Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Stem Cells. Sep 26, 2021; 13(9): 1197-1214
Published online Sep 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i9.1197
Published online Sep 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i9.1197
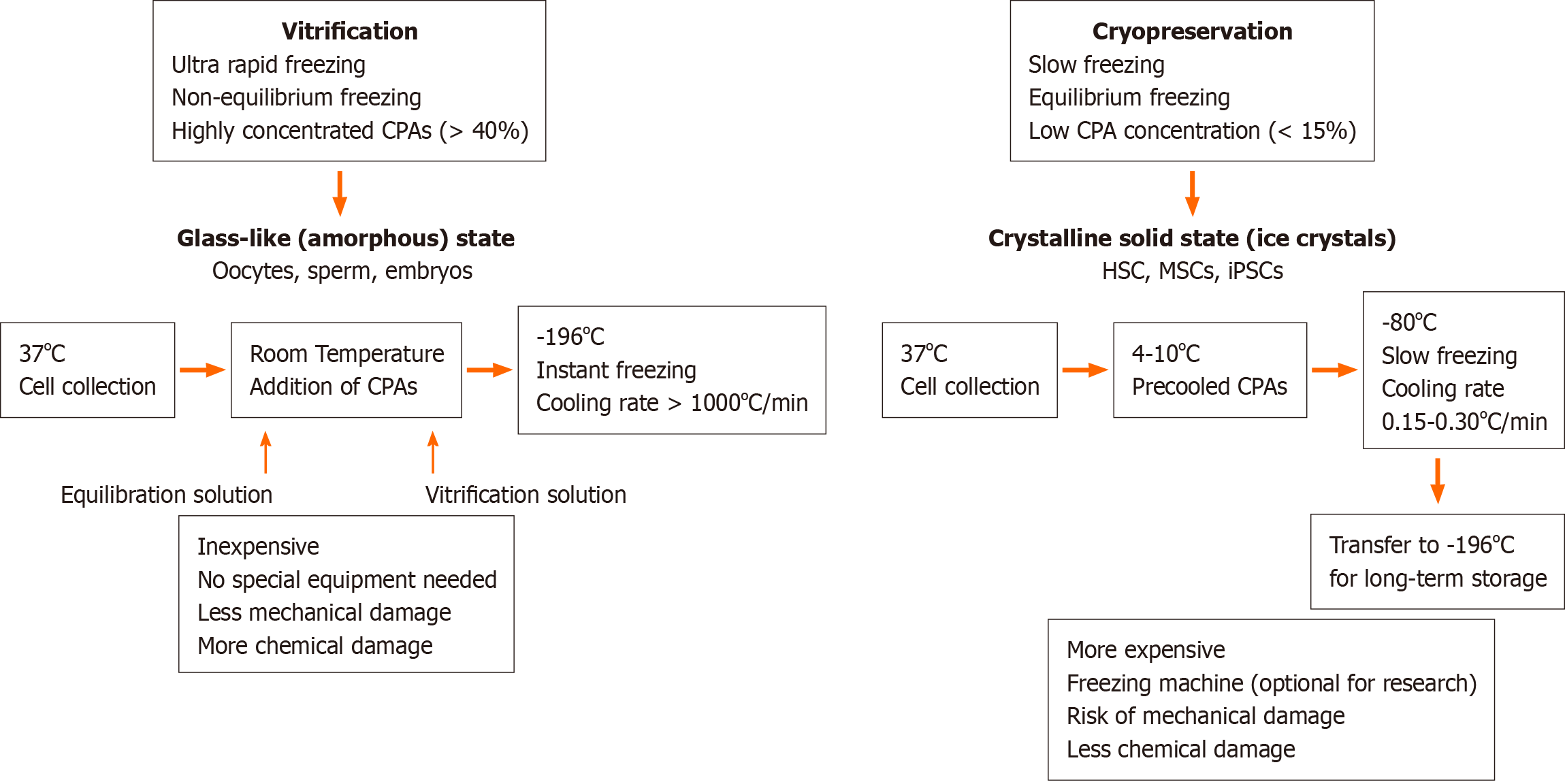
Figure 1 Comparison of vitrification and cryopreservation procedures.
