Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Psychiatr. Oct 19, 2021; 11(10): 681-695
Published online Oct 19, 2021. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v11.i10.681
Published online Oct 19, 2021. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v11.i10.681
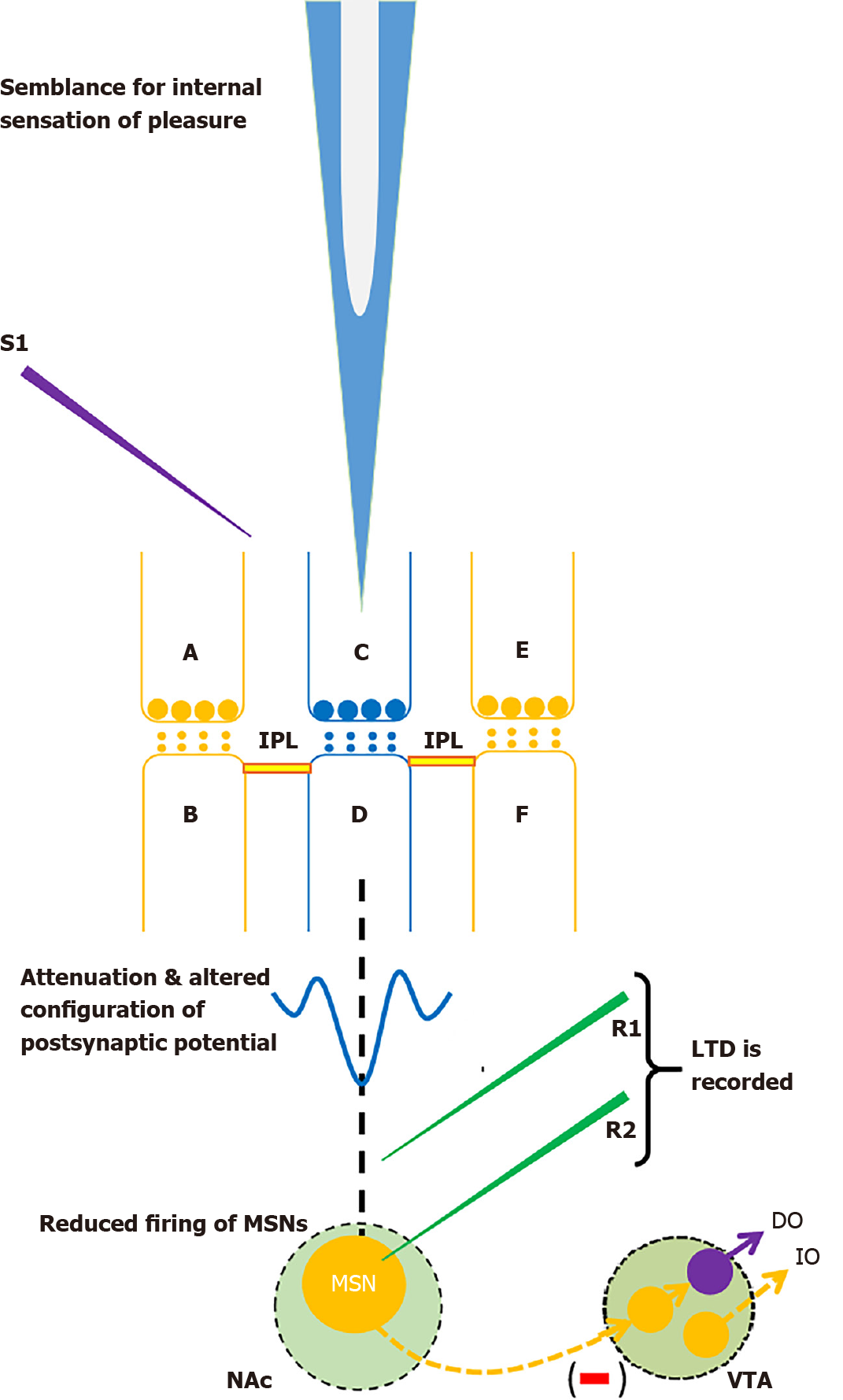
Figure 5 Nucleus accumbens circuitry that matches with constraints from several findings.
Spines B and F belonging to different medium spiny neurons (MSNs) synapse with inhibitory inputs arriving through presynaptic terminals A and E respectively. Spine D on a third MSN synapses with excitatory input arriving through presynaptic terminal C. Two inter-postsynaptic functional LINKs (IPLs) are formed between spines B, D and F. These IPLs between spines that synapse with excitatory and inhibitory inputs lead to mixing of depolarization on the spines that synapse with excitatory input and hyperpolarization on the spines that synapse with inhibitory inputs. This leads to alternation of configuration of the net postsynaptic potentials as shown in a trace. Net semblance from a large number of inter-LINKed spines is expected to generate a special semblance for internal sensation of pleasure. Due to propagation of hyperpolarization, sum of potentials reaching many MSNs may not cross the threshold for firing, which leads to reduced firing of MSNs. A specific stimulation pattern applied at the presynaptic region using stimulating electrode S1 results in the formation of a large number of the above-mentioned types of IPLs in a time-dependent manner (inferred from delay between stimulation and long-term depression (LTD) induction[17,18]) resulting in LTD recorded from either recording electrode R1 (extracellular field recording) or R2 (whole-cell recording). Two inhibitory inputs to MSN and one inhibitory output from MSN are shown in orange. Excitatory synapse is shown in blue. Dopaminergic neuron of ventral tegmental area is shown in violet. DO: Dopaminergic output; IO: Inhibitory output; VTA: Ventral tegmental area.
- Citation: Vadakkan KI. Framework for internal sensation of pleasure using constraints from disparate findings in nucleus accumbens. World J Psychiatr 2021; 11(10): 681-695
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v11/i10/681.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v11.i10.681