Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Stem Cells. Feb 26, 2022; 14(2): 200-213
Published online Feb 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i2.200
Published online Feb 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i2.200
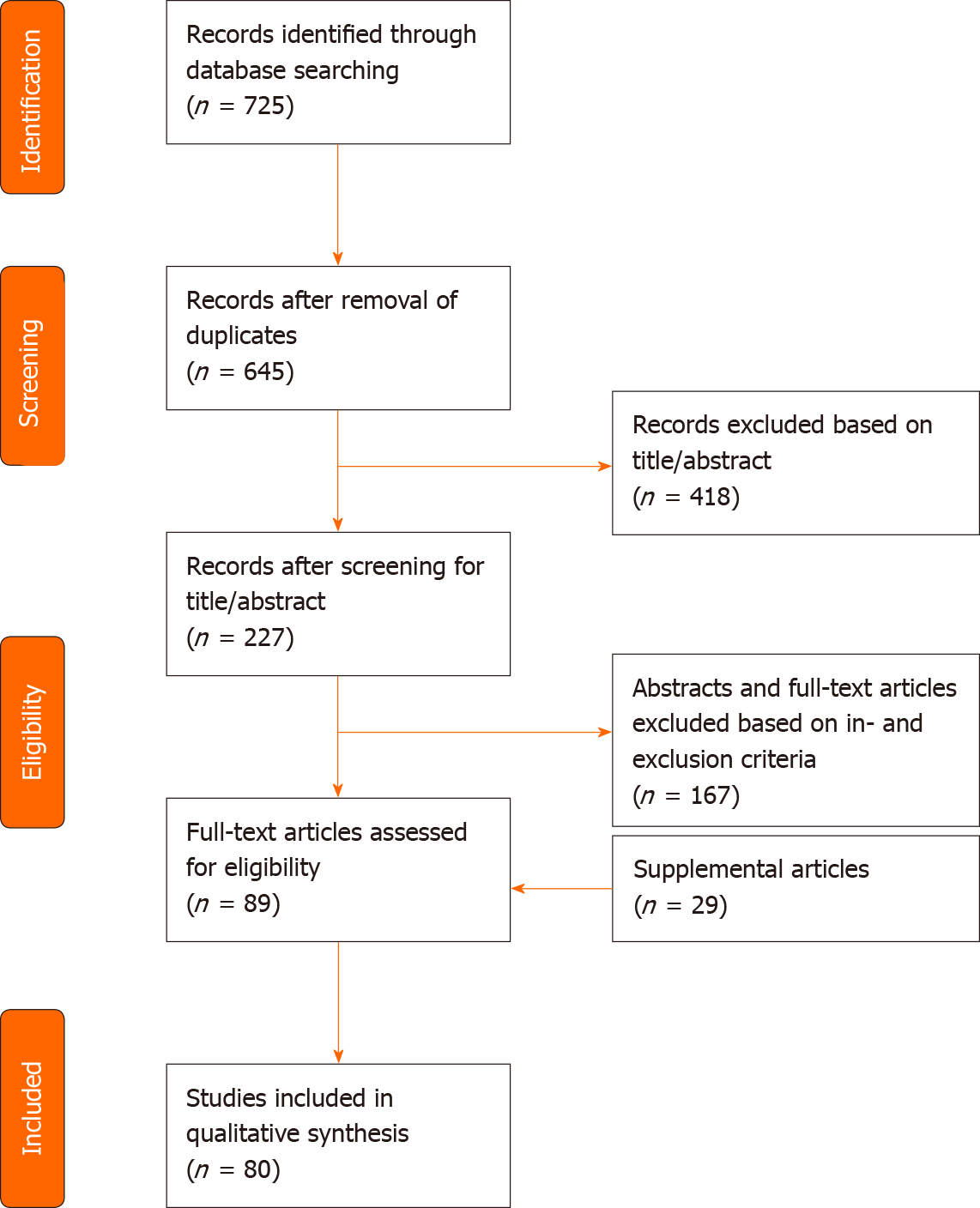
Figure 1 PRISMA flow diagram of search strategy and study selection.
