Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2023; 29(1): 110-125
Published online Jan 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i1.110
Published online Jan 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i1.110
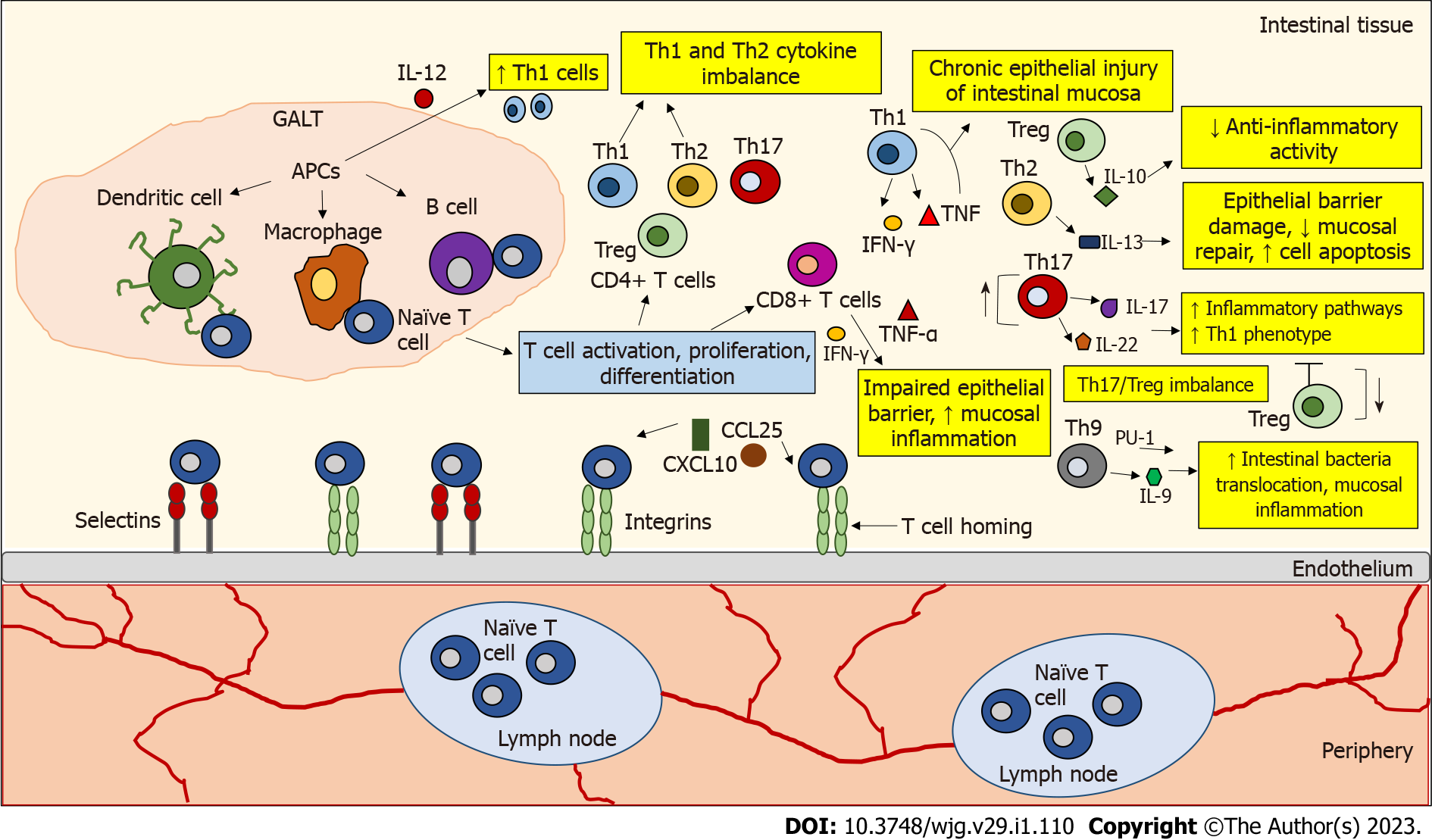
Figure 1 The role of T lymphocytes in inflamed Inflammatory bowel disease tissue.
Naive T cells circulate through secondary lymphoid organs until they interact with antigen-presenting cells (APCs) (e.g., dendritic cells, macrophages, B cells) in gut-associated lymphoid tissue, where they encounter their cognate antigen presented by APCs. This interaction leads to T cell activation, proliferation, and differentiation. T cell homing begins with the binding and rolling of T cells across the endothelium, which is mediated by the binding of selectins and integrins on the T cells to their ligands expressed on the endothelial cells. This binding slows T cell activation by tissue-activated chemokines (C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10, chemokine ligand 25). The development of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is associated with dysregulated activity of T helper (Th) cell subtypes. In IBD, an imbalance has been observed between pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines released by the intestinal mucosa that influence the duration and intensity of inflammatory responses. In IBD, an accumulation of interleukin 12 (IL-12)-induced Th1 cells was observed. Th1 cells produce interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), which may enhance chronic epithelial injury of the intestinal mucosa. IL-10 secreted by regulatory T cells (Tregs) is not sufficient to counteract inflammatory activity in IBD. IL-13 secreted by Th2 cells is associated with epithelial barrier damage, decreased mucosal repair, and increased cell apoptosis. Th17 cells produce IL-17 and IL-22 cytokines that trigger multiple inflammatory pathways. Th17 cells can also be converted to a Th1 cell phenotype. A disturbed Th17/Treg balance is thought to be responsible for the development of IBD. Th9 cells can promote the translocation of intestinal bacteria and inflammation of the intestinal mucosa by expressing the transcription factor PU.1 and the cytokine IL-9. CD8+ T cells can disrupt the intestinal epithelial barrier by releasing IFN-γ and TNF-α and increase mucosal inflammation. APCs: Antigen-presenting cells; CXCL10: C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10; CCL25: Chemokine ligand 25; GALT: Gut-associated lymphoid tissue; IL: Interleukin; IFN-γ: Interferon-gamma; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; Th: T helper; Treg: T regulatory cells.
