Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2013; 19(28): 4447-4454
Published online Jul 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i28.4447
Published online Jul 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i28.4447
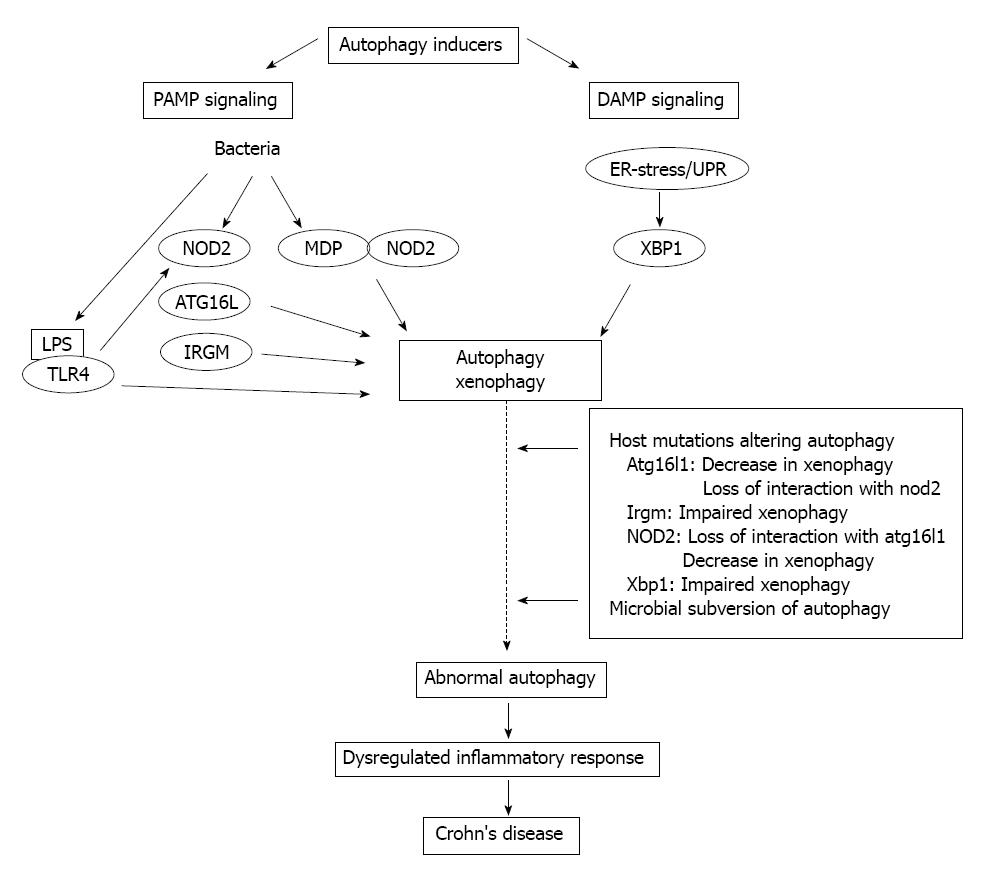
Figure 2 Schematic illustration of the crosstalk between autophagy and innate immunity in Crohn’s disease.
PAMP: Pathogen-associated molecular patterns; DAMP: Damage-associated molecular pattern; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; UPR: Unfolded protein response; NOD: Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing protein; MDP: N-acetyl-muramyl-peptide; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; TLR: Toll-like receptor; XBP1: X-box binding protein 1; IRGM: Immunity-related GTPase family M protein.
- Citation: Műzes G, Tulassay Z, Sipos F. Interplay of autophagy and innate immunity in Crohn's disease: A key immunobiologic feature. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(28): 4447-4454
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i28/4447.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i28.4447