Published online May 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i5.453
Peer-review started: December 26, 2022
First decision: January 31, 2023
Revised: February 14, 2023
Accepted: April 12, 2023
Article in press: April 12, 2023
Published online: May 26, 2023
Processing time: 150 Days and 18.5 Hours
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are nanometric particles that enclose cell-derived bioactive molecules in a lipid bilayer and serve as intercellular communication tools. Accordingly, in various biological contexts, EVs are reported to engage in immune modulation, senescence, and cell proliferation and differentiation. Therefore, EVs could be key elements for potential off-the-shelf cell-free therapy. Little has been studied regarding EVs derived from human pluripotent stem cells (hPSC-EVs), even though hPSCs offer good opportunities for induction of tissue regeneration and unlimited proliferative ability. In this review article, we provide an overview of studies using hPSC-EVs, focusing on identifying the conditions in which the cells are cultivated for the isolation of EVs, how they are characterized, and applications already demonstrated. The topics reported in this article highlight the incipient status of the studies in the field and the significance of hPSC-EVs’ prospective applications as PSC-derived cell-free therapy products.
Core Tip: The research on extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from different cell types, such as adult stem cells, has shown potential in the treatment of various pathologies. However, little has been explored regarding EVs derived from human pluripotent stem cells (hPSC-EVs). In this review, we provide an overview of studies carried out on these EVs, highlighting methodologies used for the culture of hPSCs for isolating EVs, their characteristics, and potential applications. We note the potential of hPSC-EVs as future acellular therapies. However, studies are in the infancy, and more research is needed to confirm their benefits.
- Citation: Matos BM, Stimamiglio MA, Correa A, Robert AW. Human pluripotent stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: From now to the future. World J Stem Cells 2023; 15(5): 453-465
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v15/i5/453.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v15.i5.453
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are nanometric particles that are enclosed by a lipid bilayer and released by all cell types. They lack a functional nucleus and are therefore unable to replicate[1]. EVs are composed of bioactive factors such as lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, including mRNAs and non-coding RNAs[2]. EV is an umbrella term that encompasses a heterogeneous population of membrane vesicles generated through a variety of mechanisms. The two major EV subpopulations include microvesicles (MVs) and exosomes (EXOs). EXOs are intraluminal vesicles of endosomal origin released when multivesicular bodies fuse with the plasma membrane, whereas MVs or ectosomes are generated from the outer budding of the plasma membrane[3]. Due to their distinct biogenesis, MVs are generally larger (up to 1000 nm in diameter) than EXOs (less than 200 nm). However, these vesicle populations overlap not only in terms of size but also in composition[4]. Recently, other nomenclatures were described in the “Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018” guidelines (MISEV2018) based on the physical characteristics of EVs, for example, size (< 200 nm, small EVs; > 200 nm, medium or large EVs) or density (low, middle, or high)[1].
Potential uses of EVs, such as for the diagnosis and treatment of pathologies or as potential drug carriers, have been investigated. In the field of regenerative medicine, the secretomes of adult stem cells, primarily mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (MSCs), including their EVs, are of great interest as they have been shown to act mainly in a paracrine manner rather than their potential for differentiation[5]. An interesting list of advantages and disadvantages of the use of EVs instead of stem cells has been presented by Öztürk et al[6]. Among the advantages of using EVs cited by them and others are low immunogenicity and toxicity; minimal risk of malign transformation; minimal risk of getting trapped in the lung or causing vasculature obstruction; avoidance of contamination with undesired cell types; avoidance of uncontrolled cell division; the ability to manipulate EVs in order to obtain potential improvements; optimization of MSC culture to obtain a higher amount of EVs; and their ability to cross the blood-brain barrier, among others[4,6]. In addition, EVs mimic the beneficial effects of MSCs in cell therapies in a wide range of animal models for different diseases[7-9].
MSC-derived EV (MSC-EV) has been extensively studied and has demonstrated several promising effects, as reviewed by Gowen et al[10], Tieu et al[11], Fuloria et al[12], Kou et al[13], and Yudintceva et al[14]. However, despite the high potential of MSC-EVs, several factors limit their use. Recently some reviews highlighted the difficulty of establishing criteria to define the specific characteristics of MSC-EV and discussed the great variation in the MSC-EV preparations[15,16]. Disadvantages of MSCs as a source for EVs include the variability between cells derived from different tissues, the variability between different donors, their limited ability to proliferate, the fact that they enter senescence, and genomic instability after a few passages[17]. This raises the question of whether pluripotent stem cell (PSC) derived EVs have a similar to or better therapeutic potential than adult stem cell-derived EVs.
In this context, our objective is to show, using a non-systematic search, studies that use or characterize EVs derived from human PSC (hPSC-EVs) to understand the advances in the area. We also aim to identify the conditions in which the cells are cultivated for the isolation of EVs, how these are characterized, and any demonstrated applications (in vivo or in vitro).
hPSCs are characterized by unlimited proliferation and the potential to generate specialized cell lineages[18]. Human embryonic stem cells (hESC) were first isolated from human blastocysts in 1998 by Thomson et al[19], and to date, hundreds of hESC lineages have been established worldwide. hESC-based therapeutic technologies have applications in many diseases and conditions, such as spinal cord injuries, age-related tissue degeneration, and diabetes[20]. However, ethical issues related to using cells from embryos have hindered the application of hESCs in research and treatment, leading to the development of the induced PSC (iPSC) technology by Takahashi and Yamanaka[21] and Takahashi et al[22]. Since the generation of the first iPSC, many research groups have developed human iPSC (hiPSC) lineages reprogrammed from different adult cells, and obtained lineages very similar to hESC in terms of morphology and differentiation potential[23]. For more information about hPSCs, see Karagiannis et al[24], Liu et al[25], and Yamanaka[26].
Especially after the discovery of hiPSCs, pluripotent cells represented a promising alternative for regenerative medicine, transplants, disease modeling, and many other research applications[27-29]. The possibility of generating pluripotent cells from patients and, from them, differentiated cells for tissue repair may mitigate common transplant issues, such as immunologic rejection. Nevertheless, the immunogenicity of pluripotent cells remains controversial[30], and the potential for tumorigenesis hinders the wide application of these cells in clinics. The risks of contaminating the differentiated cell populations with remaining pluripotent or proliferative cells, as well as the transmission of active pluripotency transcription factors or the acquisition of mutations by the pluripotent cells during in vitro culture[26,31], limit the acceptance of hPSC-based therapies. Therefore, cell-free therapeutic approaches, including EVs, offer promising possibilities for applying hPSC-derived products[32].
It seems that the role of the secretomes of these cells has only recently begun to be investigated, possibly due to the difficulties still encountered in using hPSCs in the clinic. Some interesting studies show that EVs from ESCs could help with embryo implantation[33] and maintaining ESC stemness[34], while others have investigated the biogenesis of ESC-EVs[35,36], although they used murine PSCs. We will focus this review on studies with hPSCs due to their potential clinical applications.
The first investigation on the isolation of EVs from hPSC dates from 2015. In this initial approach, EVs were isolated from hiPSC cultured in Essential 8™ medium using differential centrifugation (DF)/ultracentrifugation (UC). It was shown that the hiPSC-derived EVs (hiPSC-EV) contain a variety of microRNAs (miRNAs) (such as miR-382, miR-611, and others) related to pathways such as focal adhesion, Wnt, PI3K-Akt, and MAPK signaling, as well as proteins related to processes involved in signal transduction, receptor binding, and others. In addition, the EVs positively affected the metabolism, proliferation, apoptosis rate, and differentiation capacity of cardiac MSCs. Better results were obtained when cells were exposed for only 22 h to EVs[37]. This initial attempt demonstrated how hPSC-EVs could be beneficial and of interest for future acellular therapy applications.
