Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2012; 18(48): 7158-7165
Published online Dec 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i48.7158
Published online Dec 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i48.7158
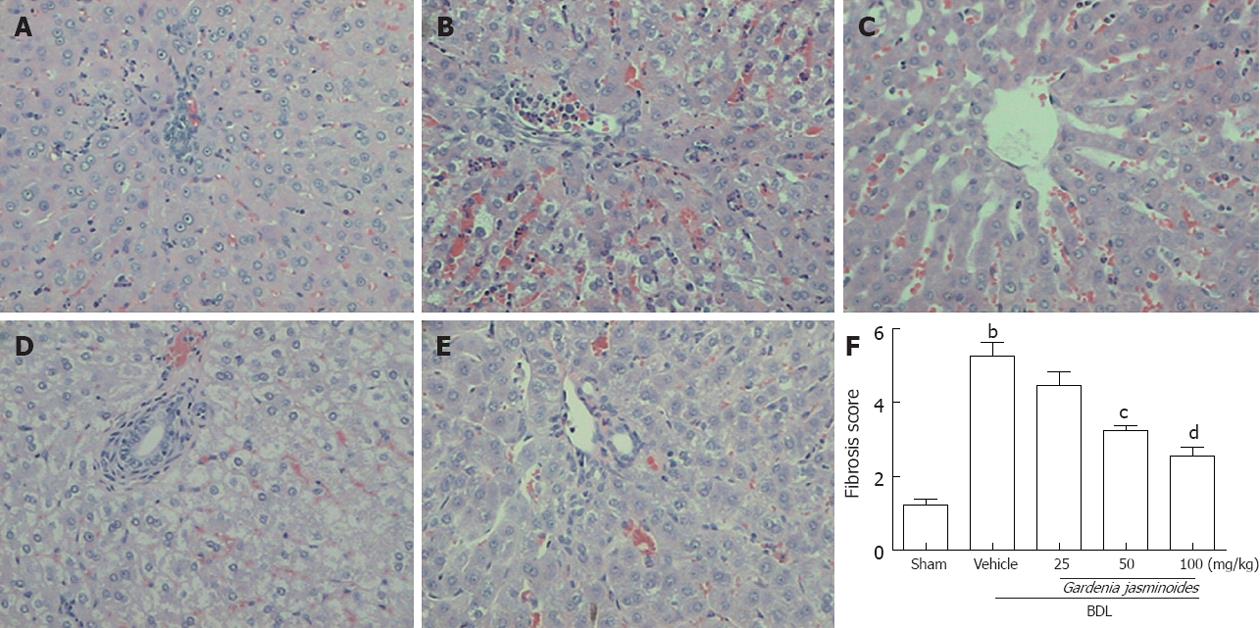
Figure 1 Gardenia jasminoides markedly improved the histology in bile duct ligation rats.
Representative pictures of hematoxylin and eosin staining (magnification ×200) from rats subjected to bile duct ligation (BDL) or sham-operated rats treated with vehicle or Gardenia jasminoides. A: Sham; B: BDL + vehicle; C: BDL + Gardenia jasminoides (25 mg/kg per day); D: BDL+ Gardenia jasminoides (50 mg/kg per day); E: BDL+ Gardenia jasminoides (100 mg/kg per day); F: Scores of double-blinded assessments of liver histology with respect to fibrosis. bP < 0.01 vs sham; cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01 vs BDL + vehicle (n = 8).
