Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2013; 19(28): 4486-4494
Published online Jul 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i28.4486
Published online Jul 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i28.4486
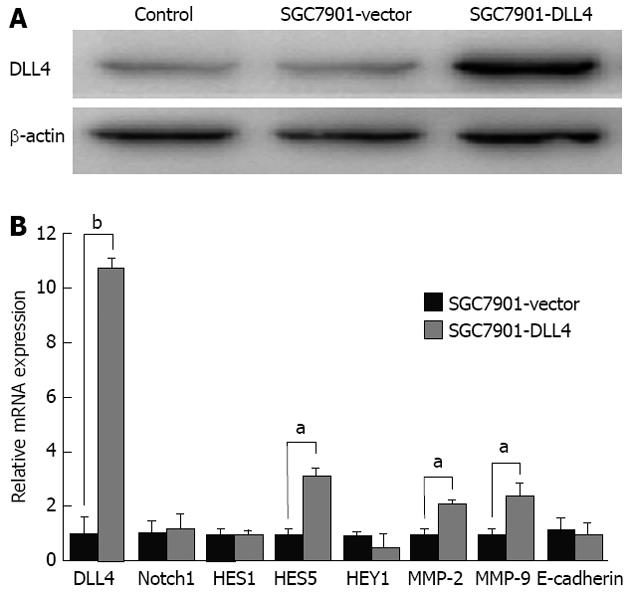
Figure 1 Up-regulation of Delta-like ligand 4 changed downstream gene expression in SGC7901 cells.
A: Western blotting confirmed the up-regulation of Delta-like ligand 4 (DLL4) in the SGC7901-DLL4 group at the protein level; B: Real-time polymerase chain reaction was used to assess Notch1, DLL4, and downstream genes HES1, HES5, HEY1, as well as the matrix metalloproteinases-2 (MMP-2), MMP-9, and the adhesion protein E-cadherin at the mRNA level. The results showed increased expression of DLL4, HES5, MMP-2, and MMP-9, but no significant change of HES1 and HEY1 (aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs the SGC7901-vector group). Data show mean ± SD of gene expression compared with the control group. Endogenous references was glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; SGC7901-vector: SGC7901 cells transfected with an empty vector; SGC7901-DLL4: SGC7901 cells transfected with a vector encoding human DLL4 gene; Control: Non-transfected SGC7901 cells.
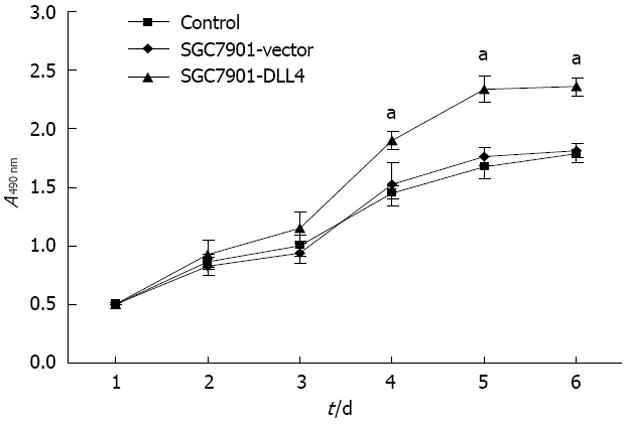
Figure 2 Up-regulation of Delta-like ligand 4 promoted cell proliferation in SGC7901 cells.
Growth curve comparing SGC7901-Delta-like ligand 4 (DLL4), SGC7901-vector and SGC7901 cells over a 6-d time course. Up-regulation of DLL4 significantly promoted the proliferation of SGC7901 cells in vitro. Data are shown as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments (aP < 0.05 vs the SGC7901-vector group); SGC7901-vector: SGC7901 cells transfected with an empty vector; SGC7901-DLL4: SGC7901 cells transfected with a vector encoding human DLL4 gene; Control: Non-transfected SGC7901 cells.
