Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2009; 15(46): 5871-5874
Published online Dec 14, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.5871
Published online Dec 14, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.5871
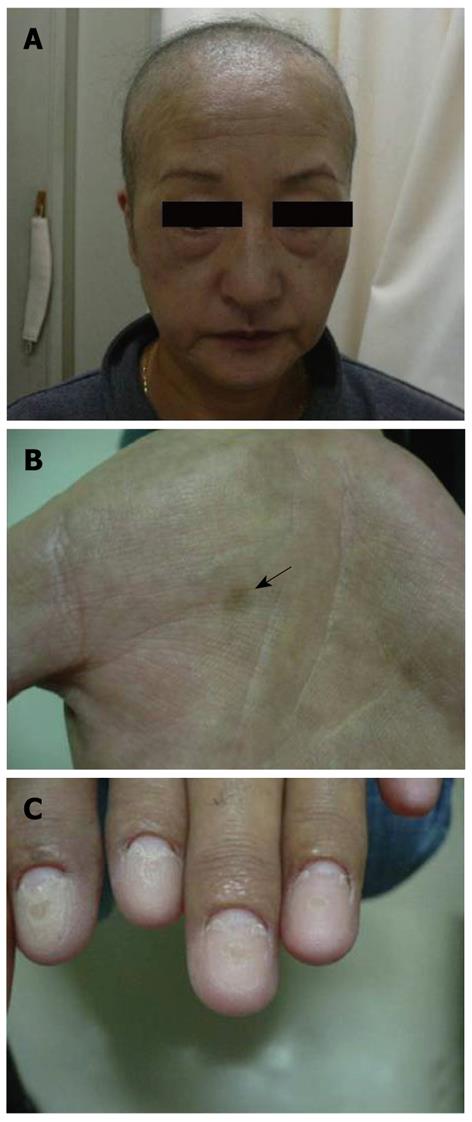
Figure 1 Physical findings in our case at her first visit.
A: Partial loss of the capillus and supercilia; B: Blackish brown pigmentation in both palms (black arrow); C: Atrophic nail change.
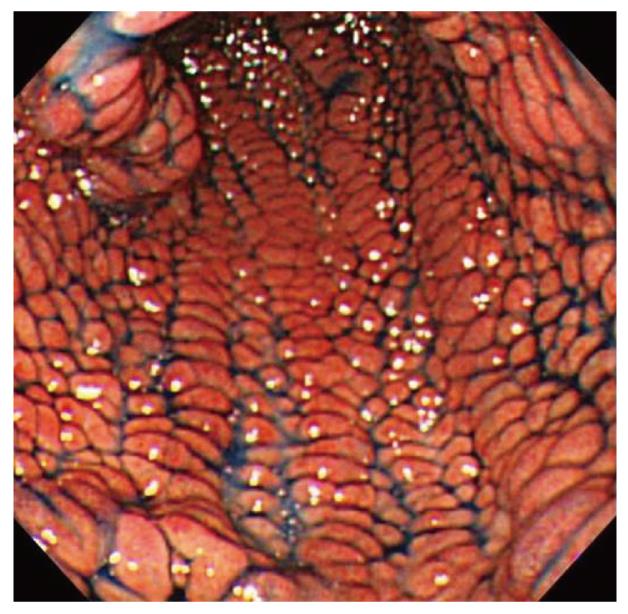
Figure 2 Esophagogastroduodenoscopy.
Red and edematous granular polyps with giant folds, the so-called red-carpet-like polyposis of the stomach before treatment.
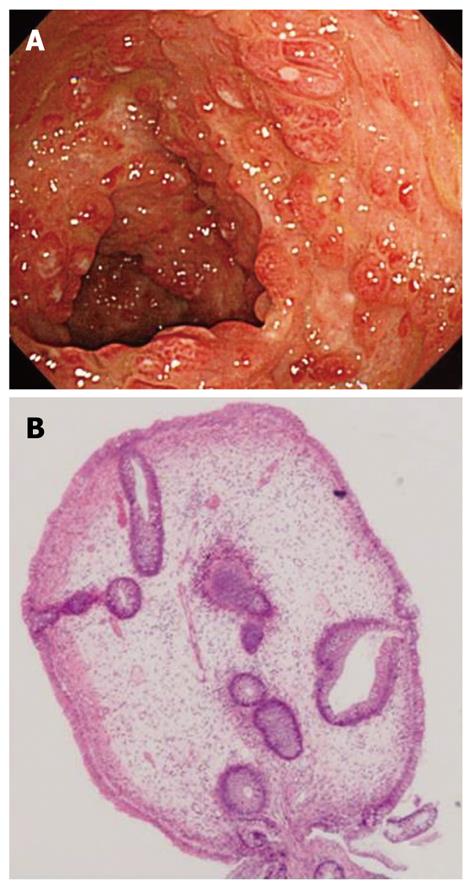
Figure 3 Colonoscopy (CS) findings.
A: Numerous, dense, red polyps throughout the colon and rectum; B: Biopsy specimen from colon displaying cystic dilation of crypts and edematous stroma with inflammatory cell infiltration before treatment (HE, × 100).