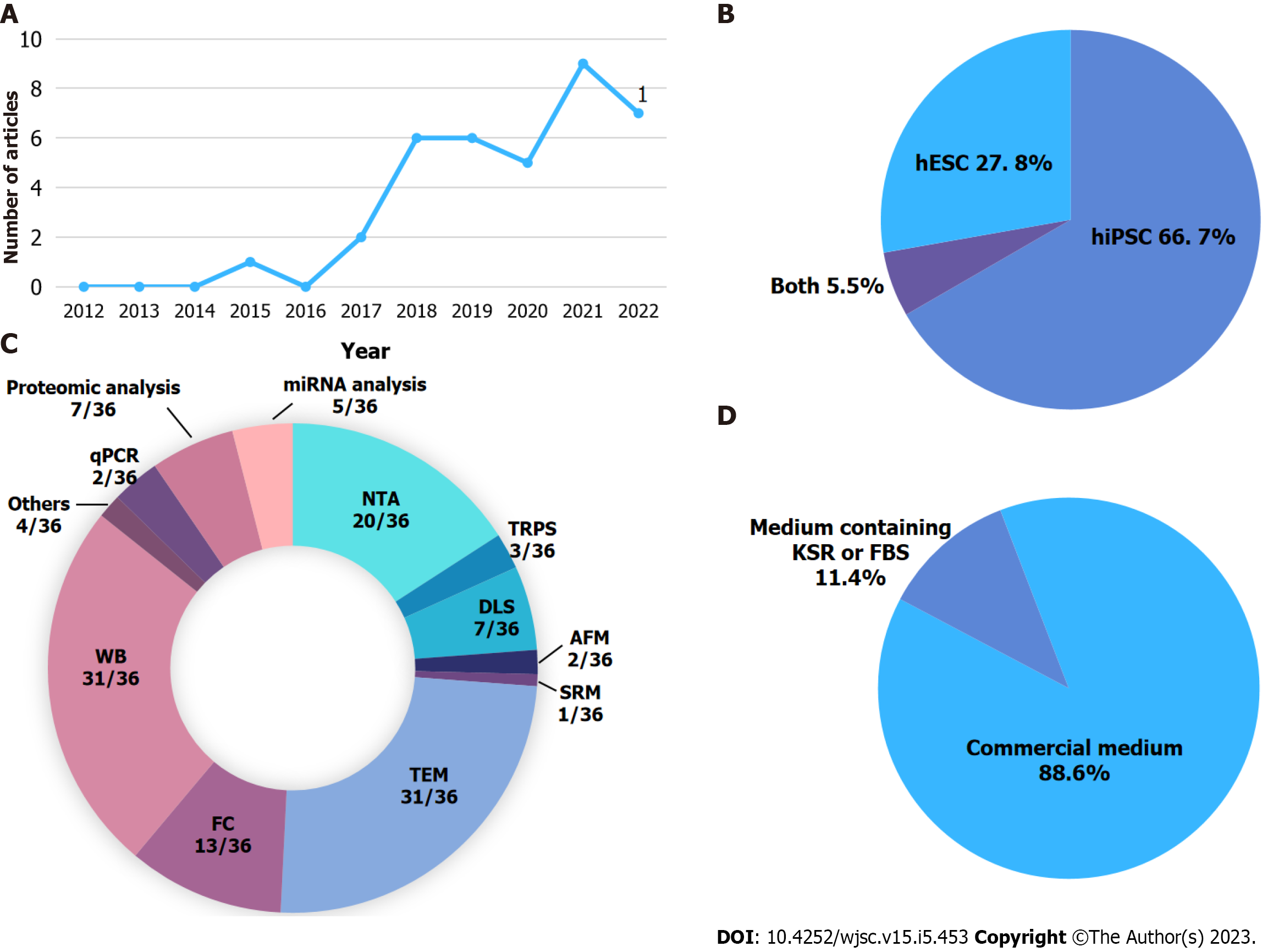
Despite the potential of hPSC-EVs, we observed that the number of publications in this area is still low, and most of the existing publications date from the last five years (Figure 1A, Table 1). Some studies evaluate EVs that were isolated during the differentiation process or from cells that differentiated from PSCs, such as hiPSC-derived keratinocytes[38]; hPSC-derived cardiac progenitors or cardiomyocytes[39-41]; hPSC-derived MSCs[42-44]; hiPSC-derived neurons[45-47]; and hESC-derived chondroprogenitor cells[48]. However, our review explores studies that isolated EVs from undifferentiated hPSCs.
| Ref. | Culture medium | EV collection time | EV isolation method | EV mean size (nm) |
| Bobis-Wozowicz et al[37], 2015 | Essential 8™ medium | NI (cells in 70%-90% confluency) | DC + UC | 146 |
| Ju et al[50], 2017 | PSCeasy medium (Cellapy) | 24 h | DC + UC | 122, 132 |
| Zhou et al[51], 2017 | mTeSR™-1 medium | NI (cells in 60%-90% confluency) | DC + 0.22 μm filter + UC | 101 |
| Ding et al[52], 2018 | mTeSR™-1 medium | 48 h | DC + UC | 103.1 |
| Kaur et al[53], 2018 | Essential 8™ Flex medium | 48 h | DC + UC or miR-CURY™ Exosome Isolation Kit (Exiqon A/S) | 100-200 |
| Kobayashi et al[54], 2018 | DMEM-F12 + NEAA, 200 mM L-gln, KSR, 0.1 M BME | 2-3 d before passage | MagCapture Exosome Isolation Kit PS (Wako) | 100 |
| Oh et al[55], 2018 | Essential 8 medium | Daily, from day 2 to day 5 | 0.45 μm filter + ExoQuick-TC kit | 85.8 |
| Peng et al[56], 2018 | mTeSR™-1 medium | 24 h (cells in about 80% confluency) | MV: DC + 16500 g, 1 h; EXO: DC + 120000 g, 2 h | MV = 200-600; EXO = 40-80 |
| Saito et al[57], 2018 | mTeSR™-1 medium | NI | DC + concentration in 100-KDa filter + MagCapture™ Exosome Isolation Kit PS | 179 |
| Chen et al[58], 2019 | mTeSR™-1 medium | NI | DC + UC | 50-150 |
| Liu et al[59], 2019 | Essential 8™ medium | Daily, for 3-5 d | DC + concentration in 100-kDa filter + SEC | 150 |
| Marzano et al[60], 2019 | mTeSR™-1 medium | Daily, for 4 d | 0.22 μm filter + concentration in 100-kDa filter + Total Exosome Isolation Reagent (Thermo Fisher) or DC + UC | about 240 |
| Povero et al[61], 2019 | NI | 24-48 h | DC + UC | 300-400 |
| Sun et al[62], 2019 | mTeSR™-1 medium | 48 h | DC + concentration in 100-kDa filter + Exosome Isolation Kit (PureExo) + UC + 0.22 μm filter | 70-100 (cell-dependent) |
| Zhu et al[63], 2019 | mTeSR™-1 medium | 48h (cells 80%-90% confluency) | DC + 0.22 μm filter + UC | 70.2 |
| Collino et al[64], 2020 | mTeSR™-1 medium | 24 h | DC + UC | 119 |
| Hu et al[65], 2021 | ncEpic hPSC medium | NI | DC + 0.22 μm filter + UC | 72.4 ± 21.3 |
| Kurtzwald-Josefson et al[66], 2020 | DMEM/F12 Ham 1:1 + 20% KSR, 1% NEAA, 1% L-gln, 0.2% BME, 4 ng/mL rhFGF basic | 24 h (cells in about 80% confluency) | Total exosome isolation reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific) | 115 ± 7 |
| Liu et al[67], 2020 | mTeSR™-1 medium | NI | DC + UC | 50-75 |
| Wang et al[68], 2020 | PGM1 medium | NI | DC + 0.22 μm filter + UC | 30-120 |
| Andrade et al[69], 2021 | mTeSR™-1 mediuma | Daily, for 4-5 days | TFF with or without subsequent UC | 103-109 |
| Ashok et al[39], 2021 | StemMACS medium with 10 μM ROCK inhibitor and 0.2% Pluronic F68 | Days 3, 4, and 5 prior to differentiation | DC + 0.22 μm filter + UC + SG | 50 |
| Hu et al[65], 2021 | ncEpic hPSC medium | NI | DC + 0.22 μm filter + UC | -100 |
| Karnas et al[70], 2021 | Essential 8™ medium | NI | DC + UC | 215.7 |
| Ke et al[71], 2021 | Exo-depleted FBS | 48 h | MV: DC + 16500 g, 60 min; Exo: DC + 120000 g, 120 min | MV = 200-600; Exo = 40-80 |
| Luo et al[49], 2021 | DMEM/F12 + KSR (0.5%, 2.5%, 5%, or 20%) | Daily, for 5 d | DC + 0.45 μm filter + concentration in 10-kDa filter + 0.22 μm filter + UC or ExoQuick-TC kit (SystemBioscience) | 187.8, 168.2 |
| Saito et al[46], 2021 | StemFit AK-03N medium (Ajinomoto) | NI | 15000 × g, 30 min + 0.22 μm filter + UC | 70 |
| Wang et al[72], 2021 | mTeSR™-1 medium | NI | DC + UC | 120-140 |
| Xia et al[73], 2021 | Nuwacell hiPSC/hESCs medium | 24 h | DC + 0.22 μm filter + UC | 50-150 |
| Bi et al[74], 2022 | ncTarget medium (Nuwacell. Ltd, China) | 24 h (cells in about 80% confluency) | DC + UC + 0.22 μm filter + UC | hESC = 133.1; hIPSC = 157.7 |
| Gu et al[75], 2022 | mTeSR™-1 medium | NI | 0.45 μm filter + concentration in 100-kDa filter + GC + 0.22 μm filter + UC | 143.5 |
| Gupta et al[76], 2022 | StemFlex™ medium | 48 h | DC + one-step sucrose cushion UC | 123.6 ± 60 |
| Hsueh et al[77], 2023 | StemFlex™ medium | 48 h | DC + UC | 136.8 |
| Li et al[78], 2023 | ncEpic hPSC medium | NI | DC + UC | 74.70 ± 20.77 |
| Li et al[79], 2022 | mTeSR™-1 medium | NI | DC + 0.22 μm filter + UC | 50.75-105.7 |
| Pan et al[80], 2022 | mTeSR™-1 medium | 24 h (cells in about 80% confluency) | DC + UC | 142.2 ± 64.1 |
Using a non-systematic search, we found 36 studies that isolate hPSC-EVs mainly from the hiPSC lineages (Figure 1B). Table 1 summarizes these studies, highlighting the cell culture medium used to culture the PSC, time of conditioned medium collection, EV isolation method, and EV mean size. The most common culture media were commercial, with defined components (Figure 1D). The two most common media used were mTeSR™1 (StemCell Technologies) and Essential 8™ medium (Thermo Fisher) (Table 1). A study published by Luo et al[49] aimed to optimize culture conditions for isolation of hiPSC-EVs. Using DMEM with different concentrations of EV-depleted KnockOut™ Serum Repla
The biggest variations in EV isolation methods relate to the collection time of the conditioned medium: Many studies do not state the conditioning time. In most studies, however, the EVs were isolated after 24 h of cell culture or every 24 h for 3-5 consecutive days (Table 1), avoiding exceeding the 80%-90% cell confluence in the cell cultures. This collection time is possibly related to the nature of PSCs, as the culture medium must be changed daily, and cells must not reach 100% confluence to guarantee their viability and pluripotency.
