Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Jun 26, 2020; 12(6): 488-499
Published online Jun 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i6.488
Published online Jun 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i6.488
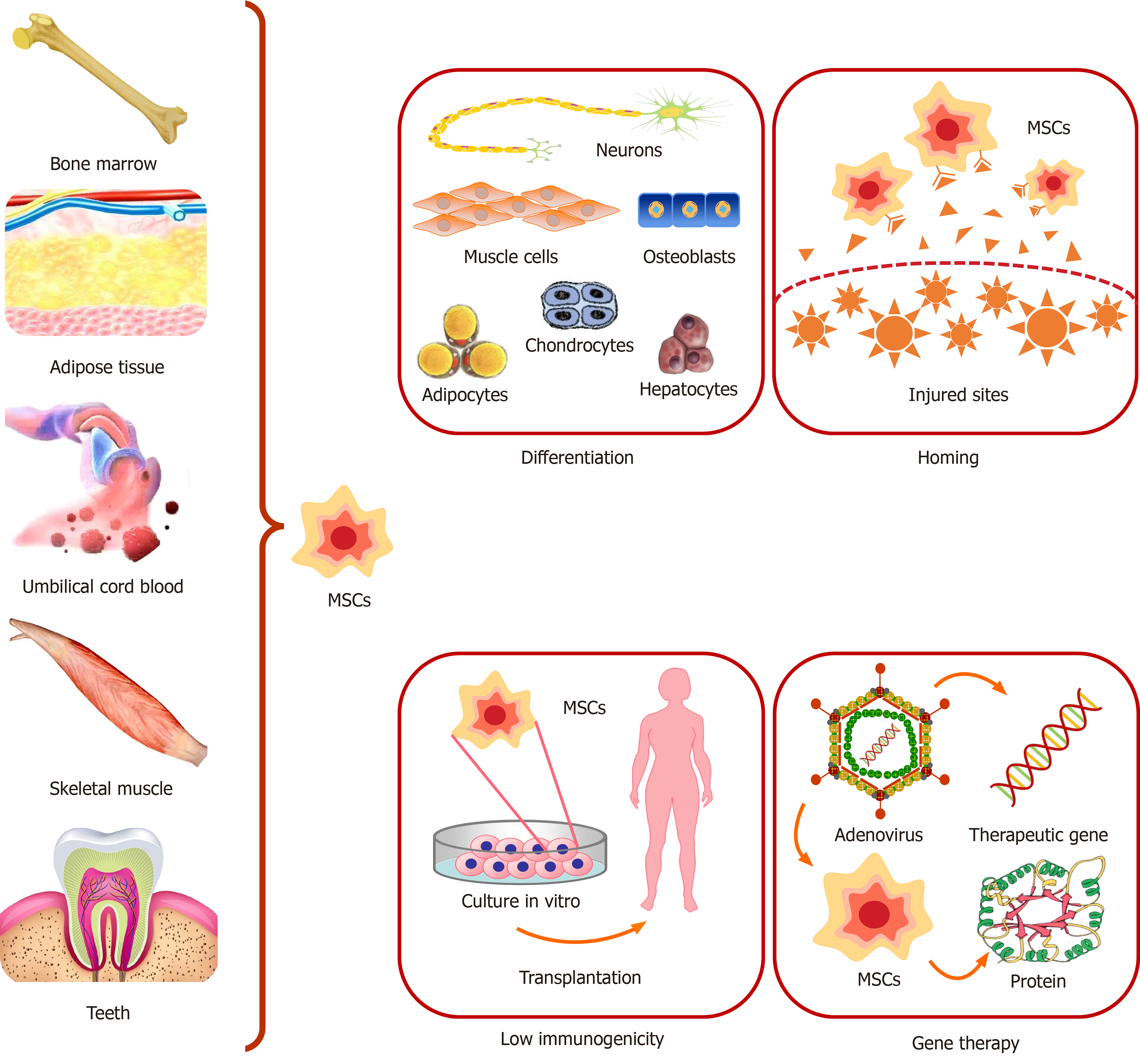
Figure 1 Sources and characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have a wide range of sources, including adult bone marrow, umbilical cord or placental blood, adipose tissue, skeletal muscle, teeth and other tissues. MSCs have the capacity for multilineage differentiation and self-renewal. They can differentiate into neurons, muscle cells, osteoblasts, chondrocytes, adipocytes, hepatocytes and so on under appropriate conditions. MSCs have the characteristic of homing, the mechanism of which is widely believed to be that sites of injury release various factors, and there are receptors for these factors on the surface of MSCs. MSCs have low immunogenicity and can be cultured and isolated artificially in vitro for transplantation. MSCs can also be used as carriers for gene therapy. MSCs can be transfected with therapeutic genes and express the protein of exogenous genes well.
- Citation: Gao Y, Jin SZ. Strategies for treating oesophageal diseases with stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(6): 488-499
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i6/488.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i6.488