Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Stem Cells. Jun 26, 2021; 13(6): 605-618
Published online Jun 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i6.605
Published online Jun 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i6.605
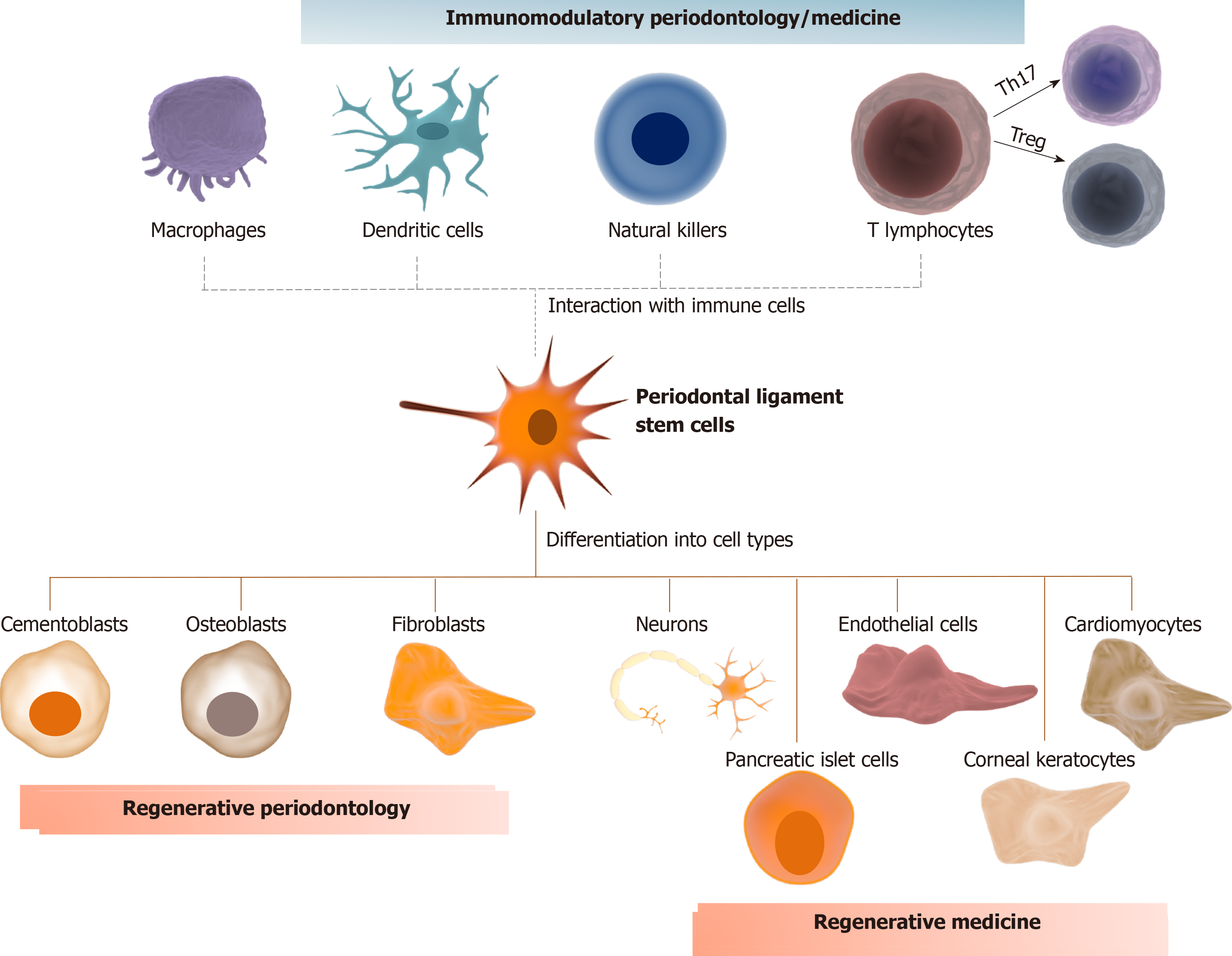
Figure 1 Immunomodulatory periodontology/medicine.
Periodontal ligament stem cells (PDLSCs) can differentiate into cementoblasts, osteoblasts, and fibroblasts, the main cell types responsible for guaranteeing tissue homeostasis of the cementum, alveolar bone, and periodontal ligament, respectively, which highlights their application in regenerative periodontology. PDLSCs can also differentiate into neurons, cardiomyocytes, endothelial cells, pancreatic islet cells, and corneal keratocytes, which further expand their application in regenerative medicine. Eventually, PDLSCs have immunomodulatory properties that can be performed by direct cell-to-cell contact or by the synthesis of specific metabolites that alter the phenotype of different immune cells. For example, PDLSCs could alter the proportion of T lymphocytes, increasing the proportion of T regulatory subsets over T helper-17. These properties could be used in future applications to modulate the host response in cases of chronic inflammatory disorders, such as periodontitis, colitis and neurodegenerative diseases.
- Citation: Queiroz A, Albuquerque-Souza E, Gasparoni LM, França BN, Pelissari C, Trierveiler M, Holzhausen M. Therapeutic potential of periodontal ligament stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2021; 13(6): 605-618
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v13/i6/605.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v13.i6.605