Other relevant aspects of EVs are their size, morphology, and estimated particle concentrations. Most studies presented the information listed in MISEV2018, including positive and negative protein markers in EVs, usually using the western blot technique (31/36 articles) and performing a single EV analysis mainly using transmission electron microscopy (31/36 articles) to verify EV morphology and nanoparticle tracking analysis (20/36 articles) to verify their mean size and concentration (Figure 1C). The greatest number of studies used small EVs/EXOs, with sizes up to 200 nm (small EVs) (Table 1).
The most common method for hPSC-EV isolation is DF (here defined as the initial centrifugations to remove cellular debris and apoptotic bodies) followed by UC (Table 1). Although this is the most common method used, it is unsuitable for isolating EVs from large-scale experiments and clinical trials. Using a large-scale 2D culture, Andrade et al[69] isolated hPSC-EVs using tangential flow filtration (TFF) with or without subsequent UC (TFF + UC). The isolated EVs presented a size of approximately 100 nm, regardless of whether UC had been performed, with similar particle concentration, although TFF + UC resulted in a smaller number of proteins. The effect of different culture conditions (hypoxia - 1% O2, physiological hypoxia - 5% O2, and normoxia) on the therapeutic potential of hPSC-EVs was also investigated. The results showed that EVs derived from hPSC cultured in 1% O2 (hypoxia) had greater angiogenic potential than those derived under other conditions and that better results were achieved when obtaining EVs using TFF[69].
Another highly discussed topic about PSCs is the possible formation of teratomas, as well as the biodistribution of these cells when applied in in vivo models. These concerns also extend to PSC-EVs. To clarify these points, Gu et al[75] evaluated the safety and biodistribution of hiPSC-EVs. They used several approaches to show that PSC-EVs are safe, have no adverse effects on cells (e.g., do not cause hemolysis), are not genotoxic, and can be administered by different routes (nasal, intramuscular, or intravenous) without generating adverse effects (e.g., inflammation at the site or pathological changes in the organs of rats).
Although few investigations have been carried out with hPSC-EVs, we notice that almost all of them have already applied hPSC-EVs to different disease models, both in vitro and in vivo. PSC-EVs have been described as having: Protective effects in in vitro and in vivo models of ischemia-reperfusion kidney injury[64]; neural protective abilities[60]; the capacity to modulate neuroinflammation and protect against ischemic stroke through Treg cell expansion[73]; antifibrotic effects in vivo and in in vivo models of liver injury[61,72]; and reduced cartilage degradation in an osteoarthritis model[77]. They have shown improvements in wound closure, angiogenesis, and increased nerve fiber density in a wound-healing diabetic mouse model[54,79]; and improved recovery of ovarian function in a premature ovarian failure mouse model[67]. EVs were also associated with acellular nerve grafts, demonstrating their potential to repair peripheral nerve defects[80].
It was also demonstrated that MVs, but not EXOs, dedifferentiated Müller cells into retinal progenitor cells in vitro[71]. Other studies showed the ability of PSC-EVs to promote regeneration of diseased or damaged retinas[56] and to accelerate corneal epithelium defect healing in vivo[68]. Other potential uses cited for PSC-EVs are: In antitumoral activity[51,63]; in angiogenesis stimulation[69]; as a gene delivery vector[50]; to increase the functional properties of cord blood-derived hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells[70]; and to improve the number of beating EBs depending on the hiPSC origin[66].
One noteworthy effect shown in some studies is the capacity of PSC-EVs to “rejuvenate” different cell types, such as senescent endothelial cells[52,58], senescent human dermal fibroblasts[55], senescent chondrocytes[77], and others. Considering this potential, the hPSC-EVs, hESC-EVs, and hiPSC-EVs were investigated as therapeutic tools for age-related diseases. Regarding neurological diseases, the hPSC-EVs showed potential in recovery of senescent hippocampal neural stem cells in rats with vascular dementia - partially through the transfer of miRNAs that inhibit mTORC1 activation - resulting in an improvement in disease status (e.g., reverse cognitive impairment)[81]. Furthermore, using mice of varying ages, hPSC-EVs were found to rejuvenate hippocampal neural stem cells partly through the transfer of SMAD proteins that activate myelin transcription factor 1 (MYT1), which is reduced in senescent cells, and activates a signaling cascade in the MYT1-Egln3-Sirt1 axis[81].
In an ischemic stroke model, hPSC-EVs reduced the expression of inflammatory cytokines and leukocyte infiltration, and increased the number of regulatory T cells and other immunomodulatory effects that alleviate neurological deficits[73]. They also reduced blood-brain barrier damage in aged stroke mice through blood-brain barrier rejuvenation, partially through the transfer of AKT1 and CALM from EVs to endothelial cells leading to activation of the endothelial nitric oxide synthase-Sirt1 axis[78]. Therefore, hPSC-EVs could be a promising cell-free therapy to treat age-related diseases associated with cellular senescence.
In order to evaluate the benefit of hPSC-EVs compared to other EVs, one interesting study demonstrated that both hiPSC-EVs and hMSC-EVs, isolated through size exclusion chromatography (Table 1), could improve the proliferation of senescent MSCs and alleviate cellular aging in a replicative aging model, possibly modulating reactive oxygen species production with peroxiredoxins presented in EVs. However, despite the similar effects, EVs derived from iPSCs enter target cells more efficiently, and the production of hiPSC-EVs was about 16-fold higher than that of MSC-EVs (using the same culture medium)[59].
