Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Stem Cells. Sep 26, 2016; 8(9): 279-287
Published online Sep 26, 2016. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v8.i9.279
Published online Sep 26, 2016. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v8.i9.279
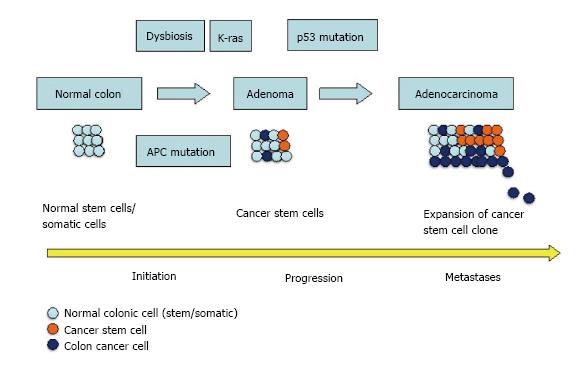
Figure 1 Cancer stem cells during development and progression of colorectal cancer.
Schematic representation of the role of dysbiosis caused by microbiome alterations and accumulation of mutations in colonic stem cells leading to development and progression of colorectal cancer. APC: Adenomatous polyposis coli.
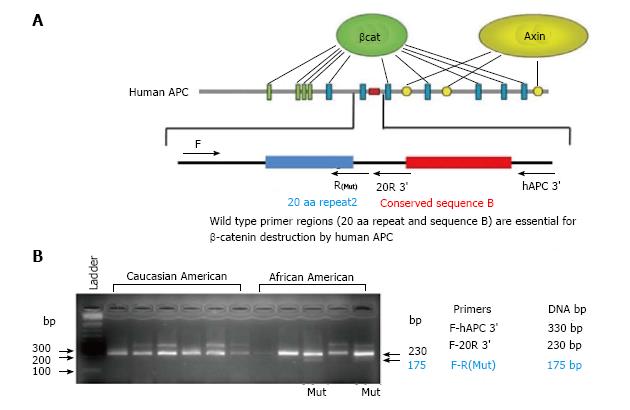
Figure 2 Schematic representation of human APC gene and design of appropriate primers for the wild type and mutant gene.
A: Human APC gene with β-catenin (green and blue bars) and Axin (yellow circles) binding sites. Red bar represents conserved sequence of APC gene. Forward (F) and reverse (R) primers were designed to demonstrate mutation in APC gene; B: Agarose gel electrophoresis of PCR products showing higher rate of APC gene mutation (Mut: 175 bp) in the colonic mucosa of AAs without adenomas than their CA counterparts. AAs: African Americans; CA: Caucasian American; APC: Adenomatous polyposis coli.
- Citation: Goyal S, Nangia-Makker P, Farhana L, Yu Y, Majumdar AP. Racial disparity in colorectal cancer: Gut microbiome and cancer stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2016; 8(9): 279-287
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v8/i9/279.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v8.i9.279