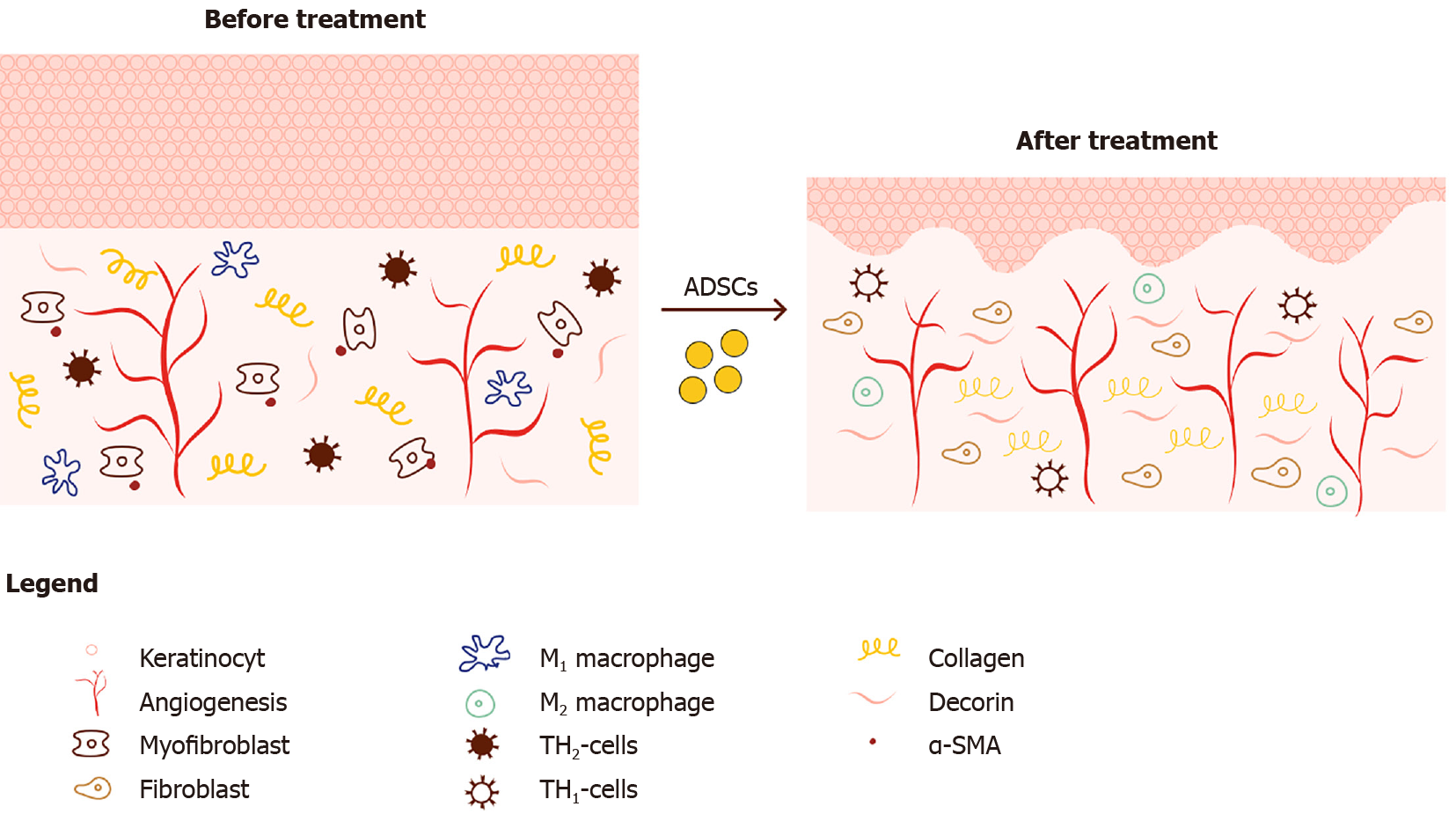
Figure 2 Schematic overview of histological changes in dermal scars before and after treatment with ADSC’s.