Even though many articles described the effects of hPSC-EVs, few made deeper characterizations of, for example, the protein and miRNA content of these EVs. Some performed proteomic analysis to help explain some of the effects[59] or as a control (time 0) to study the differentiation process[39,46]. In one interesting approach using high-density lectin microarray, Saito et al[57] demonstrated that rBC2LCN, a specific lectin for hPSCs, bound to hiPSC-derived EVs but not to adipose-derived stem cell-, hemodiafiltration-, or chondrocyte-derived EVs, which suggests a particular glycan-signature for hiPSC-EVs, resembling the glycome signature of the cell surface.
One recent study that provided a detailed description of the contents of hPSC-EVs was conducted by Bi et al[74]. The proteomics of hESC-, hiPSC-, and hMSC-EXOs showed that the main enriched proteins were related to distinct pathways between vesicles of pluripotent and multipotent cells. In hPSCs, EXO content was more focused on development, metabolism, and anti-aging properties, and in hMSCs, it was related to immune regulation. Another study in 2022 also indicated that hMSC-EV content is strongly related to immune regulation while hPSC-EV content does not present many of the proteins related to this function[76]. Actually, 79 proteins were found to be shared between hMSC- and hPSC-EVs, yet the main biological processes related to them were DNA regulation, signal transduction and cell communication[76]. Liu et al[59] also compared the protein content of hiPSC-EVs and hMSC-EVs and described more than 1100 proteins shared between the different EVs, allowing to identify proteins that could be responsible for the anti-senescent effect observed in the study.
Considering the protein content of hESCs and hiPSC-EXOs, Bi et al[74] suggested that hESC-EXOs are more prone to regulate development and pluripotency pathways, and hiPSC-EXOs have a stronger correlation with metabolism. Regarding the most enriched miRNAs for both hPSC-EVs, it was shown that they were related to cell cycle and metabolism regulation. Interestingly, miRNAs found in both hESC-EXOs and hiPSC-EXOs were involved in cell differentiation, development, and cell cycle, even though the hiPSC-EXO set of miRNAs seemed to play a less significant role in these functions than the hESC-EXO set[74].
In order to explore whether apoptosis-linked gene 2-interacting protein X (ALIX), a protein present in the endosomal sorting complex required for the transport and biogenesis of EXOs, could regulate the protein content of EV, Sun et al[62] isolated EVs from hiPSCs in which ALIX was overexpressed (using lentiviral transduction) or were knocked out (using CRISP-Cas9 system). EVs isolated from these cell lineages were of similar size, although EVs generated from knockout cells were slightly larger. The evaluation of protein content in EVs showed that those derived from knockout cells had fewer proteins, while EVs from overexpressing cells presented a higher number of proteins. These differences could be related to the differences demonstrated in functional assays, e.g., cell viability, apoptosis inhibition, and formation of capillary-like structures, where EVs from overexpressing cells had better effects. So, EVs with different protein profiles could have different therapeutic applications.
Although hPSC cultivation has been carried out for some time, the requirements for in vitro culture of these cells are very specific, as many factors are necessary to maintain them in their undifferentiated state. This, together with the cost, could be one of the reasons why secretomes and isolation of hPSC-EVs have not been extensively studied so far. Commercial media are now defined with a few components that are no longer as expensive as before, which may have contributed to the increase in publications in recent years.
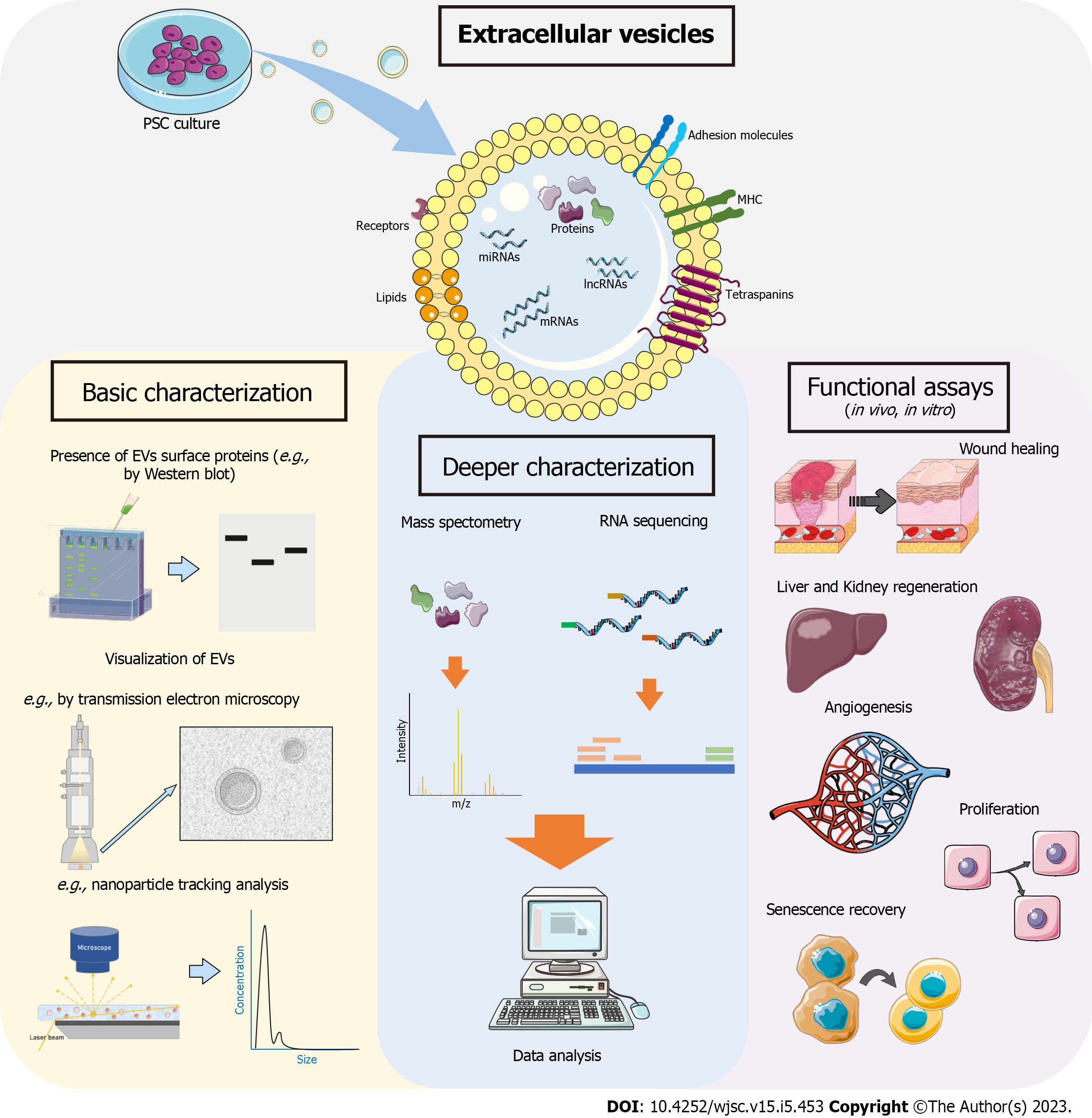
An overview of the hPSC-EV studies is shown in Figure 2, which illustrates the potential use of these EVs for regenerative medicine. Regarding EV characterization, we observed in the publications that hPSC-EVs follow the basic requirements described in MISEV2018. However, despite the recent increase in research in this area, further characterization of the content of these EVs needs to be carried out. In addition, studies with modified cells aimed to enrich the content of EVs with some specific protein or miRNA may be of great interest. One interesting approach requiring more extensive discussion is the possible use of hPSC-EVs in reprogramming adult cells into PSCs. A recent study used EVs derived from ESCs undergoing cardiac differentiation to transdifferentiate fibroblasts to cardiomyocyte-like cells with relatively high efficiency[82].
