Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
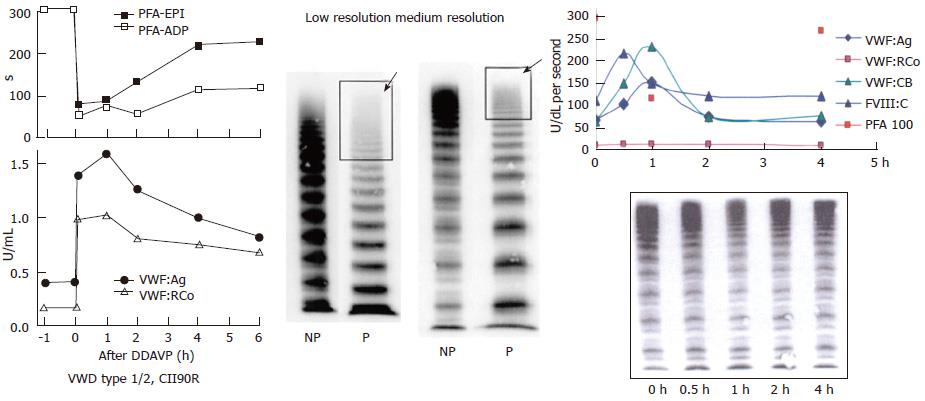
Figure 10 Von Willebrand disease 2E (left) and von Willebrand disease 2M (right).
Left: Dominant VWD type 2E: multimerization defect with loss of large VWF multimers to W1120S mutation in the A3 domain. DDAVP induced transient correction of PFA-100 closure time and restricted increase of VWF parameters from around 0.20-0.40 U/mL to around 1.0 U/mL. In VWD type 2E, VWF multimeric pattern is characterized by a lack or relative decrease of large multimers and the absence of the outer sub-band of the normal triplet structure. Medium resolution gel according to Budde et al[12]. Right: VWD 2M: Poor response of VWF:RCo to DDAVP, normal VWF multimers before and after DDAVP and good responses of FVIII, VWF:Ag and VWF:CB followed by shortened half-life time indicating rapid clearance defect of the FVIII-VWF complex on top of loss of VWF:RCo function in VWD 2M[20]. Medium resolution gel according to Budde et al[12]. VWD: Von Willebrand disease; VWF: Von Willebrand factor; DDAVP: Desmopressin; PFA-EPI: Platelet function analyzer, epinephrin; PFA-ADP: Platelet function analyser adenosine di-phosphate; NP: Normal plasma; P: Patient.
- Citation: Michiels JJ, Batorova A, Prigancova T, Smejkal P, Penka M, Vangenechten I, Gadisseur A. Changing insights in the diagnosis and classification of autosomal recessive and dominant von Willebrand diseases 1980-2015. World J Hematol 2016; 5(3): 61-74
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-6204/full/v5/i3/61.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5315/wjh.v5.i3.61