Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Aug 26, 2020; 12(8): 879-896
Published online Aug 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i8.879
Published online Aug 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i8.879
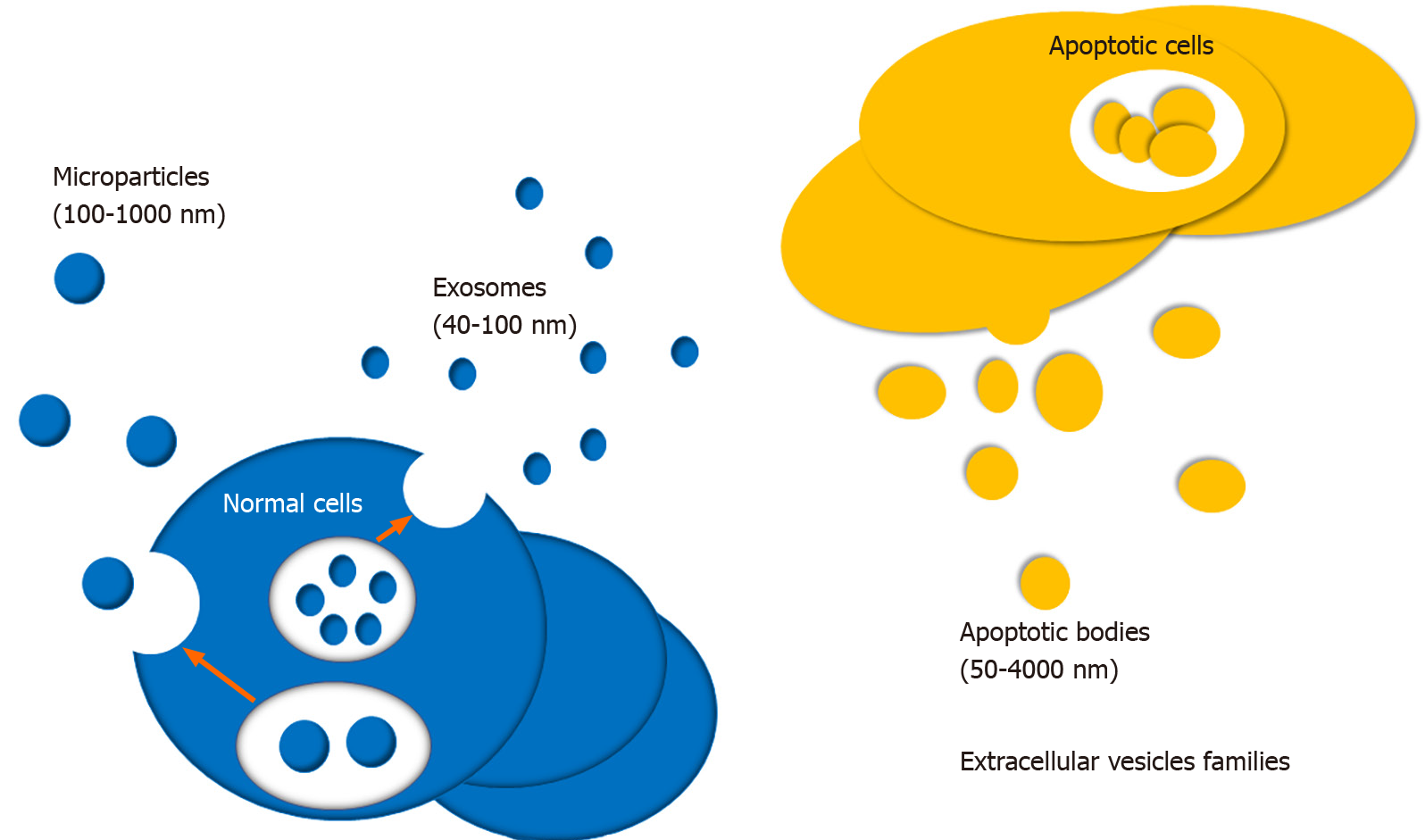
Figure 1 Various kinds of extracellular vesicles.
Extracellular vesicles primarily consist of exosomes, apoptotic bodies, and microparticles derived for normal cells or apoptotic cells.
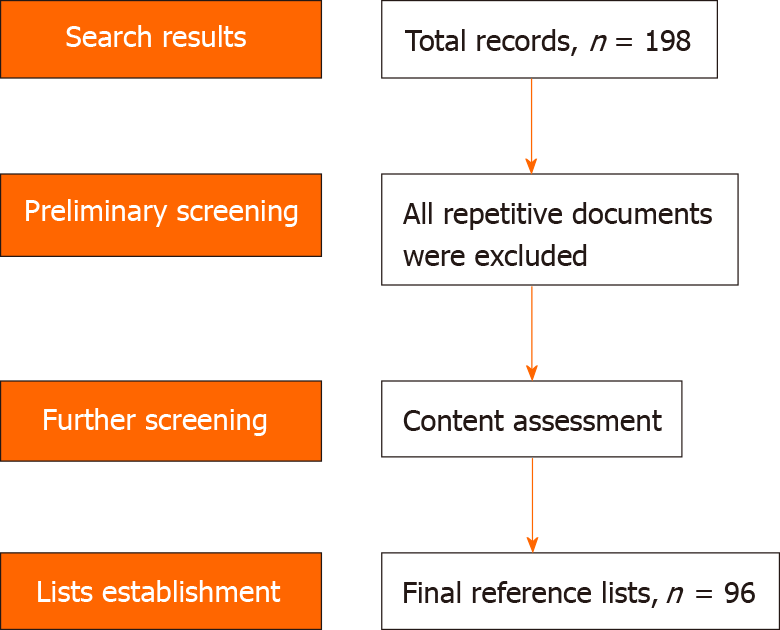
Figure 2 Flowchart for literature retrieval and screening.