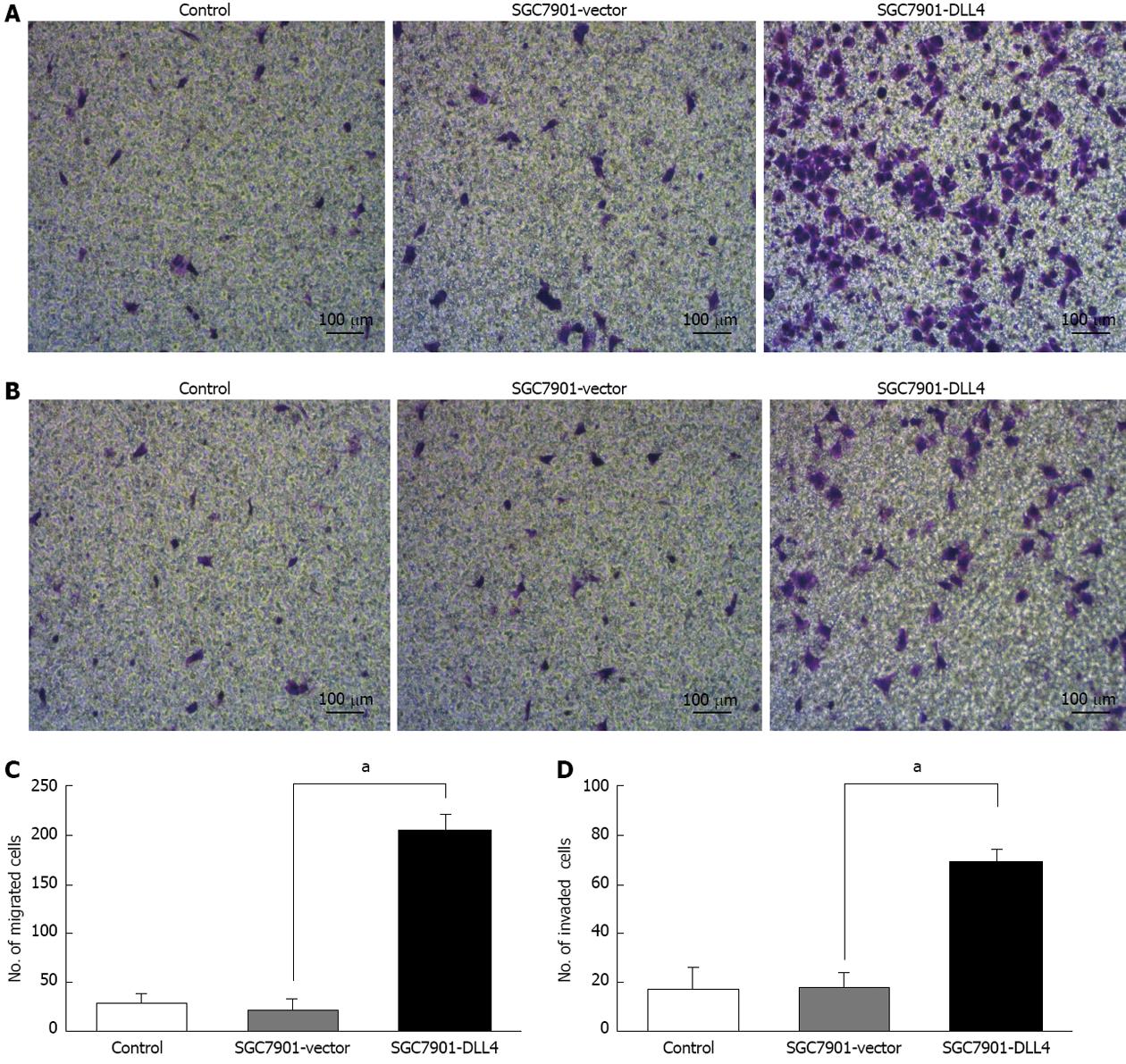
Figure 3 Up-regulation of Delta-like ligand 4 promoted cell migration and invasion in SGC7901 cells.
A: Crystal violet staining revealed the migrated cells of each group; B: Crystal violet staining reveals invaded cells from each of the groups; C: The number of cells in the SGC7901-Delta-like ligand 4 (DLL4) group that had migrated was 8.31 times higher than those transfected with an empty vector (205.4 ± 15.2 vs 22.3 ± 12.1, aP < 0.05); D: The number of cells in the SGC7901-DLL4 group that had migrated across both the Matrigel and the insert was 2.83 times higher than that in the SGC7901-vector group (68.8 ± 5.3 vs 18.2 ± 6.0, aP < 0.05). SGC7901-vector: SGC7901 cells transfected with an empty vector; SGC7901-DLL4: SGC7901 cells transfected with vector encoding human DLL4 gene; Control: Non-transfected SGC7901 cells.
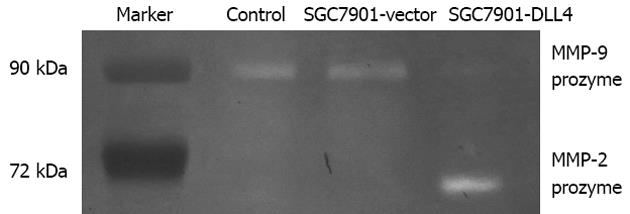
Figure 4 Effect of Delta-like ligand 4 up-regulation on the secretion and activation of extracellular matrix metalloproteinases.