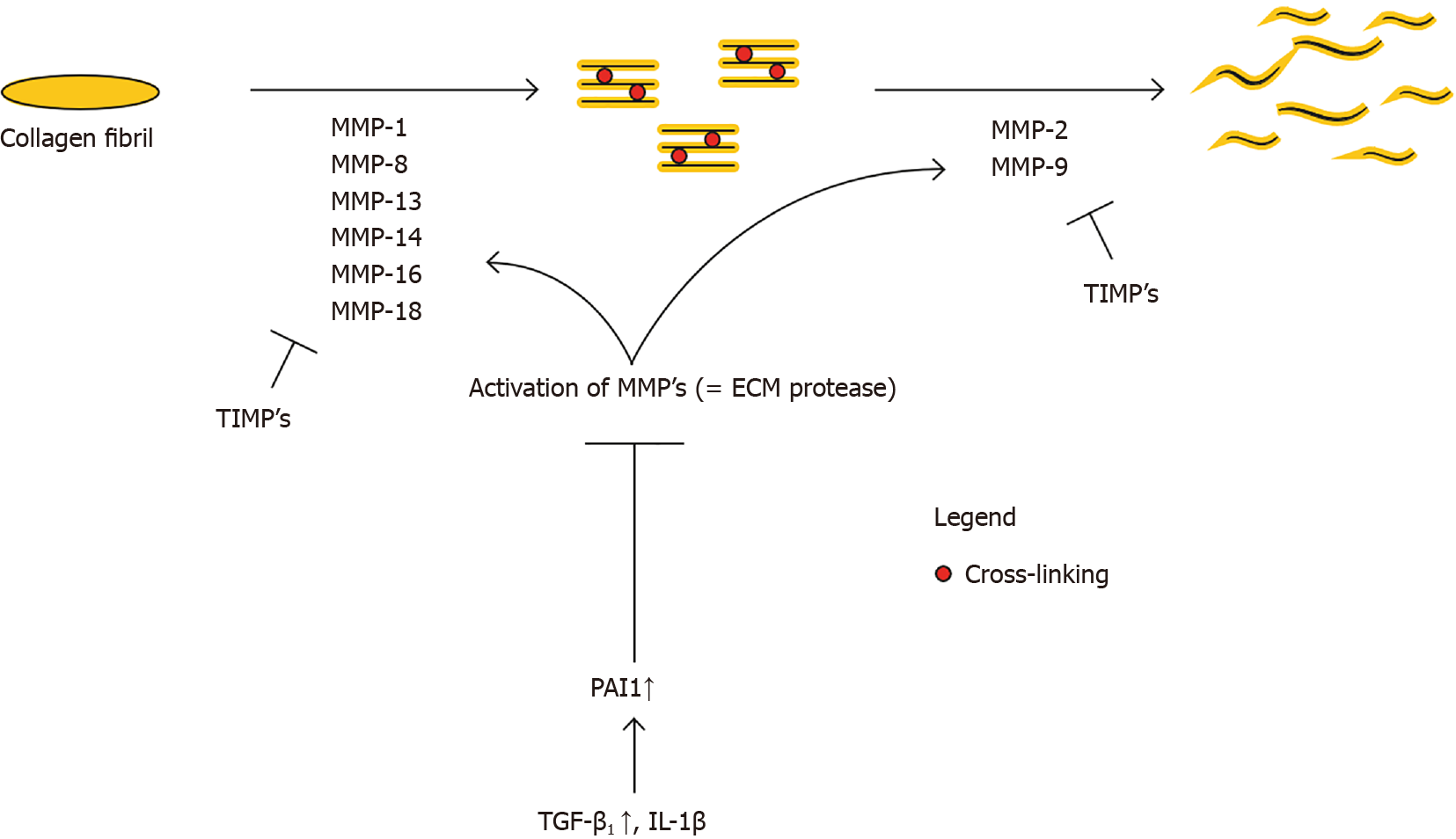
Figure 3 Collagen degradation.
Collagen type 1 and type 3 are the predominant collagen types in fibrosis. ECM homeostasis requires a balance between collagen production and collagen degradation. MMPs manage the collagen degradation, while TIMPs inhibit MMPs, therefore inhibiting degradation. MMPs need activation, which is inhibited by PAI1. So, when TGF-β1 increases, PAI1 renders more inhibition of MMPs activation, therefore inhibiting ECM turnover/ remodeling and increasing fibrosis. MMP: Matrix metalloproteinase; TIMP: Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase; TGF-β1: Transforming growth factor beta; IL-1β: Interleukin-1β; PAI1: Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1.
