Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2012; 18(47): 7093-7099
Published online Dec 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i47.7093
Published online Dec 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i47.7093
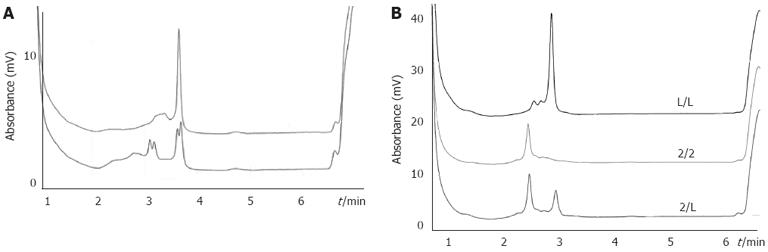
Figure 1 Typical denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography elution profiles for different genotypes.
A: Representative denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography (DHPLC) profiles for different allelic polymerase chain reaction products containing the interleukin-1B (IL-1B)-311 C/T polymorphism site. In the first DHPLC, the CT genotype (lower panel) was discriminated from homozygous (upper panel). To determine the CC or TT genotype, the second DHPLC was run for the homozygous DNA mixed with a DNA sample known as the CC genotype. The profile of the CC genotype was unaltered, while that of the TT genotype changed into the same as the lower panel; B: DHPLC elution profiles of IL-1RN and IL-1RN variable number of identical tandem repeats were determined by elution time and base pair number of the fragment.
- Citation: Zhao JD, Geng PL, Li ZQ, Cui S, Zhao JH, Wang LJ, Li JZ, Ji FX, Li GY, Shen GS, Lin MZ, Shen CF, Cao CZ. Associations between interleukin-1 polymorphisms and gastric cancers among three ethnicities. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(47): 7093-7099
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i47/7093.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i47.7093