Twenty microlitres of culture supernatant from each group was used. Coomassie Blue R-250 staining of the zymogram revealed significantly increased matrix metalloproteinases (MMP)-2 proenzyme but decreased MMP-9 proenzyme in the SGC7901-Delta-like ligand 4 (DLL4) group vs the SGC7901-vector group. SGC7901-vector: SGC7901 cells transfected with an empty vector; SGC7901-DLL4: SGC7901 cells transfected with vector encoding human DLL4 gene; Control: Non-transfected SGC7901 cells.
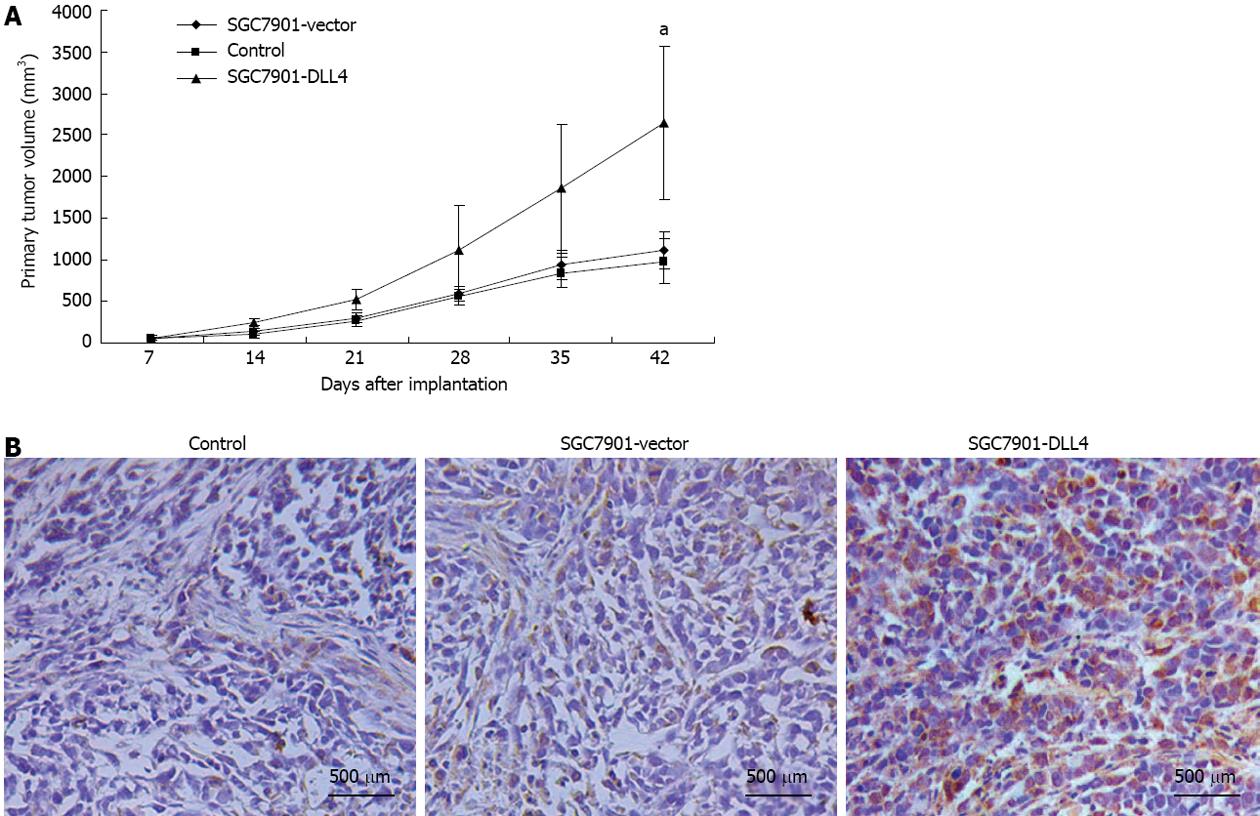
Figure 5 Up-regulation of Delta-like ligand 4 promoted tumorigenesis of SGC7901 cells in vivo.
Twenty-four 4-wk-old male BALB/c nu/nu mice were divided randomly into three groups and implanted subcutaneously with control/SGC7901-vector/SGC7901-Delta-like ligand 4 (DLL4) cells. A: Six weeks after inoculation, the size of subcutaneous formed tumor masses of the SGC7901-DLL4 group (2640.5 ± 923.6 mm3) was significantly larger than the control (1011.1 ± 273.6 mm3) and SGC7901-vector groups (1115.1 ± 223.8 mm3); B: Immunohistochemistry staining of DLL4 confirmed the up-regulation of DLL4 in the SGC7901-DLL4 group. aP < 0.05 vs the SGC7901-vector group.
- Citation: Li GG, Li L, Li C, Ye LY, Li XW, Liu DR, Bao Q, Zheng YX, Xiang DP, Chen L, Chen J. Influence of up-regulation of Notch ligand DLL4 on biological behaviors of human gastric cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(28): 4486-4494
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i28/4486.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i28.4486