Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Stem Cells. Apr 26, 2023; 15(4): 221-234
Published online Apr 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i4.221
Published online Apr 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i4.221
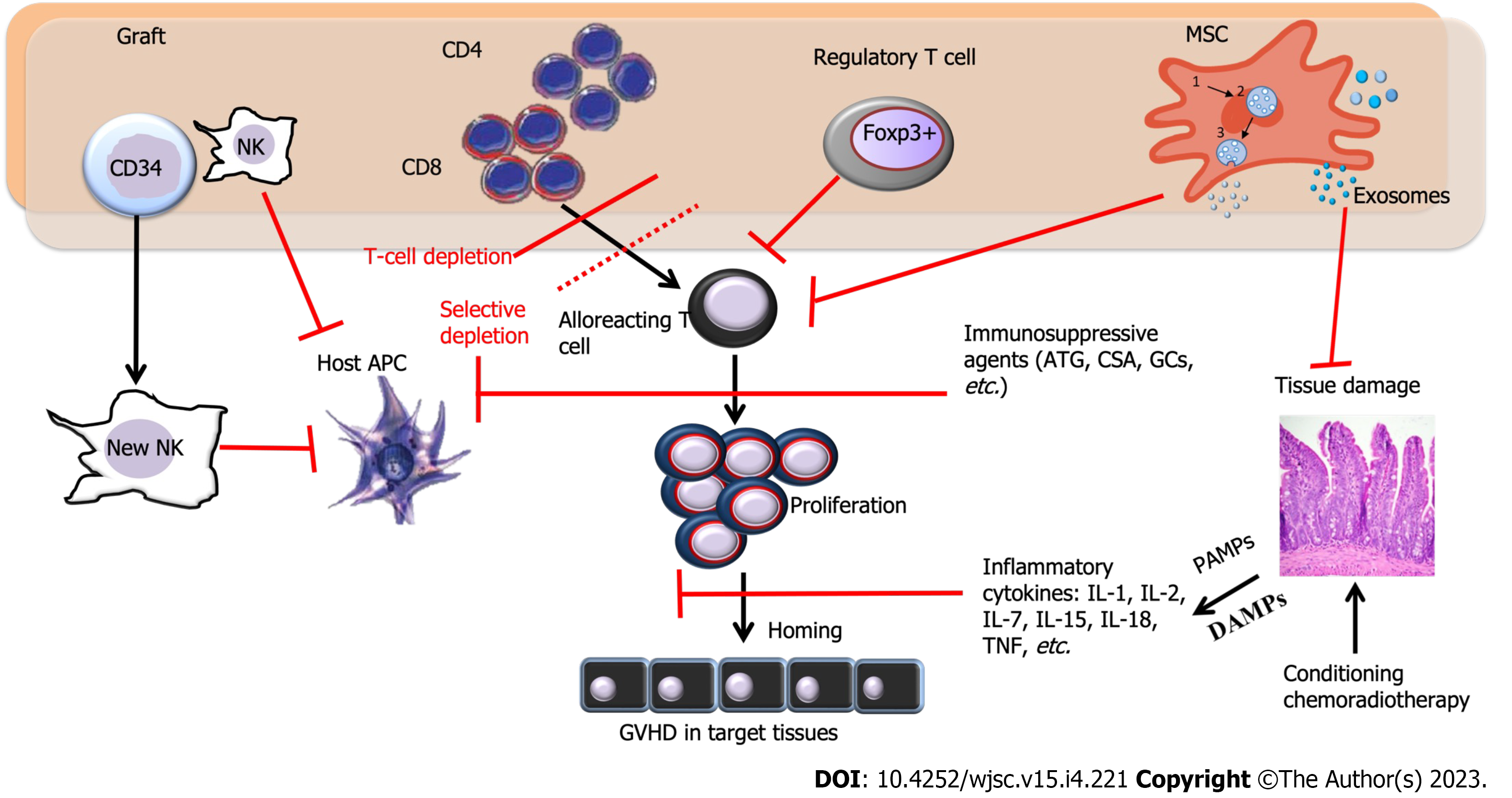
Figure 1 Immune pathways in graft-versus-host disease and sites where therapy is used to block graft-versus-host disease development (red bars).
APC: Antigen-presenting cell; ATG: Antithymocyte globulin; CSA: Cyclosporine A; DAMPs; Damage-associated molecular patterns; Foxp3+: Forkhead box P3; GCs: Glucocorticosteroids; GVHD: Graft-versus-host disease; MSC: Mesenchymal stem cell; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; NK: Natural killer cells; PAMPs: Pathogen-associated molecular patterns.
