Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
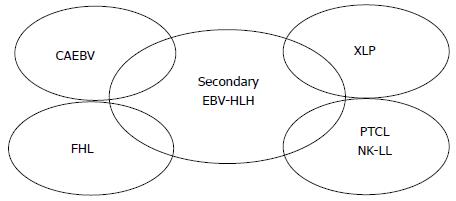
Figure 1 Underlying or other diseases overlapping with Epstein-Barr virus-related hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis.
Although the majority of cases of EBV-HLH due to secondary HLH develop without any apparent immunodeficiency, some cases may develop in association with CAEBV (see also Figure 2), XLP (type 1 or type 2), FHL (types 2-5), or EBV-positive peripheral T cell lymphoma, or NK cell leukemia or lymphoma. EBV-HLH: Epstein-Barr virus-related hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis; CAEBV: Chronic active EBV infection; XLP: X-linked lymphoproliferative disease; FHL: Familial HLH; NK: Natural killer.
- Citation: Imashuku S. Treatment of Epstein-Barr virus-related hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: Study protocol of a prospective pilot study. World J Hematol 2015; 4(4): 69-75
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-6204/full/v4/i4/69.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5315/wjh.v4.i4.69