Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Stem Cells. May 26, 2022; 14(5): 318-329
Published online May 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i5.318
Published online May 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i5.318
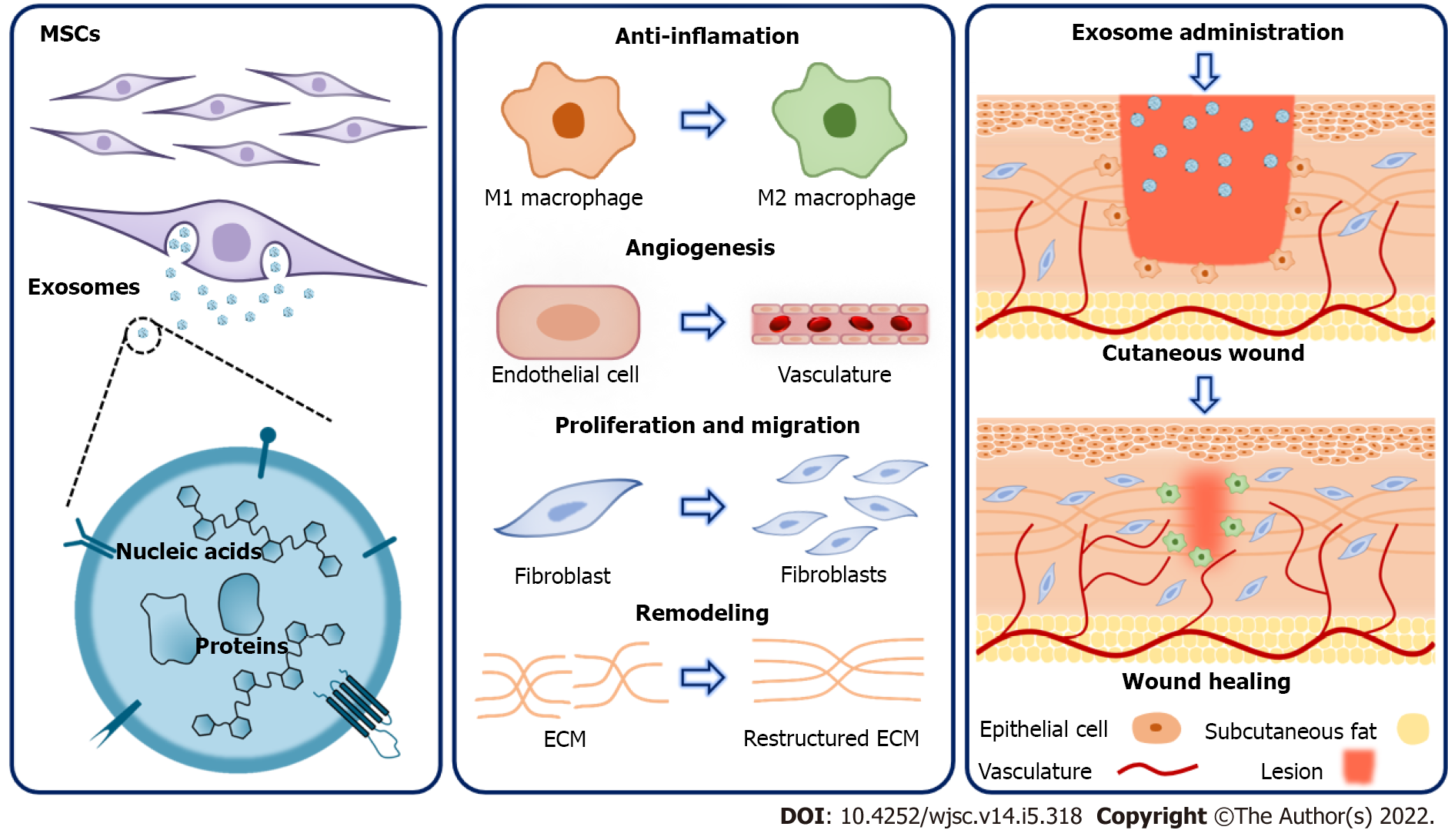
Figure 1 Mechanisms underlying the therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on cutaneous wound healing.
Mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-derived exosomes contain a variety of proteins and nucleic acids and hold great potential for promoting cutaneous wound healing. Specifically, MSC-derived exosomes exert therapeutic effects through multiple mechanisms. They can inhibit inflammation via modulating macrophage polarization. Besides, during the proliferation phase, MSC-exosomes promote angiogenesis, as well as the proliferation and migration of fibroblasts. Furthermore, MSC-exosomes can improve extracellular matrix remodeling. As a result, MSC-derived exosomes have offered a new paradigm in the treatment of cutaneous wounds. ECM: Extracellular matrix; MSC: Mesenchymal stem cell.
- Citation: Hu JC, Zheng CX, Sui BD, Liu WJ, Jin Y. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: A novel and potential remedy for cutaneous wound healing and regeneration. World J Stem Cells 2022; 14(5): 318-329
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v14/i5/318.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v14.i5.318