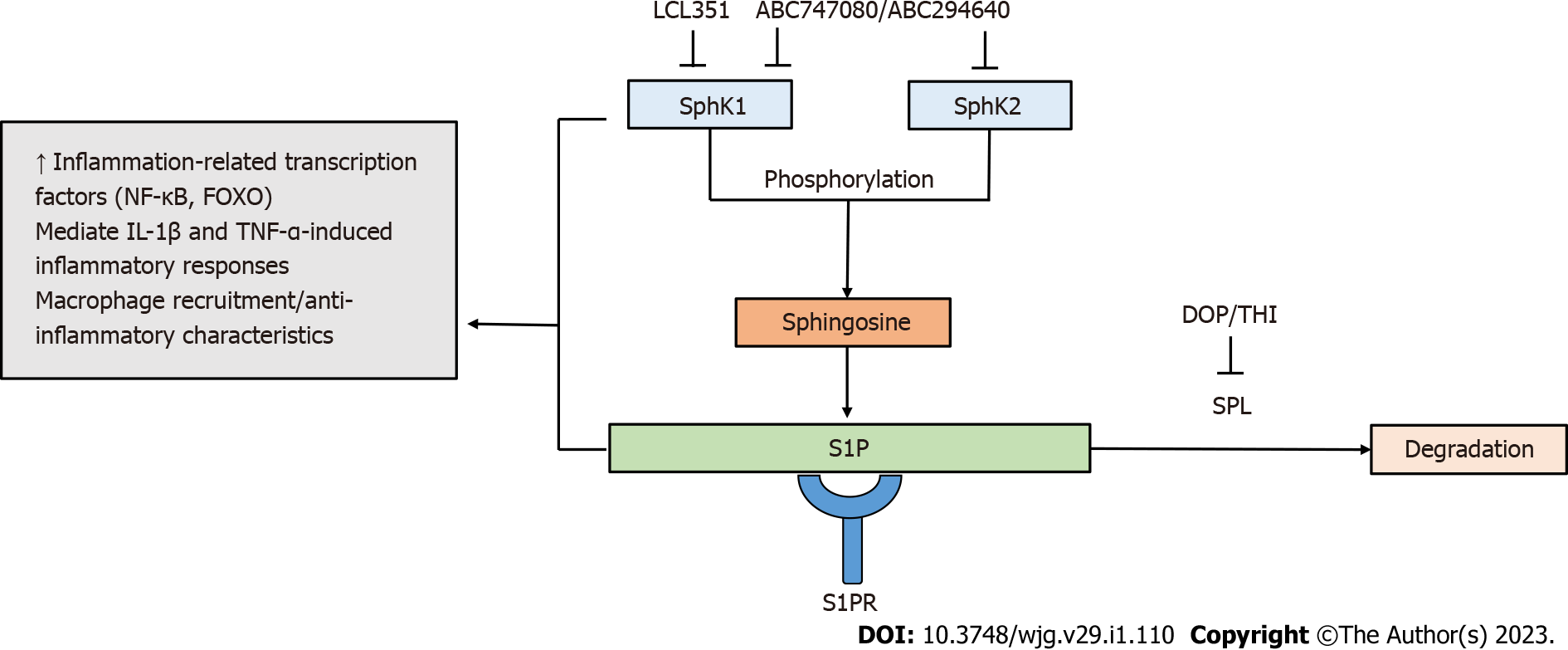
Figure 2 Targeting sphingosine-1-phosphate metabolism by sphingosine-1-phosphate modulators.
Sphingosine kinases (SphK1/SphK2) phosphorylate sphingosine to form sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P). S1P degradation is mediated by sphingosine phosphate lyase. Components of S1P metabolism are involved in inflammatory responses. The SphK/S1P receptor network is associated with the induction of inflammation-related transcription factors, including nuclear factor-kappa B and forkhead box O. The SphK/S1P axis has been shown to mediate inflammatory responses induced by pro-inflammatory cytokines interleukin 1-beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Increased activity of SphK1 modulates the recruitment of macrophages and the manifestation of their anti-inflammatory properties. S1P modulators targeting components of S1P metabolism contribute to the regulation of inflammatory immune responses. FOXO: Forkhead box O; IL: Interleukin; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; NF-Κβ: Nuclear factor-kappa B; S1P: Sphingosine-1-phosphate; SPL: Sphingosine phosphate lyase.