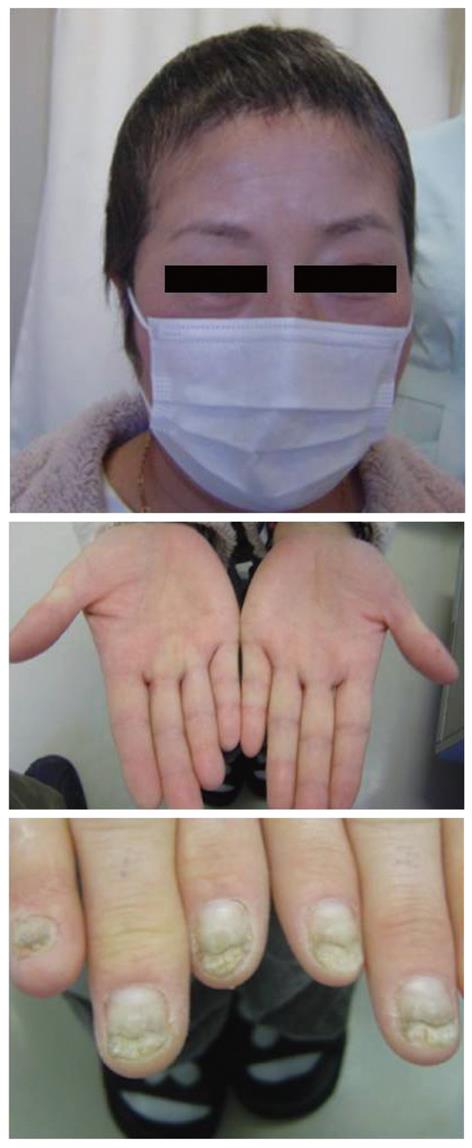
Figure 4 Clinical manifestations of the patient after treatment.
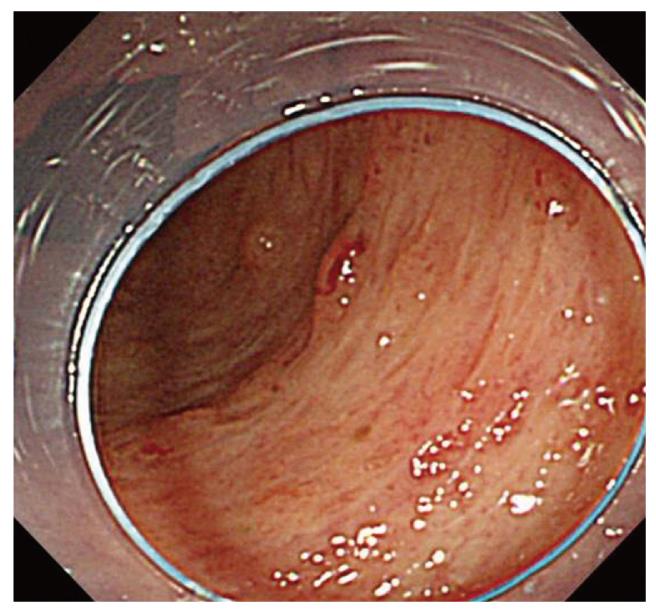
Figure 5 CS image after treatment.
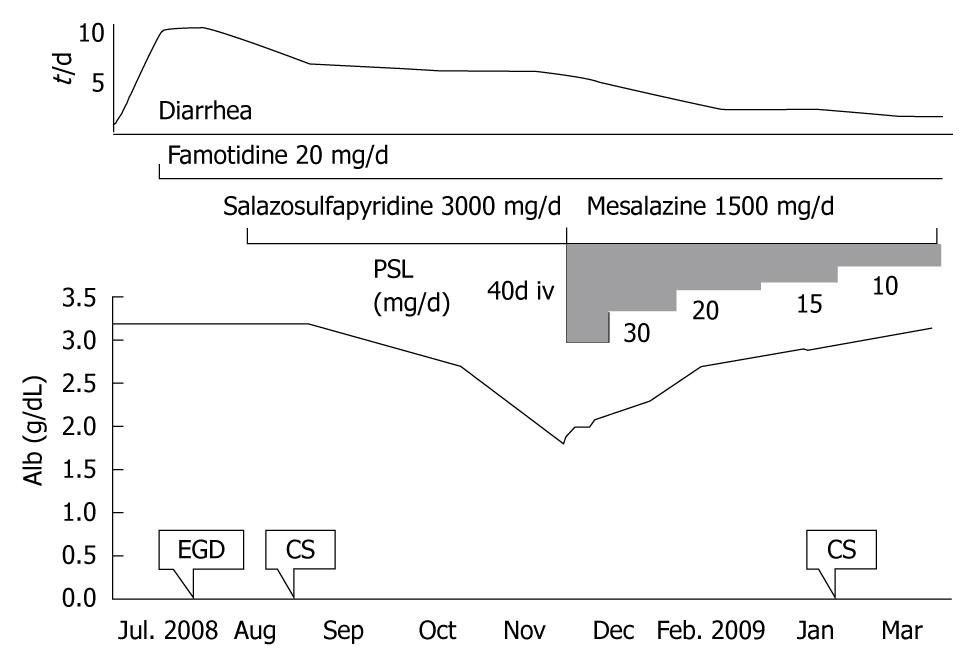
Figure 6 Clinical course of the patient.
- Citation: Suzuki R, Irisawa A, Hikichi T, Takahashi Y, Kobayashi H, Kumakawa H, Ohira H. Cronkhite-Canada syndrome associated with myelodysplastic syndrome. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(46): 5871-5874
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i46/5871.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.5871