Flowchart shows that the repeated siftings have brought 198 search records to the 96 articles for final reference lists.
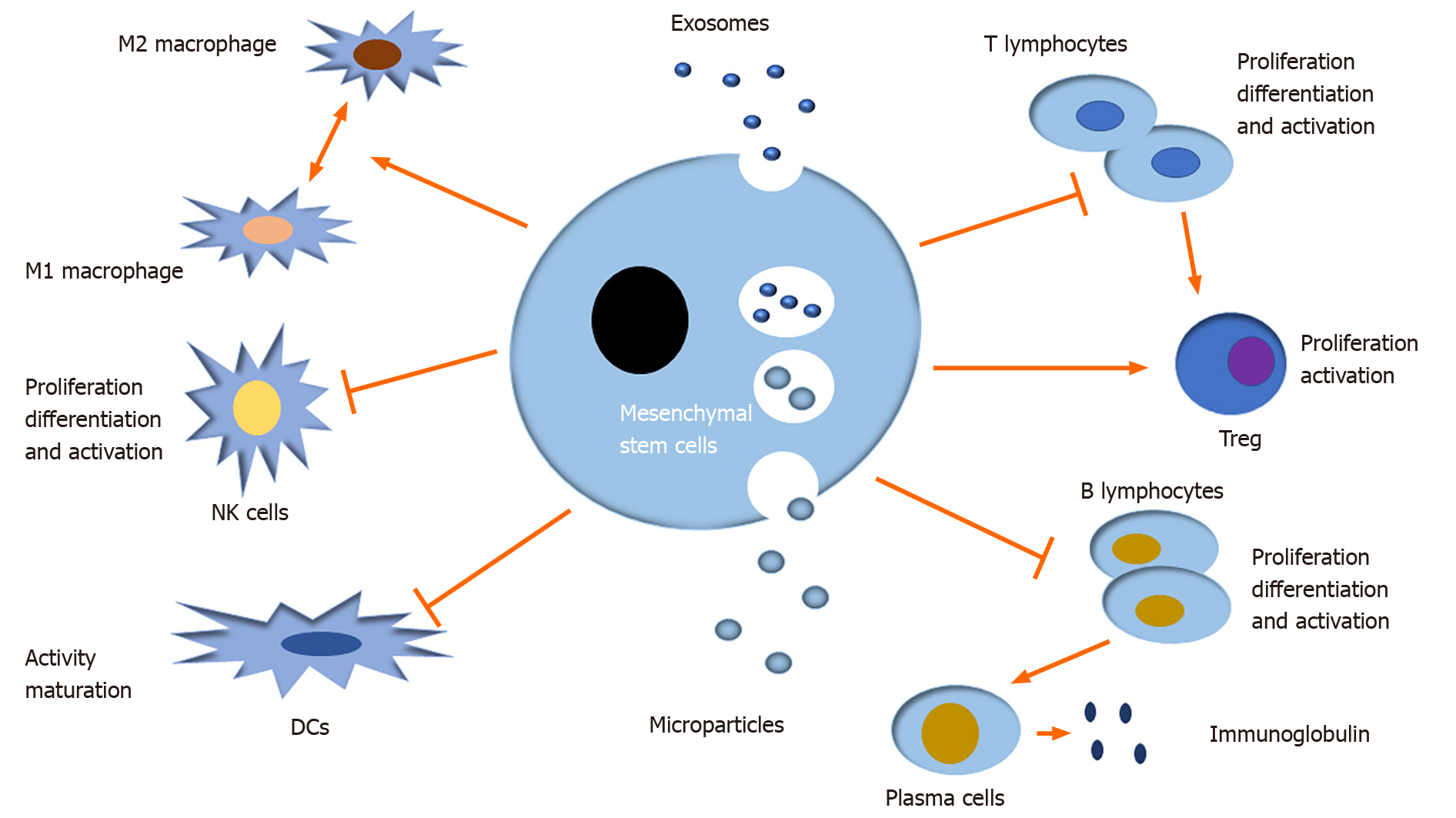
Figure 3 Immunomodulatory effects of mesenchymal stem cell derived extracellular vesicles.
Mesenchymal stem cell derived extracellular vesicles (MSC-EVs) exert immunomodulatory effect on innate and adaptive immune reactions mediated by many immune cells, primarily including T lymphocytes, B lymphocytes, natural killer cells, dendritic cells, and macrophages. In brief, MSC-EVs can inhibit the proliferation, differentiation, and activation of T, B, and natural killer cells and the pathogen-presenting function of dendritic cells and macrophages. In addition, macrophage polarization can be shifted under different microenvironments in accompany with MSC-EVs.
- Citation: Wang JH, Liu XL, Sun JM, Yang JH, Xu DH, Yan SS. Role of mesenchymal stem cell derived extracellular vesicles in autoimmunity: A systematic review. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(8): 879-896
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i8/879.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i8.879