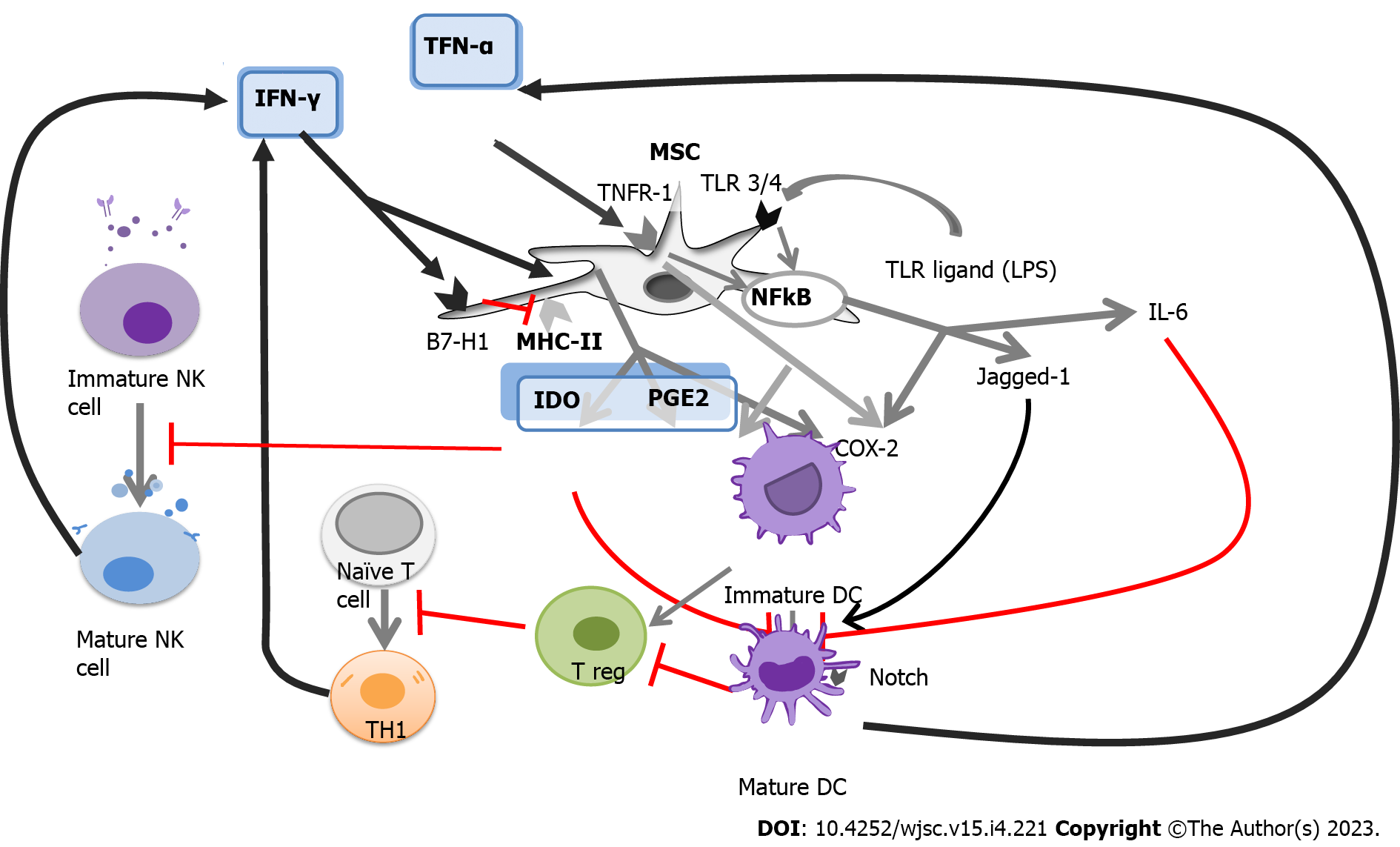
Figure 2 The complex network of antigen presentation and immunomodulation.
Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (MSCs) exert immunomodulatory functions mainly via interactions with immune cells through cell-to-cell contacts and paracrine activity. The MSC secretome includes several cytokines, growth factors, and chemokines, and their immunomodulatory functions vary depending on the source of the MSCs, the target cells, and the microenvironment. COX-2: Cyclooxygenase-2; IDO: Indoleamine-pyrrole 2,3-dioxygenase; IFN: Interferon; IL: Interleukin; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; PGE2: Prostaglandin E2; TLR: Toll-like receptors; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; DC: Dendritic cell; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; NK: Natural killer cells.
- Citation: Jaing TH, Chang TY, Chiu CC. Harnessing and honing mesenchymal stem/stromal cells for the amelioration of graft-versus-host disease. World J Stem Cells 2023; 15(4): 221-234
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v15/i4/221.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v15.i4.221