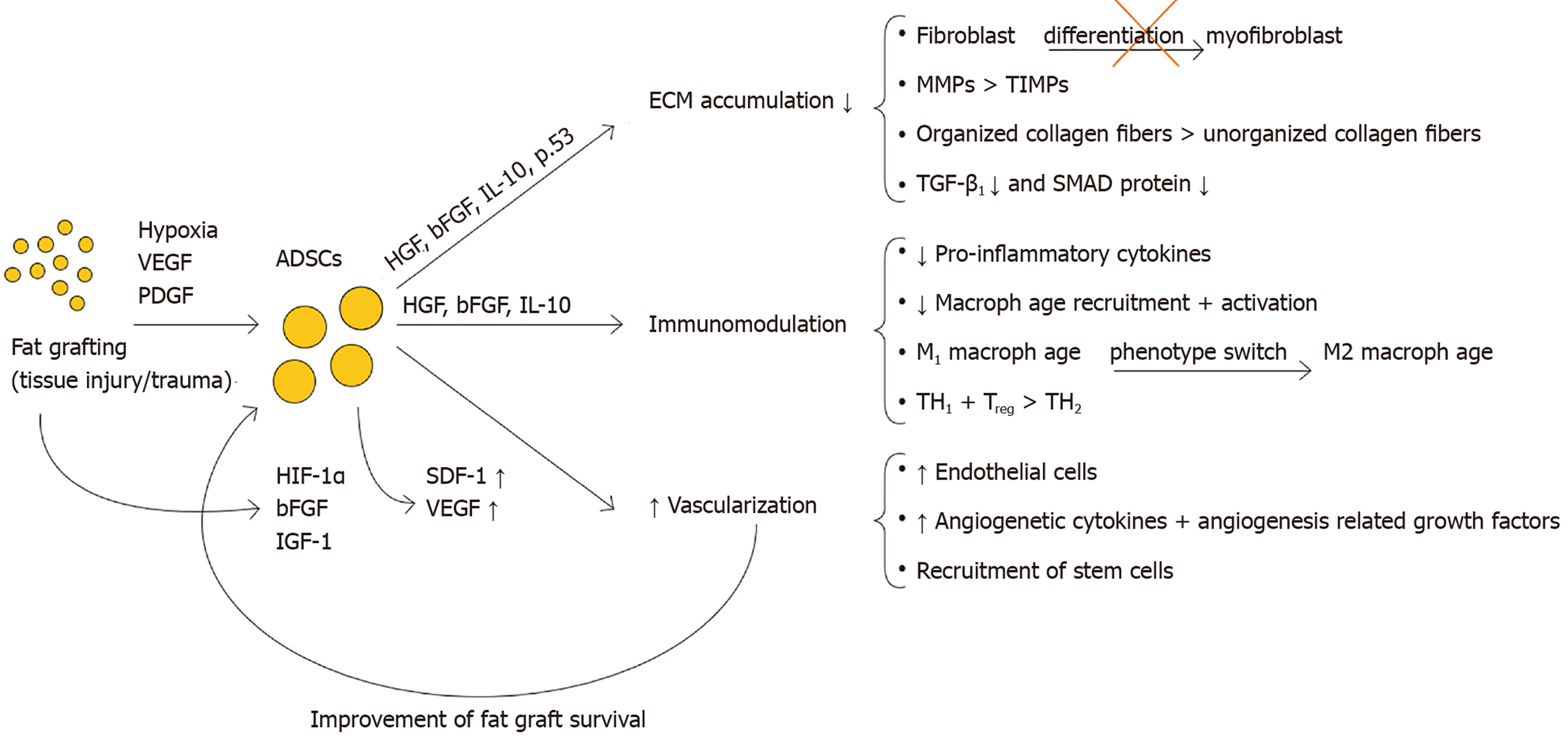
Figure 4 Main mechanisms of adipose-derived stromal cells antifibrotic action and their most important paracrine factors.
VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; PDGF: Platelet-derived growth factor; ADSCs: Adipose-derived stromal cells; HGF: Hepatocyte growth factor; bFGF: Basic fibroblast growth factor; IL-10: Interleukin-10; HIF-1β: Hypoxia-inducing factor-1β; IGF-1: Insulin-like growth factor-1; MMP: Matrix metalloproteinase; TIMP: Iissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase; TH1: T helper 1 cells; TH2: T helper 2 cells; Treg: Regulatory T cells.
