Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Psychiatry. Apr 19, 2023; 13(4): 141-148
Published online Apr 19, 2023. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v13.i4.141
Published online Apr 19, 2023. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v13.i4.141
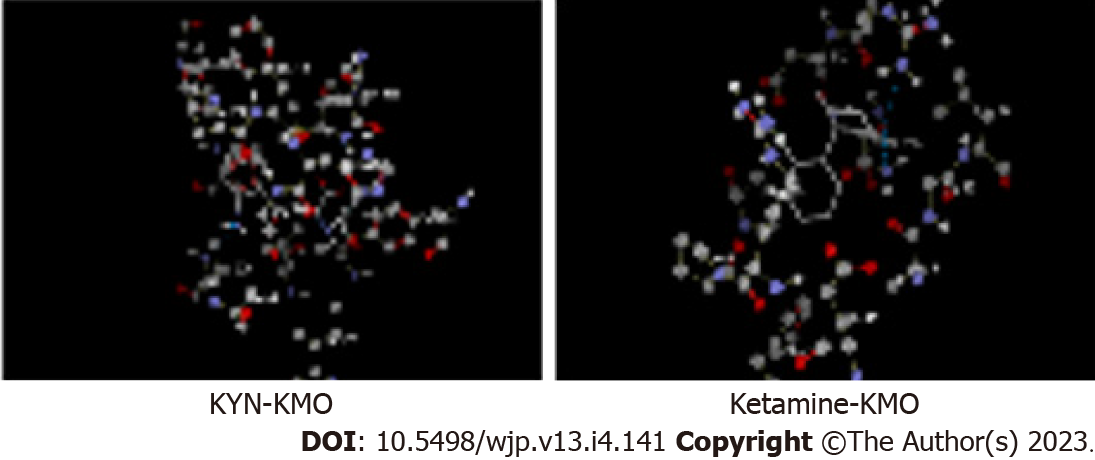
Figure 2 Molecular docking of kynurenine and ketamine to kynurenine monooxygenase.
Docking was performed using the Molegro virtual Docker software as described previously[16,17], but with kynurenine monooxygenase. With kynurenine (top), the best scored docking solution of 5y66 with the reference ligand, amino acids in the active site are presented in ball and stick with element colour and ligand is presented in thick lines with element colour (where carbon is grey, oxygen is red, nitrogen is blue, sulphur is yellow and hydrogen is white). Blue lines represent the hydrogen bonds in between the ligand and the active site of 5y66. Docking parameters were as follows: Kynurenine: Molecular weight (207.206), docking score (-95.4662), re-rank score (-81.6652), root mean square deviation (RMSD) (2.19513), torsion (4), H-bond (-6.03152). Amino acid residues at the kynurenine monooxygenase (KMO) active site are: Gly321, IIe224, Phe319, Met373, His320, Ala56, Leu226, Phe319, ligand binding amino acid residues are: Tyr404, His320, and Leu226. With ketamine (bottom), molecular weight (237.725), docking score (-81.8059), re-rank score (-65.0284), RMSD (zero), torsion (2), H-bond (-0.0342033). Amino acid residues at the KMO active site are: Asp112, Arg39, Gly16, Ala15, Glu37, Phe131, Arg111, Arg100, ligand binding amino acid residues are: Asn 115, Arg111. KMO: Kynurenine monooxygenase; KYN: Kynurenine.
- Citation: Badawy AAB, Dawood S, Bano S. Kynurenine pathway of tryptophan metabolism in pathophysiology and therapy of major depressive disorder. World J Psychiatry 2023; 13(4): 141-148
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v13/i4/141.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v13.i4.141