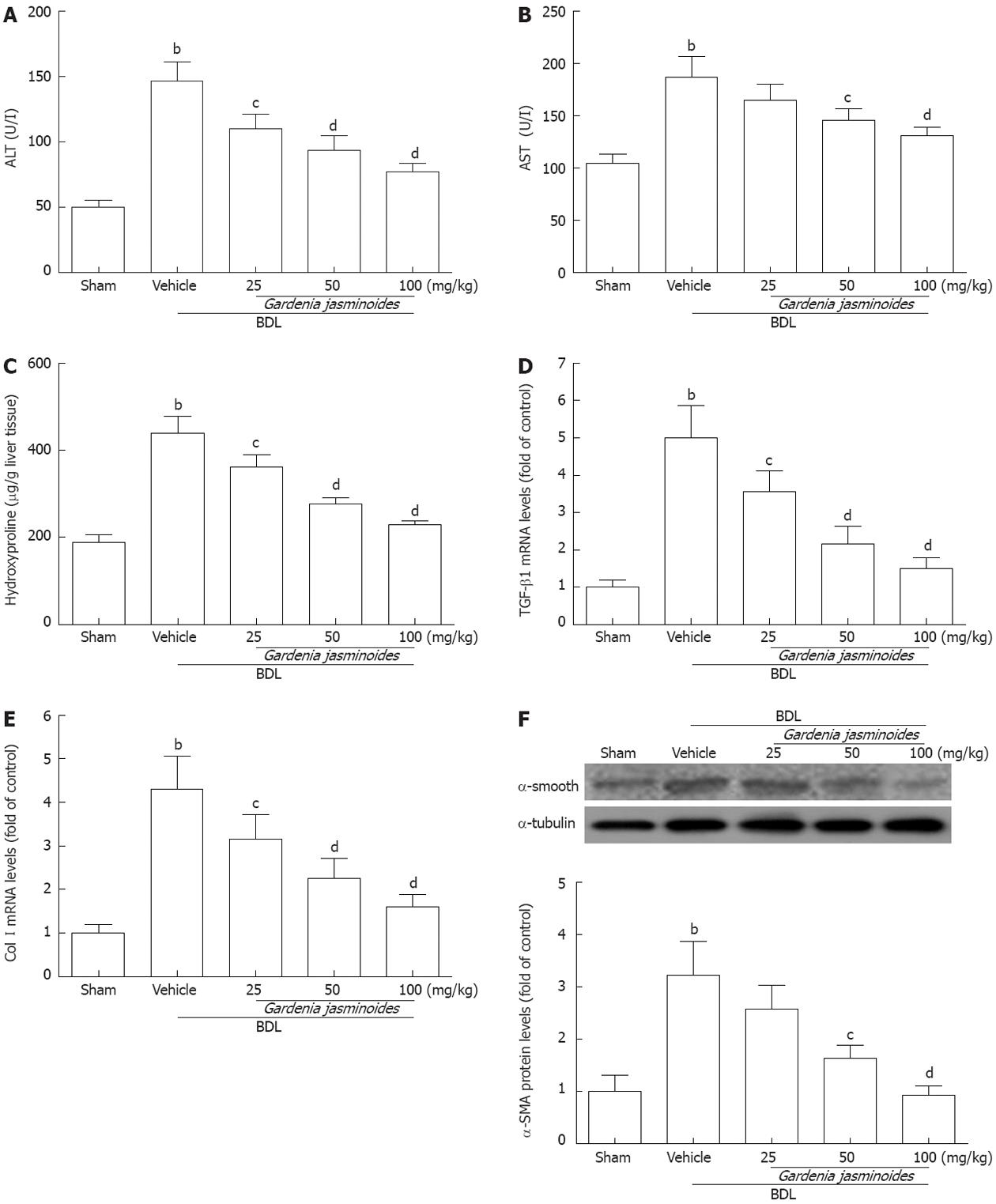
Figure 2 Biochemical and fibrotic gene expression in bile duct ligation rats.
Gardenia jasminoides significantly improved liver function and reduced the expression of liver fibrosis marker genes from rats submitted to bile duct ligation (BDL) or sham-operated rats treated with vehicle or Gardenia jasminoides. A: Serum levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT); B: Serum levels of aspartate aminotransferase (AST); C: Liver hydroxyproline content; D, E: Liver mRNA expression of transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) (D) and collagen type I(Col I) (E); F: Liver protein expression of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) detected by Western blotting. bP < 0.01 vs sham; cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01 vs BDL + vehicle (n = 8).
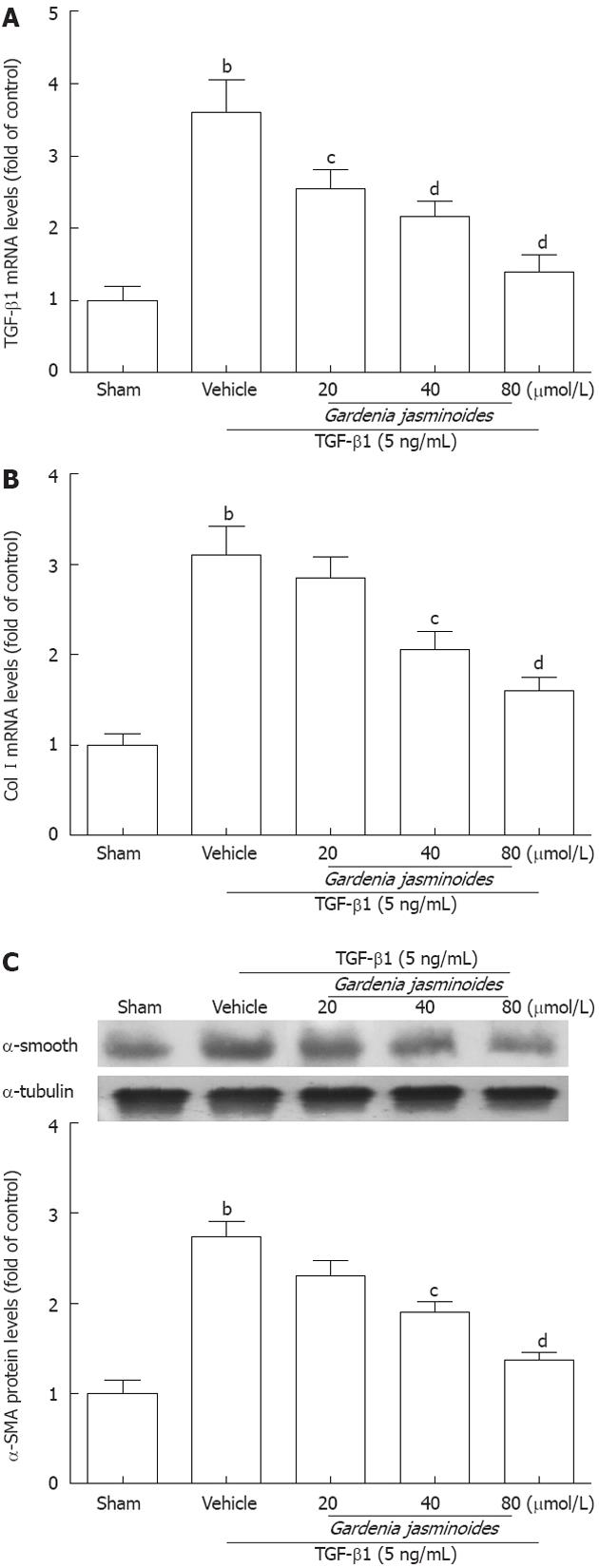
Figure 3 Gardenia jasminoides significantly reduced the expression of fibrotic marker genes in a human hepatic stellate cells line.
Cells were exposed to transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) (5 ng/mL) in combination with the indicated concentrations of Gardenia jasminoides or vehicle for 24 h. A: mRNA expression of TGF-β1 in