Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2013; 19(36): 6011-6019
Published online Sep 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i36.6011
Published online Sep 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i36.6011
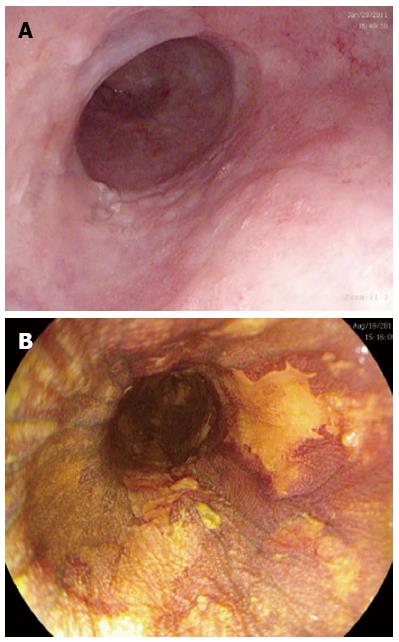
Figure 1 Endoscopic views of a segment of squamous high grade dysplasia with macroscopic lesions suggestive of dysplasia with (A) high definition white light endoscopy and confirmation of areas of dysplasia with (B) Lugol’s iodine dye spray representing unstained lesions.
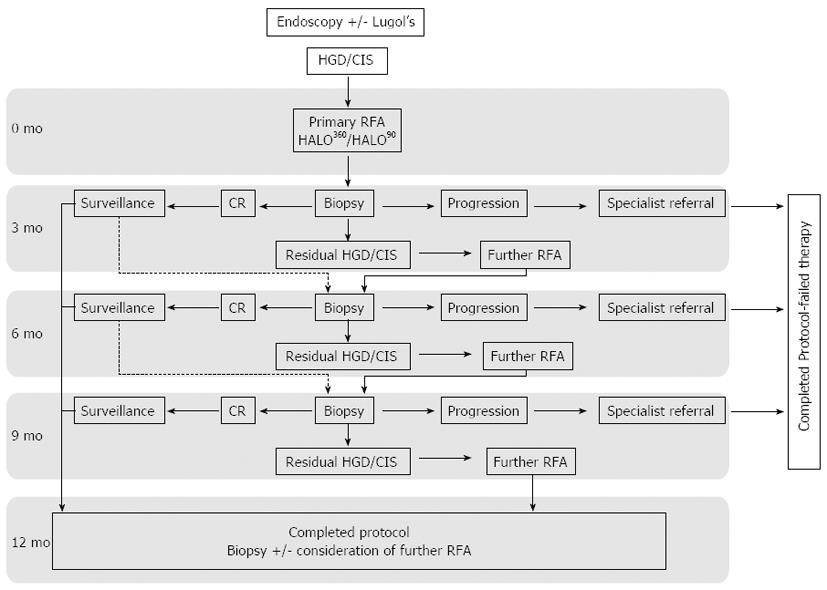
Figure 2 HALO radiofrequency ablation protocol for ablation of Squamous high grade dysplasia and carcinoma in situ.
Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) was carried out at any stage for new visible lesions. RFA: Radiofrequency ablation; HGD: High grade dysplasia; CIS: Carcinoma in situ; CR: Complete reversal.
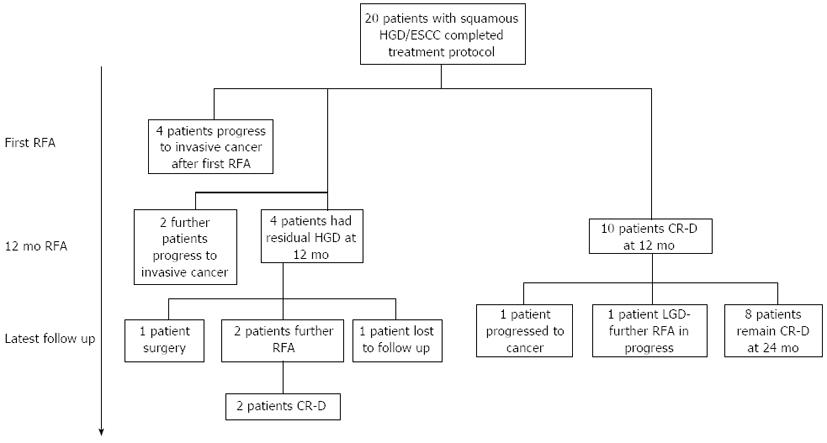
Figure 3 Outcomes for all 20 patients who have completed treatment protocol with radiofrequency ablation for squamous high grade dysplasia/early squamous cell carcinoma.
RFA: Radiofrequency ablation; HGD: High grade dysplasia; ESCC: Early squamous cell carcinoma; CR-D: Complete reversal dysplasia; LGD: Low grade dysplasia.
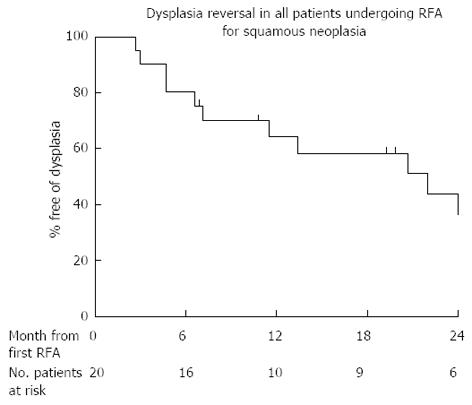
Figure 4 Kaplan Meier outcome statistics predicting the risk of recurrent dysplasia and durability of radiofrequency ablation treatment in all 20 patients treated with radiofrequency ablation.
RFA: Radiofrequency ablation.
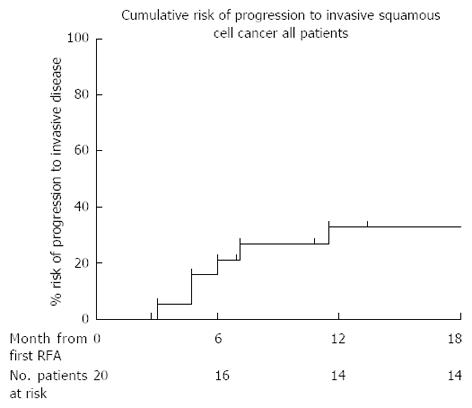
Figure 5 Cumulative risk of cancer progression in all 20 patients who completed treatment with radiofrequency ablation for high grade dysplasia/early squamous cell carcinoma in the United Kingdom radiofrequency ablation registry.
RFA: Radiofrequency ablation.
- Citation: Haidry RJ, Butt MA, Dunn J, Banks M, Gupta A, Smart H, Bhandari P, Smith LA, Willert R, Fullarton G, John M, Pietro MD, Penman I, Novelli M, Lovat LB. Radiofrequency ablation for early oesophageal squamous neoplasia: Outcomes form United Kingdom registry. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(36): 6011-6019
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i36/6011.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i36.6011