Our review shows that hPSC-EVs have therapeutic potential, although no publications demonstrate that they are effectively better than other EVs, such as hMSC-EVs. hPSC can be obtained from different sources (embryonic or reprogrammed from adult cells) and, despite showing some heterogeneity between lineages, they are highly similar in their main characteristics: They are pluripotent and with a high proliferative capacity. The latter makes it possible to obtain a large number of EVs. It should be noted that PSC-EV derived from different hPSC lineages may show some variability in their content. But considering the fact that we can isolate EVs from a single source (a homogenous culture), this can possibly bring less variability between batches compared to other common EV sources. However, studies in this area are still needed as current results are highly variable. Alternatives to EVs include the use of cell-engineered nanovesicles generated by serial extrusion of hiPSCs, as described by Lee et al[83], which presented similar results to PSC-EVs, but with higher production yield. However, more studies are needed to verify the viability of this method for future applications. Thus, challenges that remain are the large-scale production of EVs, which in the case of hPSC cultivation can be expensive, and the investment in efficient methodologies for EV isolation that could be used in good manufacturing practices for future acellular therapies.
Provenance and peer review: Invited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Cell and tissue engineering
Country/Territory of origin: Brazil
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B, B
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Chen LJ, China; Gao YT, China; Li SC, United States S-Editor: Wang JJ L-Editor: Wang TQ P-Editor: Guo X
| 1. | Théry C, Witwer KW, Aikawa E, Alcaraz MJ, Anderson JD, Andriantsitohaina R, Antoniou A, Arab T, Archer F, Atkin-Smith GK, Ayre DC, Bach JM, Bachurski D, Baharvand H, Balaj L, Baldacchino S, Bauer NN, Baxter AA, Bebawy M, Beckham C, Bedina Zavec A, Benmoussa A, Berardi AC, Bergese P, Bielska E, Blenkiron C, Bobis-Wozowicz S, Boilard E, Boireau W, Bongiovanni A, Borràs FE, Bosch S, Boulanger CM, Breakefield X, Breglio AM, Brennan MÁ, Brigstock DR, Brisson A, Broekman ML, Bromberg JF, Bryl-Górecka P, Buch S, Buck AH, Burger D, Busatto S, Buschmann D, Bussolati B, Buzás EI, Byrd JB, Camussi G, Carter DR, Caruso S, Chamley LW, Chang YT, Chen C, Chen S, Cheng L, Chin AR, Clayton A, Clerici SP, Cocks A, Cocucci E, Coffey RJ, Cordeiro-da-Silva A, Couch Y, Coumans FA, Coyle B, Crescitelli R, Criado MF, D'Souza-Schorey C, Das S, Datta Chaudhuri A, de Candia P, De Santana EF, De Wever O, Del Portillo HA, Demaret T, Deville S, Devitt A, Dhondt B, Di Vizio D, Dieterich LC, Dolo V, Dominguez Rubio AP, Dominici M, Dourado MR, Driedonks TA, Duarte FV, Duncan HM, Eichenberger RM, Ekström K, El Andaloussi S, Elie-Caille C, Erdbrügger U, Falcón-Pérez JM, Fatima F, Fish JE, Flores-Bellver M, Försönits A, Frelet-Barrand A, Fricke F, Fuhrmann G, Gabrielsson S, Gámez-Valero A, Gardiner C, Gärtner K, Gaudin R, Gho YS, Giebel B, Gilbert C, Gimona M, Giusti I, Goberdhan DC, Görgens A, Gorski SM, Greening DW, Gross JC, Gualerzi A, Gupta GN, Gustafson D, Handberg A, Haraszti RA, Harrison P, Hegyesi H, Hendrix A, Hill AF, Hochberg FH, Hoffmann KF, Holder B, Holthofer H, Hosseinkhani B, Hu G, Huang Y, Huber V, Hunt S, Ibrahim AG, Ikezu T, Inal JM, Isin M, Ivanova A, Jackson HK, Jacobsen S, Jay SM, Jayachandran M, Jenster G, Jiang L, Johnson SM, Jones JC, Jong A, Jovanovic-Talisman T, Jung S, Kalluri R, Kano SI, Kaur S, Kawamura Y, Keller ET, Khamari D, Khomyakova E, Khvorova A, Kierulf P, Kim KP, Kislinger T, Klingeborn M, Klinke DJ 2nd, Kornek M, Kosanović MM, Kovács ÁF, Krämer-Albers EM, Krasemann S, Krause M, Kurochkin IV, Kusuma GD, Kuypers S, Laitinen S, Langevin SM, Languino LR, Lannigan J, Lässer C, Laurent LC, Lavieu G, Lázaro-Ibáñez E, Le Lay S, Lee MS, Lee YXF, Lemos DS, Lenassi M, Leszczynska A, Li IT, Liao K, Libregts SF, Ligeti E, Lim R, Lim SK, Linē A, Linnemannstöns K, Llorente A, Lombard CA, Lorenowicz MJ, Lörincz ÁM, Lötvall J, Lovett J, Lowry MC, Loyer X, Lu Q, Lukomska B, Lunavat TR, Maas SL, Malhi H, Marcilla A, Mariani J, Mariscal J, Martens-Uzunova ES, Martin-Jaular L, Martinez MC, Martins VR, Mathieu M, Mathivanan S, Maugeri M, McGinnis LK, McVey MJ, Meckes DG Jr, Meehan KL, Mertens I, Minciacchi VR, Möller A, Møller Jørgensen M, Morales-Kastresana A, Morhayim J, Mullier F, Muraca M, Musante L, Mussack V, Muth DC, Myburgh KH, Najrana T, Nawaz M, Nazarenko I, Nejsum P, Neri C, Neri T, Nieuwland R, Nimrichter L, Nolan JP, Nolte-'t Hoen EN, Noren Hooten N, O'Driscoll L, O'Grady T, O'Loghlen A, Ochiya T, Olivier M, Ortiz A, Ortiz LA, Osteikoetxea X, Østergaard O, Ostrowski M, Park J, Pegtel DM, Peinado H, Perut F, Pfaffl MW, Phinney DG, Pieters BC, Pink RC, Pisetsky DS, Pogge von Strandmann E, Polakovicova I, Poon IK, Powell BH, Prada I, Pulliam L, Quesenberry P, Radeghieri A, Raffai RL, Raimondo S, Rak J, Ramirez MI, Raposo G, Rayyan MS, Regev-Rudzki N, Ricklefs FL, Robbins PD, Roberts DD, Rodrigues SC, Rohde E, Rome S, Rouschop KM, Rughetti A, Russell AE, Saá P, Sahoo S, Salas-Huenuleo E, Sánchez C, Saugstad JA, Saul MJ, Schiffelers RM, Schneider R, Schøyen TH, Scott A, Shahaj E, Sharma S, Shatnyeva O, Shekari F, Shelke GV, Shetty AK, Shiba K, Siljander PR, Silva AM, Skowronek A, Snyder OL 2nd, Soares RP, Sódar BW, Soekmadji C, Sotillo J, Stahl PD, Stoorvogel W, Stott SL, Strasser EF, Swift S, Tahara H, Tewari M, Timms K, Tiwari S, Tixeira R, Tkach M, Toh WS, Tomasini R, Torrecilhas AC, Tosar JP, Toxavidis V, Urbanelli L, Vader P, van Balkom BW, van der Grein SG, Van Deun J, van Herwijnen MJ, Van Keuren-Jensen K, van Niel G, van Royen ME, van Wijnen AJ, Vasconcelos MH, Vechetti IJ Jr, Veit TD, Vella LJ, Velot É, Verweij FJ, Vestad B, Viñas JL, Visnovitz T, Vukman KV, Wahlgren J, Watson DC, Wauben MH, Weaver A, Webber JP, Weber V, Wehman AM, Weiss DJ, Welsh JA, Wendt S, Wheelock AM, Wiener Z, Witte L, Wolfram J, Xagorari A, Xander P, Xu J, Yan X, Yáñez-Mó M, Yin H, Yuana Y, Zappulli V, Zarubova J, Žėkas V, Zhang JY, Zhao Z, Zheng L, Zheutlin AR, Zickler AM, Zimmermann P, Zivkovic AM, Zocco D, Zuba-Surma EK. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles. 2018;7:1535750. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 6453] [Cited by in RCA: 7624] [Article Influence: 1089.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 2. | Bister N, Pistono C, Huremagic B, Jolkkonen J, Giugno R, Malm T. Hypoxia and extracellular vesicles: A review on methods, vesicular cargo and functions. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020;10:e12002. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 94] [Cited by in RCA: 135] [Article Influence: 27.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | van Niel G, Carter DRF, Clayton A, Lambert DW, Raposo G, Vader P. Challenges and directions in studying cell-cell communication by extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2022;23:369-382. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 30] [Cited by in RCA: 639] [Article Influence: 213.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Park KS, Bandeira E, Shelke GV, Lässer C, Lötvall J. Enhancement of therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10:288. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 116] [Cited by in RCA: 181] [Article Influence: 30.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Miceli V, Bulati M, Iannolo G, Zito G, Gallo A, Conaldi PG. Therapeutic Properties of Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells: The Need of Cell Priming for Cell-Free Therapies in Regenerative Medicine. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 113] [Cited by in RCA: 105] [Article Influence: 26.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Öztürk S, Elçin AE, Koca A, Elçin YM. Therapeutic Applications of Stem Cells and Extracellular Vesicles in Emergency Care: Futuristic Perspectives. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2021;17:390-410. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 28] [Article Influence: 7.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Jin Y, Xu M, Zhu H, Dong C, Ji J, Liu Y, Deng A, Gu Z. Therapeutic effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes on osteoarthritis. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25:9281-9294. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 96] [Article Influence: 24.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Yu L, Liu S, Wang C, Zhang C, Wen Y, Zhang K, Chen S, Huang H, Liu Y, Wu L, Han Z, Chen X, Li Z, Liu N. Embryonic stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles promote the recovery of kidney injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12:379. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 23] [Article Influence: 5.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Xiong J, Hu H, Guo R, Wang H, Jiang H. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Exosomes as a New Strategy for the Treatment of Diabetes Complications. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:646233. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 72] [Article Influence: 18.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Gowen A, Shahjin F, Chand S, Odegaard KE, Yelamanchili SV. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Challenges in Clinical Applications. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:149. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 116] [Cited by in RCA: 238] [Article Influence: 47.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Tieu A, Lalu MM, Slobodian M, Gnyra C, Fergusson DA, Montroy J, Burger D, Stewart DJ, Allan DS. An Analysis of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles for Preclinical Use. ACS Nano. 2020;14:9728-9743. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 54] [Cited by in RCA: 84] [Article Influence: 16.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Fuloria S, Subramaniyan V, Dahiya R, Dahiya S, Sudhakar K, Kumari U, Sathasivam K, Meenakshi DU, Wu YS, Sekar M, Malviya R, Singh A, Fuloria NK. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Regenerative Potential and Challenges. Biology (Basel). 2021;10. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 45] [Cited by in RCA: 35] [Article Influence: 8.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Kou M, Huang L, Yang J, Chiang Z, Chen S, Liu J, Guo L, Zhang X, Zhou X, Xu X, Yan X, Wang Y, Zhang J, Xu A, Tse HF, Lian Q. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles for immunomodulation and regeneration: a next generation therapeutic tool? Cell Death Dis. 2022;13:580. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 296] [Cited by in RCA: 287] [Article Influence: 95.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Yudintceva N, Mikhailova N, Fedorov V, Samochernych K, Vinogradova T, Muraviov A, Shevtsov M. Mesenchymal Stem Cells and MSCs-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Infectious Diseases: From Basic Research to Clinical Practice. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022;9. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 18] [Article Influence: 6.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Adlerz K, Patel D, Rowley J, Ng K, Ahsan T. Strategies for scalable manufacturing and translation of MSC-derived extracellular vesicles. Stem Cell Res. 2020;48:101978. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 23] [Cited by in RCA: 68] [Article Influence: 13.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Witwer KW, Van Balkom BWM, Bruno S, Choo A, Dominici M, Gimona M, Hill AF, De Kleijn D, Koh M, Lai RC, Mitsialis SA, Ortiz LA, Rohde E, Asada T, Toh WS, Weiss DJ, Zheng L, Giebel B, Lim SK. Defining mesenchymal stromal cell (MSC)-derived small extracellular vesicles for therapeutic applications. J Extracell Vesicles. 2019;8:1609206. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 340] [Cited by in RCA: 439] [Article Influence: 73.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Weng Z, Wang Y, Ouchi T, Liu H, Qiao X, Wu C, Zhao Z, Li L, Li B. Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cell Senescence: Hallmarks, Mechanisms, and Combating Strategies. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2022;11:356-371. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 130] [Article Influence: 43.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Vazin T, Freed WJ. Human embryonic stem cells: derivation, culture, and differentiation: a review. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2010;28:589-603. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 75] [Cited by in RCA: 89] [Article Influence: 5.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Thomson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS, Waknitz MA, Swiergiel JJ, Marshall VS, Jones JM. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science. 1998;282:1145-1147. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 11399] [Cited by in RCA: 10418] [Article Influence: 385.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Ilic D, Ogilvie C. Concise Review: Human Embryonic Stem Cells-What Have We Done? Stem Cells. 2017;35:17-25. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 103] [Cited by in RCA: 115] [Article Influence: 12.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006;126:663-676. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17989] [Cited by in RCA: 18138] [Article Influence: 954.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, Narita M, Ichisaka T, Tomoda K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell. 2007;131:861-872. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 14327] [Cited by in RCA: 14288] [Article Influence: 840.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Diecke S, Jung SM, Lee J, Ju JH. Recent technological updates and clinical applications of induced pluripotent stem cells. Korean J Intern Med. 2014;29:547-557. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 27] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Karagiannis P, Takahashi K, Saito M, Yoshida Y, Okita K, Watanabe A, Inoue H, Yamashita JK, Todani M, Nakagawa M, Osawa M, Yashiro Y, Yamanaka S, Osafune K. Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells and Their Use in Human Models of Disease and Development. Physiol Rev. 2019;99:79-114. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 136] [Cited by in RCA: 232] [Article Influence: 38.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Liu G, David BT, Trawczynski M, Fessler RG. Advances in Pluripotent Stem Cells: History, Mechanisms, Technologies, and Applications. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2020;16:3-32. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 311] [Cited by in RCA: 305] [Article Influence: 61.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Yamanaka S. Pluripotent Stem Cell-Based Cell Therapy-Promise and Challenges. Cell Stem Cell. 2020;27:523-531. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 243] [Cited by in RCA: 729] [Article Influence: 182.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Singh VK, Kalsan M, Kumar N, Saini A, Chandra R. Induced pluripotent stem cells: applications in regenerative medicine, disease modeling, and drug discovery. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2015;3:2. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 233] [Cited by in RCA: 266] [Article Influence: 26.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Kwon SG, Kwon YW, Lee TW, Park GT, Kim JH. Recent advances in stem cell therapeutics and tissue engineering strategies. Biomater Res. 2018;22:36. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 80] [Cited by in RCA: 129] [Article Influence: 18.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Dakhore S, Nayer B, Hasegawa K. Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Culture: Current Status, Challenges, and Advancement. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:7396905. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 73] [Cited by in RCA: 65] [Article Influence: 9.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Cao J, Li X, Lu X, Zhang C, Yu H, Zhao T. Cells derived from iPSC can be immunogenic - yes or no? Protein Cell. 2014;5:1-3. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 40] [Cited by in RCA: 43] [Article Influence: 3.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Martin U. Therapeutic Application of Pluripotent Stem Cells: Challenges and Risks. Front Med (Lausanne). 2017;4:229. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 59] [Cited by in RCA: 52] [Article Influence: 6.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Jarrige M, Frank E, Herardot E, Martineau S, Darle A, Benabides M, Domingues S, Chose O, Habeler W, Lorant J, Baldeschi C, Martinat C, Monville C, Morizur L, Ben M'Barek K. The Future of Regenerative Medicine: Cell Therapy Using Pluripotent Stem Cells and Acellular Therapies Based on Extracellular Vesicles. Cells. 2021;10. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 22] [Cited by in RCA: 59] [Article Influence: 14.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Desrochers LM, Bordeleau F, Reinhart-King CA, Cerione RA, Antonyak MA. Microvesicles provide a mechanism for intercellular communication by embryonic stem cells during embryo implantation. Nat Commun. 2016;7:11958. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 126] [Cited by in RCA: 175] [Article Influence: 19.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Hur YH, Feng S, Wilson KF, Cerione RA, Antonyak MA. Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Maintain ESC Stemness by Activating FAK. Dev Cell. 2021;56:277-291.e6. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 22] [Cited by in RCA: 49] [Article Influence: 9.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 35. | Zhou J, Ghoroghi S, Benito-Martin A, Wu H, Unachukwu UJ, Einbond LS, Guariglia S, Peinado H, Redenti S. Characterization of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Microvesicle Genesis, Morphology and Pluripotent Content. Sci Rep. 2016;6:19743. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 26] [Cited by in RCA: 31] [Article Influence: 3.