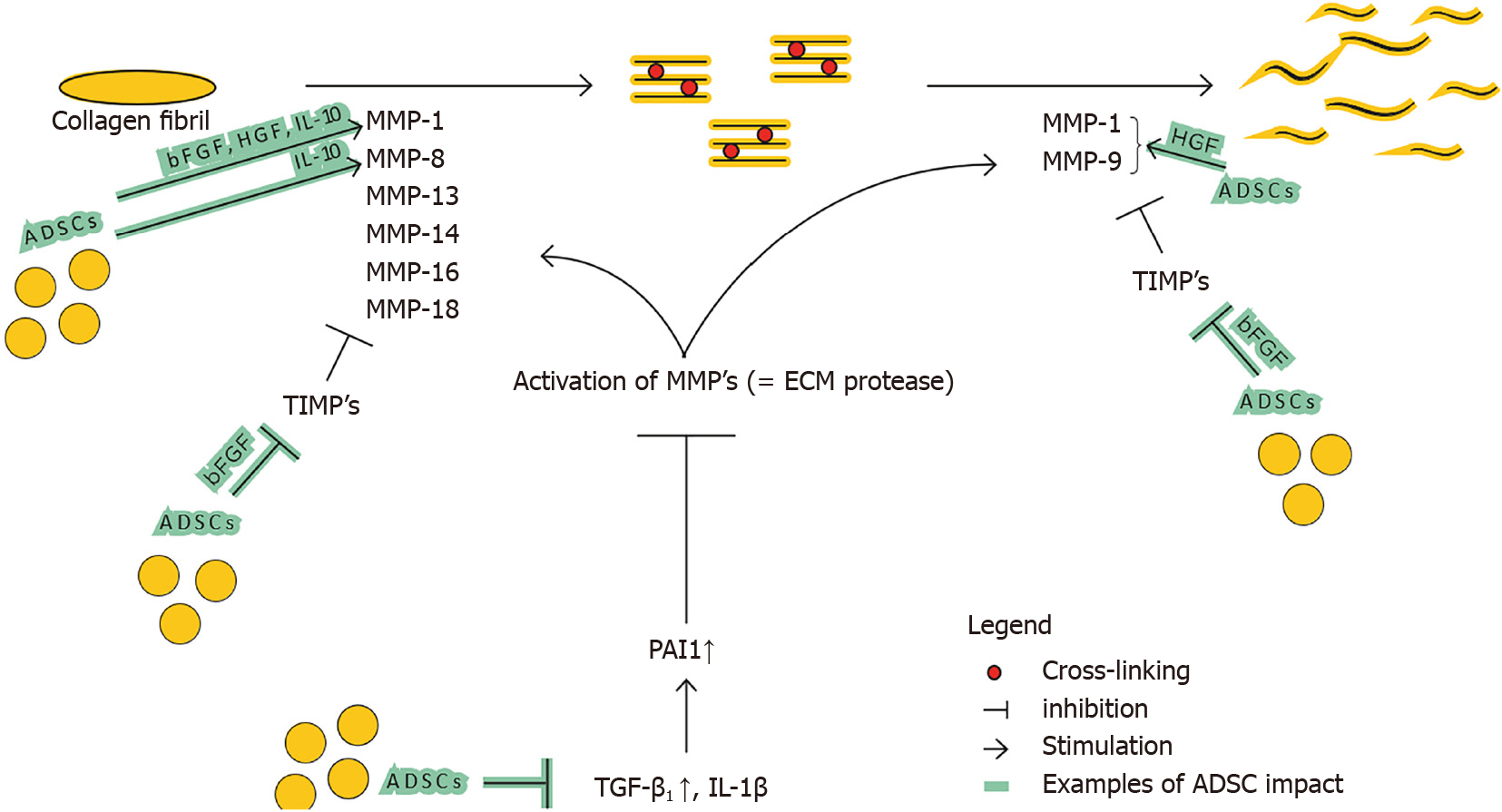
Figure 5 Impact of adipose-derived stromal cells on matrix metalloproteinase and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase balance.
ADSCs: Adipose-derived stromal cells; MMP: Matrix metalloproteinase; TIMP: Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase; TGF-β1: Transforming growth factor beta; IL-1β: Interleukin-1β; PAI1: Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1; HGF: Hepatocyte growth factor; bFGF: Basic fibroblast growth factor; IL-10: Interleukin-10.
- Citation: Vanderstichele S, Vranckx JJ. Anti-fibrotic effect of adipose-derived stem cells on fibrotic scars. World J Stem Cells 2022; 14(2): 200-213
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v14/i2/200.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v14.i2.200