CPAs: Cryoprotective agents; HSCs: Hematopoietic stem cells; MSCs: Mesenchymal stem cells; iPSCs: İnduced pluripotent stem cells.
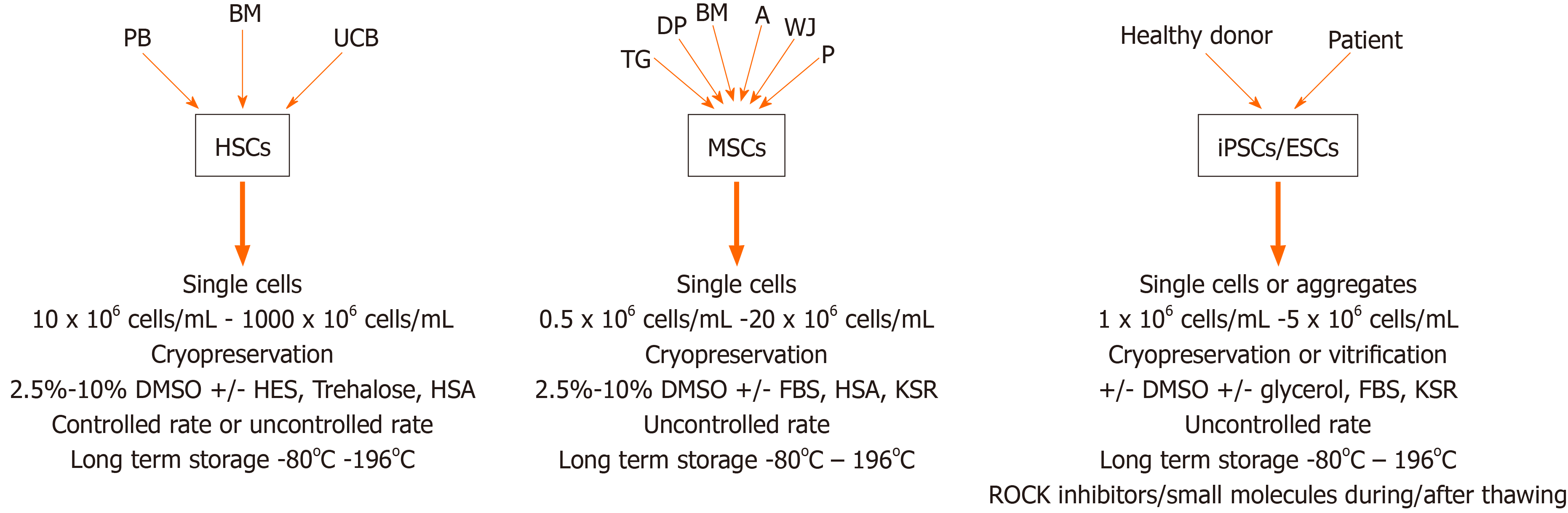
Figure 2 Preferred cryopreservation protocols for different types of stem cells.
PB: Peripheral blood; BM: Bone marrow; UCB: Umbilical cord blood; HSCs: Hematopoietic stem cells; DMSO: Dimethyl sulfoxide; HES: Hydroxyethyl starch; HSA: Human serum albumin; TG: Tooth germ; DP: Dental pulp; A: Adipose tissue; WJ: Wharton Jelly; P: Placenta; MSCs: Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells; FBS: Fetal bovine serum; KSR: Knockout serum replacement; iPSCs: Induced pluripotent stem cells; ESCs: Embryonic stem cells; ROCK: Rho-associated protein kinase.
- Citation: Erol OD, Pervin B, Seker ME, Aerts-Kaya F. Effects of storage media, supplements and cryopreservation methods on quality of stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2021; 13(9): 1197-1214
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v13/i9/1197.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v13.i9.1197