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 36. | Cruz L, Arevalo Romero JA, Brandão Prado M, Santos TG, Hohmuth Lopes M. Evidence of Extracellular Vesicles Biogenesis and Release in Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2018;14:262-276. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 37. | Bobis-Wozowicz S, Kmiotek K, Sekula M, Kedracka-Krok S, Kamycka E, Adamiak M, Jankowska U, Madetko-Talowska A, Sarna M, Bik-Multanowski M, Kolcz J, Boruczkowski D, Madeja Z, Dawn B, Zuba-Surma EK. Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Microvesicles Transmit RNAs and Proteins to Recipient Mature Heart Cells Modulating Cell Fate and Behavior. Stem Cells. 2015;33:2748-2761. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 65] [Cited by in RCA: 83] [Article Influence: 8.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 38. | Bo Y, Yang L, Liu B, Tian G, Li C, Zhang L, Yan Y. Exosomes from human induced pluripotent stem cells-derived keratinocytes accelerate burn wound healing through miR-762 mediated promotion of keratinocytes and endothelial cells migration. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022;20:291. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in RCA: 27] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 39. | Ashok P, Tzanakakis ES. Proteomic Analysis of Exosomes during Cardiogenic Differentiation of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. Cells. 2021;10. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 40. | El Harane N, Kervadec A, Bellamy V, Pidial L, Neametalla HJ, Perier MC, Lima Correa B, Thiébault L, Cagnard N, Duché A, Brunaud C, Lemitre M, Gauthier J, Bourdillon AT, Renault MP, Hovhannisyan Y, Paiva S, Colas AR, Agbulut O, Hagège A, Silvestre JS, Menasché P, Renault NKE. Acellular therapeutic approach for heart failure: in vitro production of extracellular vesicles from human cardiovascular progenitors. Eur Heart J. 2018;39:1835-1847. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 94] [Cited by in RCA: 128] [Article Influence: 21.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 41. | Wu Q, Wang J, Tan WLW, Jiang Y, Wang S, Li Q, Yu X, Tan J, Liu S, Zhang P, Tiang Z, Chen Z, Foo RS, Yang HT. Extracellular vesicles from human embryonic stem cell-derived cardiovascular progenitor cells promote cardiac infarct healing through reducing cardiomyocyte death and promoting angiogenesis. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:354. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 43] [Cited by in RCA: 115] [Article Influence: 23.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 42. | La Greca A, Solari C, Furmento V, Lombardi A, Biani MC, Aban C, Moro L, García M, Guberman AS, Sevlever GE, Miriuka SG, Luzzani C. Extracellular vesicles from pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells acquire a stromal modulatory proteomic pattern during differentiation. Exp Mol Med. 2018;50:1-12. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 37] [Cited by in RCA: 44] [Article Influence: 6.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 43. | Qi X, Zhang J, Yuan H, Xu Z, Li Q, Niu X, Hu B, Wang Y, Li X. Exosomes Secreted by Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Repair Critical-Sized Bone Defects through Enhanced Angiogenesis and Osteogenesis in Osteoporotic Rats. Int J Biol Sci. 2016;12:836-849. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 267] [Cited by in RCA: 407] [Article Influence: 45.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 44. | Sun Y, Zhang W, Li X. Induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells deliver exogenous miR-105-5p via small extracellular vesicles to rejuvenate senescent nucleus pulposus cells and attenuate intervertebral disc degeneration. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12:286. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 61] [Article Influence: 15.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 45. | Hicks DA, Jones AC, Corbett NJ, Fisher K, Pickering-Brown SM, Ashe MP, Hooper NM. Extracellular Vesicles Isolated from Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Neurons Contain a Transcriptional Network. Neurochem Res. 2020;45:1711-1728. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 46. | Saito H, Kato M, Hirai K, Kiyama M, Ohyama K, Hanzawa H, Nakane A, Sekiya S, Yoshida K, Kishino A, Tsuchida A, Kimura T, Takahashi J, Takeda S. Analysis of extracellular vesicles as a potential index for monitoring differentiation of neural lineage cells from induced pluripotent stem cells. J Biosci Bioeng. 2021;132:381-389. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 47. | Podvin S, Jones A, Liu Q, Aulston B, Ransom L, Ames J, Shen G, Lietz CB, Jiang Z, O'Donoghue AJ, Winston C, Ikezu T, Rissman RA, Yuan S, Hook V. Dysregulation of Exosome Cargo by Mutant Tau Expressed in Human-induced Pluripotent Stem Cell (iPSC) Neurons Revealed by Proteomics Analyses. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2020;19:1017-1034. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 30] [Cited by in RCA: 32] [Article Influence: 6.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 48. | Luo L, Foster NC, Man KL, Brunet M, Hoey DA, Cox SC, Kimber SJ, El Haj AJ. Hydrostatic pressure promotes chondrogenic differentiation and microvesicle release from human embryonic and bone marrow stem cells. Biotechnol J. 2022;17:e2100401. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 49. | Luo Y, Gao D, Wang P, Lou C, Li T, Niu W, Gao Y. Optimized culture methods for isolating small extracellular vesicles derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021;10:e12065. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 16] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 50. | Ju Z, Ma J, Wang C, Yu J, Qiao Y, Hei F. Exosomes from iPSCs Delivering siRNA Attenuate Intracellular Adhesion Molecule-1 Expression and Neutrophils Adhesion in Pulmonary Microvascular Endothelial Cells. Inflammation. 2017;40:486-496. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 45] [Cited by in RCA: 55] [Article Influence: 6.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 51. | Zhou S, Abdouh M, Arena V, Arena M, Arena GO. Reprogramming Malignant Cancer Cells toward a Benign Phenotype following Exposure to Human Embryonic Stem Cell Microenvironment. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0169899. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 35] [Cited by in RCA: 57] [Article Influence: 7.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 52. | Ding Q, Sun R, Wang P, Zhang H, Xiang M, Meng D, Sun N, Chen AF, Chen S. Protective effects of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived exosomes on high glucose-induced injury in human endothelial cells. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15:4791-4797. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 53. | Kaur S, Abu-Shahba AG, Paananen RO, Hongisto H, Hiidenmaa H, Skottman H, Seppänen-Kaijansinkko R, Mannerström B. Small non-coding RNA landscape of extracellular vesicles from human stem cells. Sci Rep. 2018;8:15503. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 39] [Cited by in RCA: 48] [Article Influence: 6.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 54. | Kobayashi H, Ebisawa K, Kambe M, Kasai T, Suga H, Nakamura K, Narita Y, Ogata A, Kamei Y. <Editors' Choice> Effects of exosomes derived from the induced pluripotent stem cells on skin wound healing. Nagoya J Med Sci. 2018;80:141-153. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in RCA: 35] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 55. | Oh M, Lee J, Kim YJ, Rhee WJ, Park JH. Exosomes Derived from Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Ameliorate the Aging of Skin Fibroblasts. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 94] [Cited by in RCA: 157] [Article Influence: 22.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 56. | Peng Y, Baulier E, Ke Y, Young A, Ahmedli NB, Schwartz SD, Farber DB. Human embryonic stem cells extracellular vesicles and their effects on immortalized human retinal Müller cells. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0194004. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 57. | Saito S, Hiemori K, Kiyoi K, Tateno H. Glycome analysis of extracellular vesicles derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells using lectin microarray. Sci Rep. 2018;8:3997. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 25] [Cited by in RCA: 28] [Article Influence: 4.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 58. | Chen B, Sun Y, Zhang J, Zhu Q, Yang Y, Niu X, Deng Z, Li Q, Wang Y. Human embryonic stem cell-derived exosomes promote pressure ulcer healing in aged mice by rejuvenating senescent endothelial cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10:142. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 62] [Cited by in RCA: 124] [Article Influence: 20.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 59. | Liu S, Mahairaki V, Bai H, Ding Z, Li J, Witwer KW, Cheng L. Highly Purified Human Extracellular Vesicles Produced by Stem Cells Alleviate Aging Cellular Phenotypes of Senescent Human Cells. Stem Cells. 2019;37:779-790. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 74] [Cited by in RCA: 122] [Article Influence: 20.