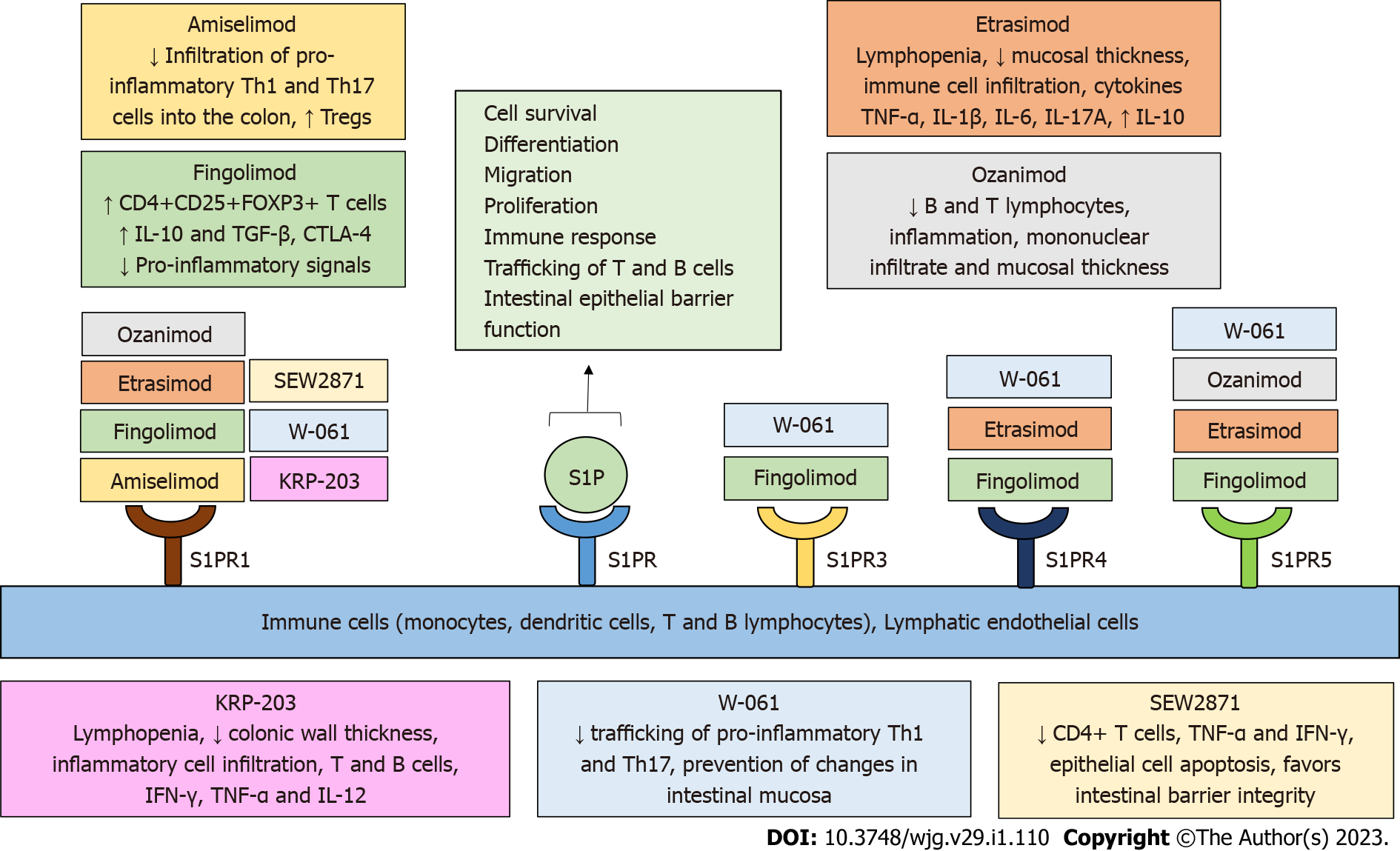
Figure 3 Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor modulators in preclinical and clinical studies in inflammatory bowel disease.
Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) receptors (S1PRs) have been highlighted as important research targets in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). S1PRs are expressed on immune cells and lymphatic endothelial cells. Binding of S1P to S1PR regulates a variety of biological processes, including cell survival, differentiation, migration, proliferation, immune response, trafficking of T and B cells, and intestinal epithelial barrier function. Several novel, selective S1PR modulators are currently being tested in IBD and contribute to the amelioration of the inflammatory process in inflamed intestinal tissue by regulating immune cell concentration, activity, trafficking, and cytokine secretion, as well as intestinal barrier function and integrity. S1P: Sphingosine 1 phosphate; S1PR: Sphingosine 1 phosphate receptor; IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease; Th: T helper; Tregs: Regulatory T cells.
- Citation: Tourkochristou E, Mouzaki A, Triantos C. Unveiling the biological role of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor modulators in inflammatory bowel diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(1): 110-125
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i1/110.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i1.110