LX-2 cells; B: mRNA expression of collagen type I(Col I) in LX-2 cells; C: Western blotting analysis of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) expression in LX-2 cells. bP < 0.01 vs sham; cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01 vs TGF-β1 + vehicle (n = 3).
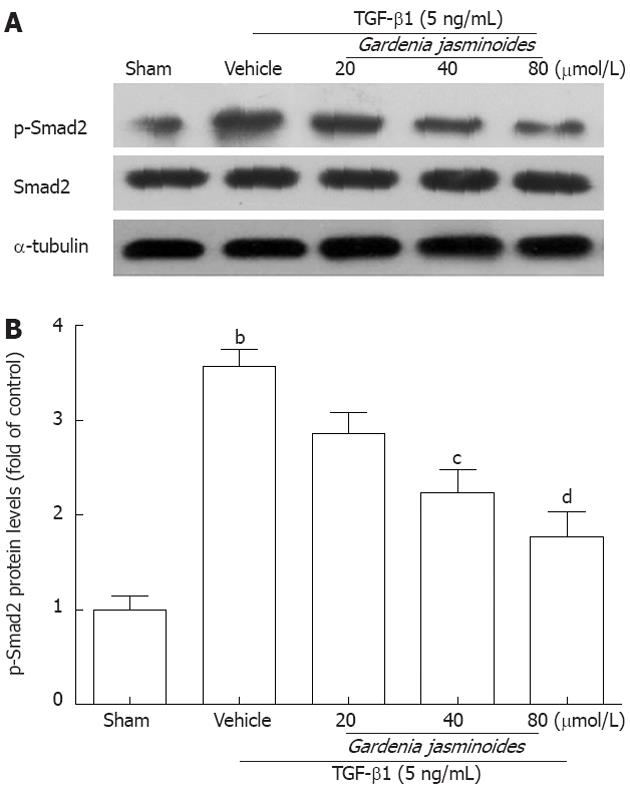
Figure 4 Gardenia jasminoides significantly reduced transforming growth factor-β1-induced Smad2 phosphorylation and Smad2 protein expression in LX-2 cells.
Cells were exposed to transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) (5 ng/mL) in combination with the indicated concentrations of Gardenia jasminoides or vehicle for 24 h. The expression of p-Smad2 and Smad2 in LX-2 cells was evaluated by Western blotting. bP < 0.01 vs sham; cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01 vs TGF-β1 + vehicle (n = 3).
-
Citation: Chen YH, Lan T, Li J, Qiu CH, Wu T, Gou HJ, Lu MQ.
Gardenia jasminoides attenuates hepatocellular injury and fibrosis in bile duct-ligated rats and human hepatic stellate cells. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(48): 7158-7165 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i48/7158.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i48.7158