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 60. | Marzano M, Bejoy J, Cheerathodi MR, Sun L, York SB, Zhao J, Kanekiyo T, Bu G, Meckes DG Jr, Li Y. Differential Effects of Extracellular Vesicles of Lineage-Specific Human Pluripotent Stem Cells on the Cellular Behaviors of Isogenic Cortical Spheroids. Cells. 2019;8. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 32] [Article Influence: 5.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 61. | Povero D, Pinatel EM, Leszczynska A, Goyal NP, Nishio T, Kim J, Kneiber D, de Araujo Horcel L, Eguchi A, Ordonez PM, Kisseleva T, Feldstein AE. Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles reduce hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis. JCI Insight. 2019;5. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 72] [Cited by in RCA: 77] [Article Influence: 12.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 62. | Sun R, Liu Y, Lu M, Ding Q, Wang P, Zhang H, Tian X, Lu P, Meng D, Sun N, Xiang M, Chen S. ALIX increases protein content and protective function of iPSC-derived exosomes. J Mol Med (Berl). 2019;97:829-844. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 4.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 63. | Zhu Q, Ling X, Yang Y, Zhang J, Li Q, Niu X, Hu G, Chen B, Li H, Wang Y, Deng Z. Embryonic Stem Cells-Derived Exosomes Endowed with Targeting Properties as Chemotherapeutics Delivery Vehicles for Glioblastoma Therapy. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2019;6:1801899. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 192] [Cited by in RCA: 209] [Article Influence: 34.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 64. | Collino F, Lopes JA, Tapparo M, Tortelote GG, Kasai-Brunswick TH, Lopes GMC, Almeida DB, Skovronova R, Wendt CHC, Miranda KR, Bussolati B, Vieyra A, Lindoso RS. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Promote Renoprotection in Acute Kidney Injury Model. Cells. 2020;9. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 40] [Article Influence: 8.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 65. | Hu G, Xia Y, Chen B, Zhang J, Gong L, Chen Y, Li Q, Wang Y, Deng Z. ESC-sEVs Rejuvenate Aging Hippocampal NSCs by Transferring SMADs to Regulate the MYT1-Egln3-Sirt1 Axis. Mol Ther. 2021;29:103-120. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 27] [Article Influence: 6.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 66. | Kurtzwald-Josefson E, Zeevi-Levin N, Rubchevsky V, Bechar Erdman N, Schwartz Rohaker O, Nahum O, Hochhauser E, Ben-Avraham B, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Aravot D, Barac YD. Cardiac Fibroblast-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes as a Potential Therapeutic Mean for Heart Failure. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 24] [Article Influence: 4.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 67. | Liu M, Qiu Y, Xue Z, Wu R, Li J, Niu X, Yuan J, Wang Y, Wu Q. Small extracellular vesicles derived from embryonic stem cells restore ovarian function of premature ovarian failure through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11:3. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 46] [Cited by in RCA: 73] [Article Influence: 14.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 68. | Wang S, Hou Y, Li X, Song Z, Sun B, Zhang H. Comparison of exosomes derived from induced pluripotent stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells as therapeutic nanoparticles for treatment of corneal epithelial defects. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12:19546-19562. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 16] [Cited by in RCA: 46] [Article Influence: 9.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 69. | Andrade AC, Wolf M, Binder HM, Gomes FG, Manstein F, Ebner-Peking P, Poupardin R, Zweigerdt R, Schallmoser K, Strunk D. Hypoxic Conditions Promote the Angiogenic Potential of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 3.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 70. | Karnas E, Sekuła-Stryjewska M, Kmiotek-Wasylewska K, Bobis-Wozowicz S, Ryszawy D, Sarna M, Madeja Z, Zuba-Surma EK. Extracellular vesicles from human iPSCs enhance reconstitution capacity of cord blood-derived hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Leukemia. 2021;35:2964-2977. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 71. | Ke Y, Fan X, Hao R, Dong L, Xue M, Tan L, Yang C, Li X, Ren X. Human embryonic stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles alleviate retinal degeneration by upregulating Oct4 to promote retinal Müller cell retrodifferentiation via HSP90. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12:21. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 29] [Article Influence: 7.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 72. | Wang N, Li X, Zhong Z, Qiu Y, Liu S, Wu H, Tang X, Chen C, Fu Y, Chen Q, Guo T, Li J, Zhang S, Zern MA, Ma K, Wang B, Ou Y, Gu W, Cao J, Chen H, Duan Y. 3D hESC exosomes enriched with miR-6766-3p ameliorates liver fibrosis by attenuating activated stellate cells through targeting the TGFβRII-SMADS pathway. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19:437. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 50] [Article Influence: 12.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 73. | Xia Y, Hu G, Chen Y, Yuan J, Zhang J, Wang S, Li Q, Wang Y, Deng Z. Embryonic Stem Cell Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Modulate Regulatory T Cells to Protect against Ischemic Stroke. ACS Nano. 2021;15:7370-7385. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 39] [Cited by in RCA: 76] [Article Influence: 19.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 74. | Bi Y, Qiao X, Liu Q, Song S, Zhu K, Qiu X, Zhang X, Jia C, Wang H, Yang Z, Zhang Y, Ji G. Systemic proteomics and miRNA profile analysis of exosomes derived from human pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13:449. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in RCA: 50] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 75. | Gu Z, Yin Z, Song P, Wu Y, He Y, Zhu M, Wu Z, Zhao S, Huang H, Wang H, Tong C, Qi Z. Safety and biodistribution of exosomes derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:949724. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 76. | Gupta S, Krishnakumar V, Soni N, Rao EP, Banerjee A, Mohanty S. Comparative proteomic profiling of Small Extracellular vesicles derived from iPSCs and tissue specific mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Cell Res. 2022;420:113354. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 77. | Hsueh YH, Buddhakosai W, Le PN, Tu YY, Huang HC, Lu HE, Chen WL, Tu YK. Therapeutic effect of induced pluripotent stem cell -derived extracellular vesicles in an in vitro and in vivo osteoarthritis model. J Orthop Translat. 2023;38:141-155. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in RCA: 23] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 78. | Li Q, Niu X, Yi Y, Chen Y, Yuan J, Zhang J, Li H, Xia Y, Wang Y, Deng Z. Inducible Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Rejuvenate Senescent Blood-Brain Barrier to Protect against Ischemic Stroke in Aged Mice. ACS Nano. 2023;17:775-789. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 46] [Article Influence: 23.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 79. | Li J, Gao H, Xiong Y, Wang L, Zhang H, He F, Zhao J, Liu S, Gao L, Guo Y, Deng W. Enhancing Cutaneous Wound Healing Based on Human Induced Neural Stem Cell-derived Exosomes. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022;17:5991-6006. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 80. | Pan J, Zhao M, Yi X, Tao J, Li S, Jiang Z, Cheng B, Yuan H, Zhang F. Acellular nerve grafts supplemented with induced pluripotent stem cell-derived exosomes promote peripheral nerve reconstruction and motor function recovery. Bioact Mater. 2022;15:272-287. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 6.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 81. | Hu G, Xia Y, Zhang J, Chen Y, Yuan J, Niu X, Zhao B, Li Q, Wang Y, Deng Z. ESC-sEVs Rejuvenate Senescent Hippocampal NSCs by Activating Lysosomes to Improve Cognitive Dysfunction in Vascular Dementia. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020;7:1903330. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 26] [Cited by in RCA: 40] [Article Influence: 8.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 82. | Kim H, Song BW, Park SJ, Choi SW, Moon H, Hwang KC, Kang SW, Moon SH, Yang Y, Kwon IC, Kim SH. Ultraefficient extracellular vesicle-guided direct reprogramming of fibroblasts into functional cardiomyocytes. Sci Adv. 2022;8:eabj6621. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 23] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 6.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 83. | Lee H, Cha H, Park JH. Derivation of Cell-Engineered Nanovesicles from Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells and Their Protective Effect on the Senescence of Dermal Fibroblasts. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 31] [Cited by in RCA: 37] [Article Influence: 7.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |