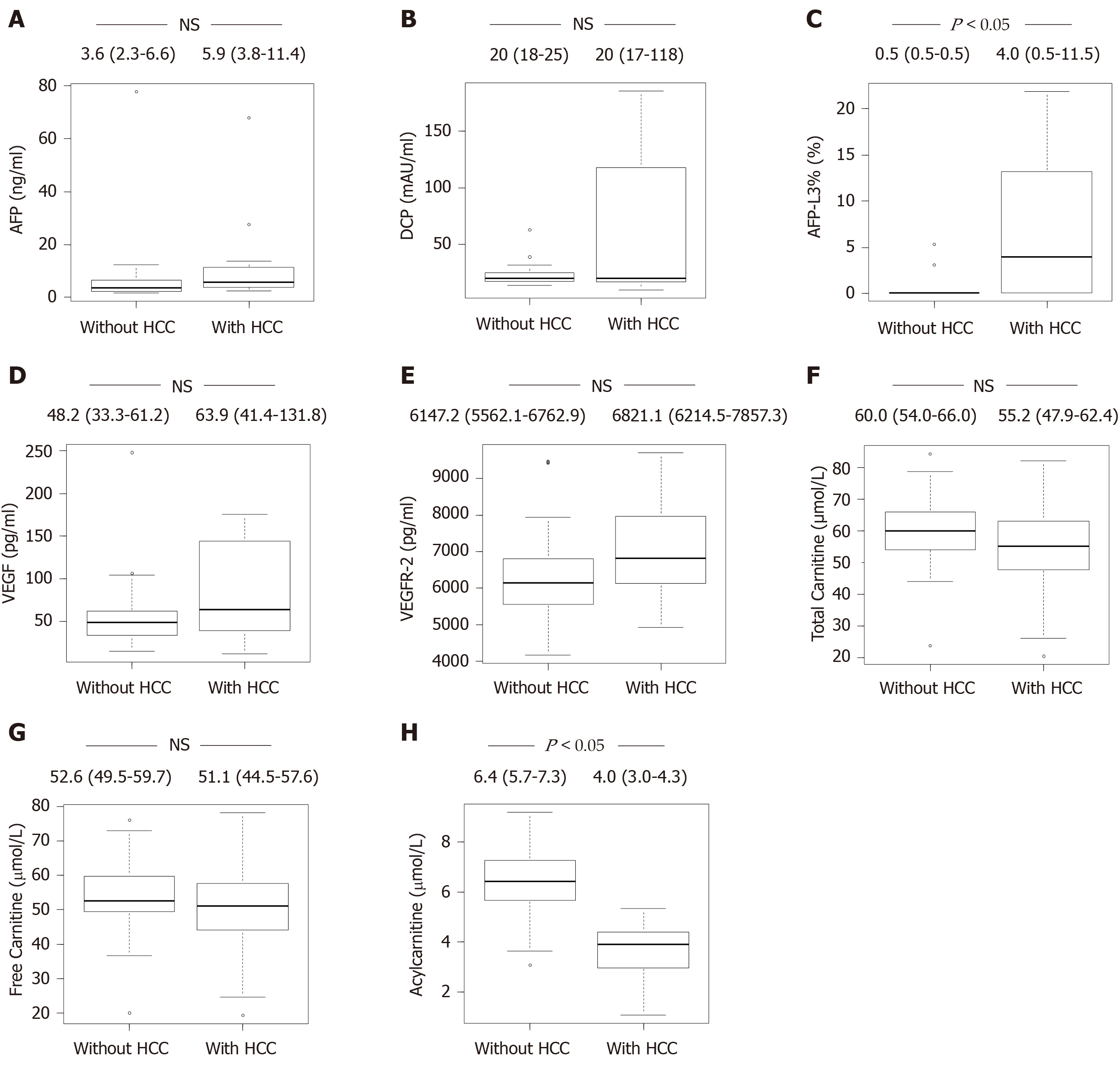
Figure 1 Differences in carnitine, tumor markers, and angiogenic factors between non-steatohepatitis patients with and without hepatocellular carcinoma.
A: Level of AFP; B: Level of DCP; C: Level of AFP-L3%; D: Level of VEGF; E: Level of VEGFR-2; F: Level of total carnitine; G: Level of free carnitine; H: Level of acylcarnitine. The level of acylcarnitine (H) was significantly lower in non-SH patients with HCC vs that observed in non-SH patients without HCC (P < 0.05). In addition, the level of AFP-L3% (C) was significantly higher in non-SH patients with HCC compared with that reported in non-SH patients without HCC (P < 0.05). However, the levels of AFP, DCP, VEGF, VEGFR-2, total carnitine, and free carnitine (A, B, D, E, F, and G) were not different between the two groups of patients. SH: Steatohepatitis; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; AFP: α-Fetoprotein; DCP: Des-γ-carboxy prothrombin; AFP-L3%: Lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive α-fetoprotein; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR-2: VEGF receptor-2.
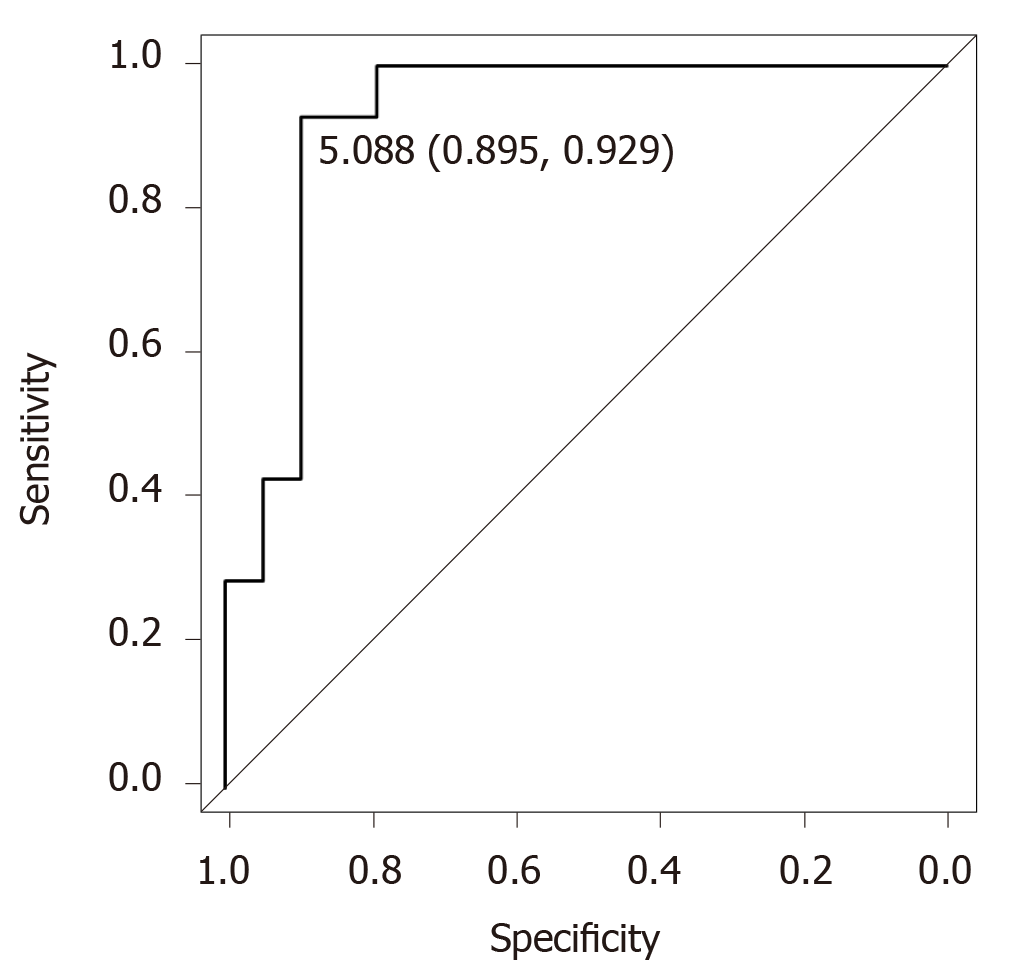
Figure 2 Diagnostic accuracy of acylcarnitine for the early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in non-steatohepatitis patients.
ROC analysis of acylcarnitine revealed that the cutoff value was 5.088, the specificity was 89.5%, the sensitivity was 92.9%, and the AUC was 0.925.
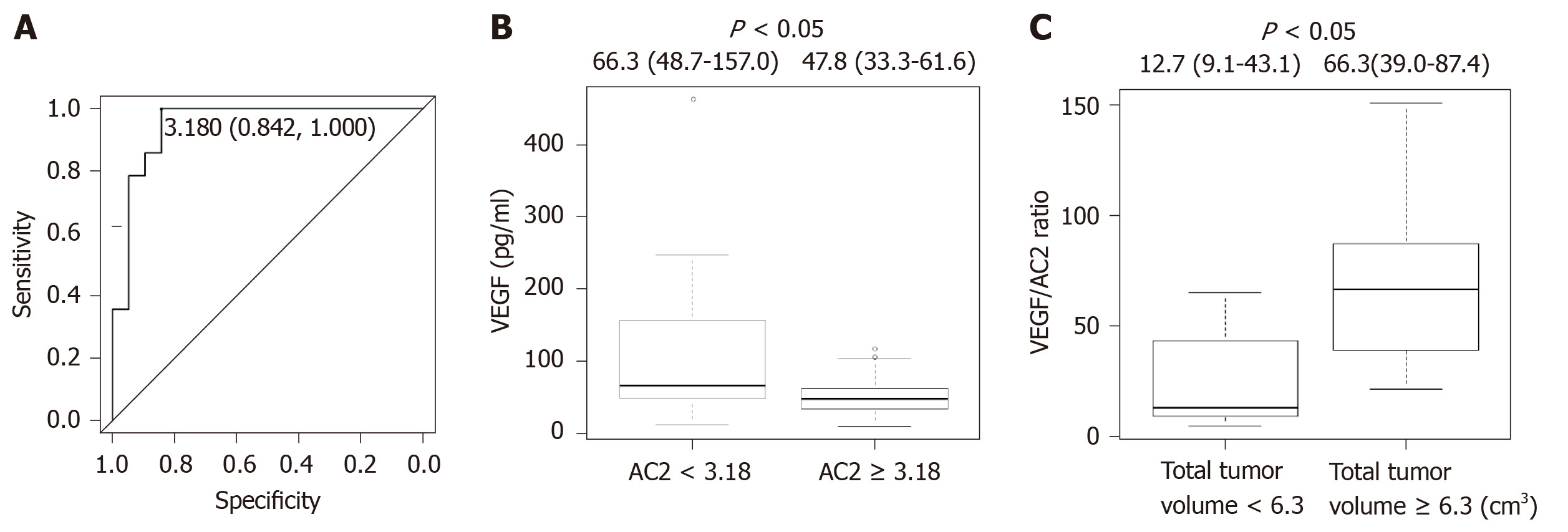
Figure 3 Acetylcarnitine is associated with vascular endothelial growth factor and hepatocellular carcinoma progression in non-steatohepatitis patients.
A: ROC analysis of acetylcarnitine (AC2) for the early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in non-steatohepatitis patients revealed that the cutoff value was 3.18, the specificity was 84.2%, the sensitivity was 100%, and the AUC was 0.925; B: The patients were categorized into two groups according to the ROC cutoff vale for AC2 (low, < 3.18; and high, ≥ 3.18). The patients with AC2 < 3.18 had a significantly higher level of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) compared with those with AC2 ≥ 3.18. The patients with HCC were categorized into two groups according to the median cutoff value for total tumor volume (low, < 6.3 and high, ≥ 6.3); C: The HCC patients with a total tumor volume of ≥ 6.3 had a significantly higher VEGF/AC2 ratio compared with those with a total tumor volume of < 6.3. AC2: acetylcarnitine; VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor.
- Citation: Takaya H, Namisaki T, Kitade M, Shimozato N, Kaji K, Tsuji Y, Nakanishi K, Noguchi R, Fujinaga Y, Sawada Y, Saikawa S, Sato S, Kawaratani H, Moriya K, Akahane T, Yoshiji H. Acylcarnitine: Useful biomarker for early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in non-steatohepatitis patients. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2019; 11(10): 887-897
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v11/i10/887.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v11.i10.887