Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Diabetes. Aug 15, 2023; 14(8): 1226-1233
Published online Aug 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i8.1226
Published online Aug 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i8.1226
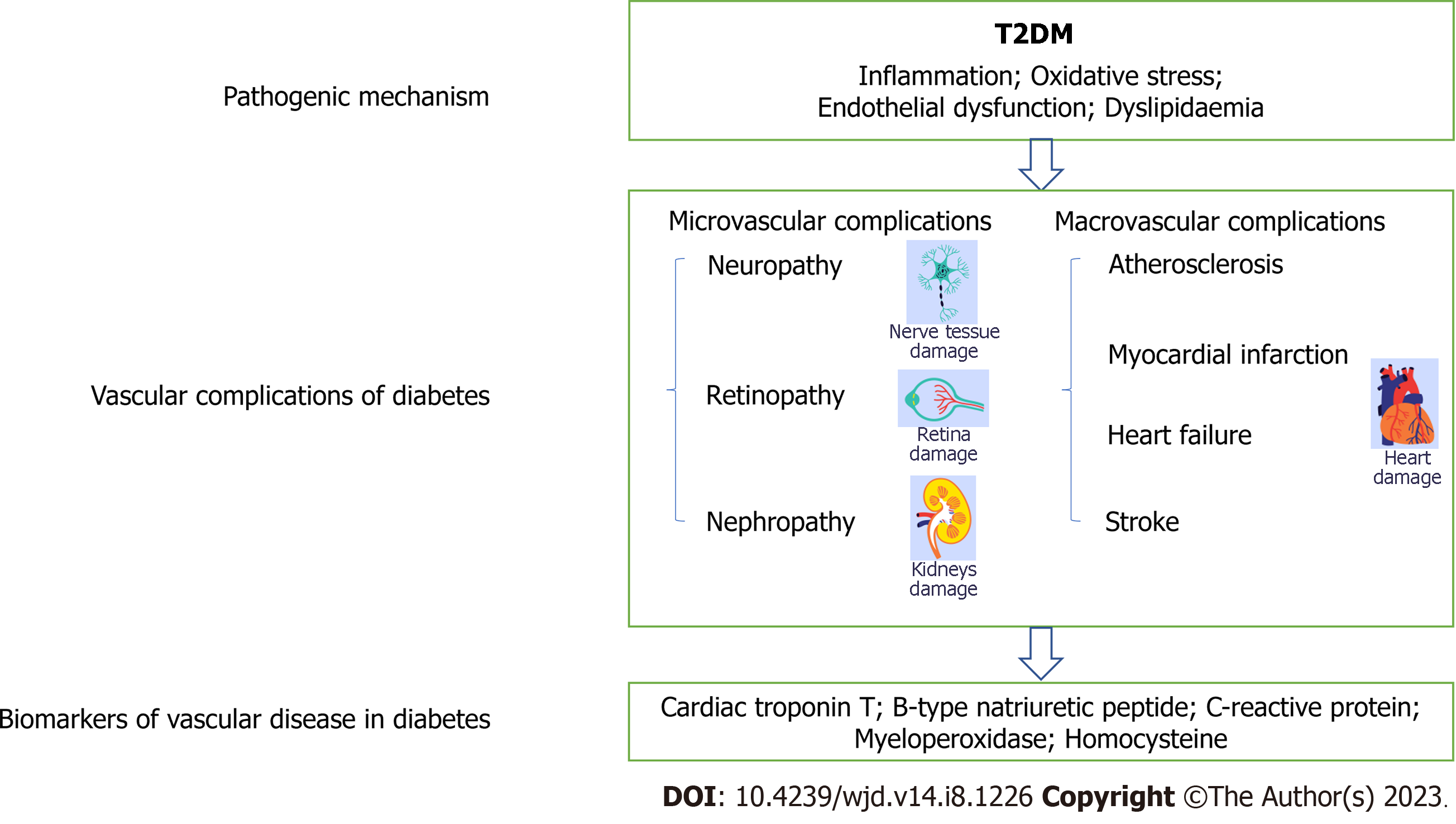
Figure 1 A brief introduction to vascular-related complications of diabetes and their common diagnostic markers.
Common pathogenic mechanisms for macrovascular and microvascular complications include inflammation, oxidative stress, abnormal lipid metabolism and endothelial dysfunction. Cardiac troponin T is a marker of impaired microvascular circulation, which can affect myocardial blood supply and vascular endothelial cell function, resulting in the release of large amounts of troponin in the blood. B-type natriuretic peptide regulates blood pressure, blood volume, sodium balance, and glucose and fat metabolism. C-reactive protein is a marker of early myocardial injury and nonspecific inflammation. Myeloperoxidase is involved in the regulation of inflammatory response and oxidative stress in vivo and can induce acute coronary syndrome. Homocysteine is a marker of impaired neurons and vascular endothelial cells that induces oxidative stress and excessive proliferation of vascular endothelial cells. T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Image from FreePik.
- Citation: Cheng MK, Guo YY, Kang XN, Zhang L, Wang D, Ren HH, Yuan G. Advances in cardiovascular-related biomarkers to predict diabetic peripheral neuropathy. World J Diabetes 2023; 14(8): 1226-1233
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v14/i8/1226.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v14.i8.1226