Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2013; 19(13): 2073-2079
Published online Apr 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i13.2073
Published online Apr 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i13.2073
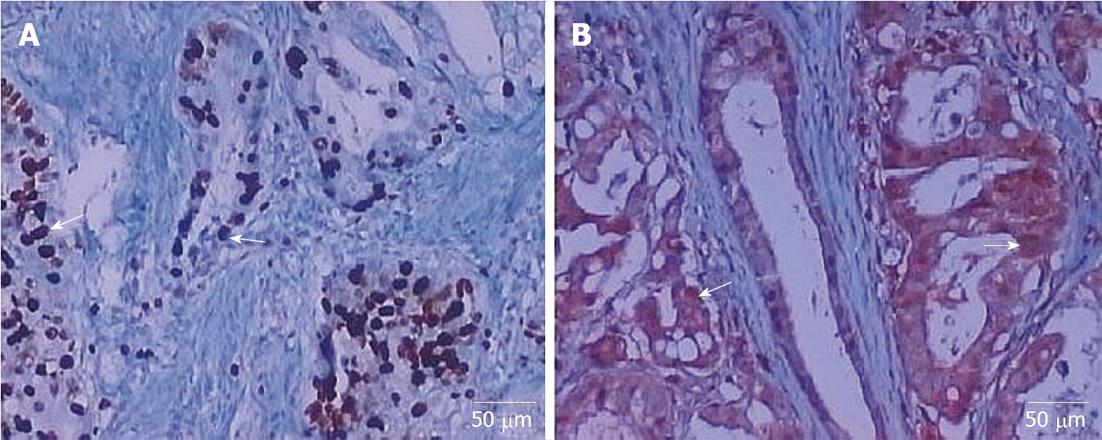
Figure 1 Immunohistochemical staining for galectin-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor (original magnification, × 200).
A: Positive galectin-1 expression in gastric cancer tissue; B: Positive vascular endothelial growth factor expression in gastric cancer tissue. The over-expressed markers are shown with arrows.
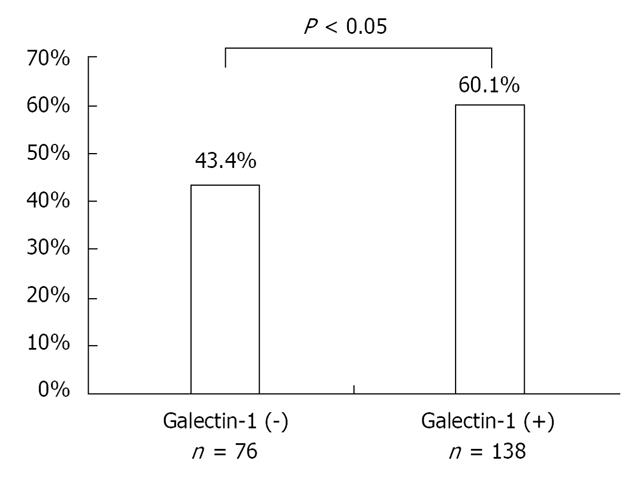
Figure 2 Vascular endothelial growth factor was expressed more frequently in galectin-1-positive gastric cancers than galectin-1-negative.
Figure 3 Overall survival rate of patients.
A: The overall survival rate of patients relative to galectin-1-positive expression and galectin-1-negative expression in gastric cancer tissue samples. Galectin-1 overexpression was significantly associated with poor patient survival (P < 0.05); B: The overall survival rate of patients relative to vascular endothelial growth factor-positive expression and vascular endothelial growth factor -negative expression in gastric cancer tissue samples. Vascular endothelial growth factor overexpression was significantly associated with poor patient survival (P < 0.05); C: The overall survival rates of patients relative to groups I, II, III and IV. Both galectin-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor overexpression was significantly associated with poor patient survival (P < 0.05).
- Citation: Chen J, Zhou SJ, Zhang Y, Zhang GQ, Zha TZ, Feng YZ, Zhang K. Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of galectin-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor expression in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(13): 2073-2079
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i13/2073.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i13.2073