Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2013; 19(13): 2080-2086
Published online Apr 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i13.2080
Published online Apr 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i13.2080
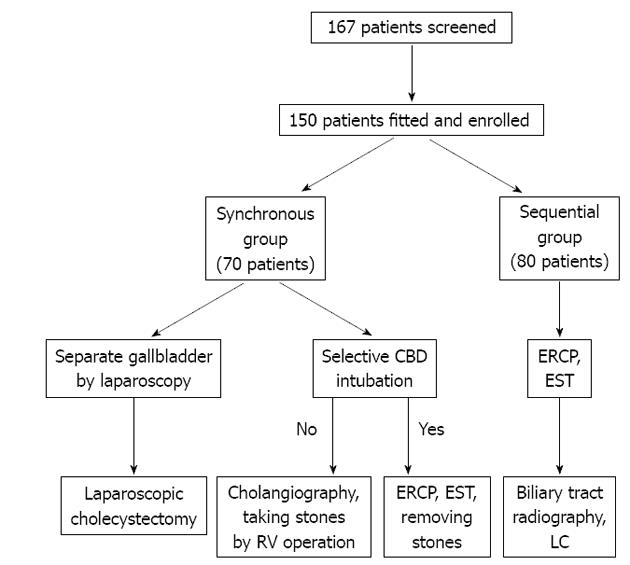
Figure 1 Treatment procedure for this study.
CBD: Common bile duct; ERCP: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography; EST: Endoscopic sphincterotomy; RV: Rendezvous; LC: Laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
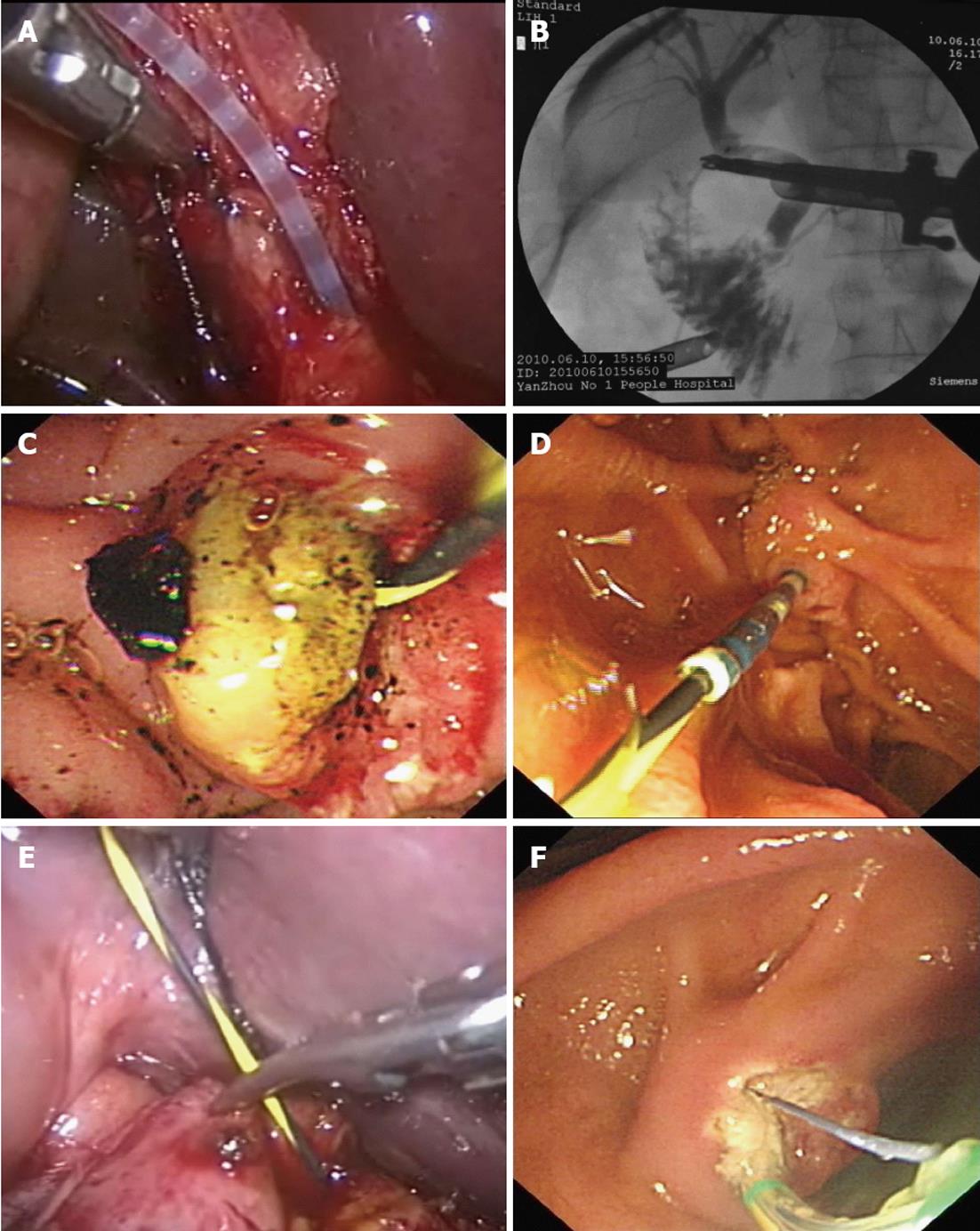
Figure 2 Surgical procedures.
A: Angiographic catheter was inserted; B: Choledochography was performed; C: Stones were removed by balloon or basket; D: Yellow zebra guide wire was inserted into cystic duct; E: Angiographic catheter was inserted following the guide wire; F: Duodenal papillary muscle was cut.
-
Citation: Ding YB, Deng B, Liu XN, Wu J, Xiao WM, Wang YZ, Ma JM, Li Q, Ju ZS. Synchronous
vs sequential laparoscopic cholecystectomy for cholecystocholedocholithiasis. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(13): 2080-2086 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i13/2080.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i13.2080