Published online Feb 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i4.838
Peer-review started: August 25, 2020
First decision: November 8, 2020
Revised: November 19, 2020
Accepted: December 10, 2020
Article in press: December 10, 2020
Published online: February 6, 2021
Processing time: 145 Days and 4.5 Hours
Gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) is the most common etiology of gastroduodenal intussusception. Although gastroduodenal intussusception caused by gastric GIST is mostly treated by surgical resection, the first case of gastroduodenal intussusception caused by gastric GIST was treated by endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) in Japan in 2017.
An 84-year-old woman presented with symptoms of postprandial fullness with nausea and occasional vomiting for a month. Initially, she visited a local clinic for help, where abdominal sonography revealed a space-occupying lesion around the liver, so she was referred to our hospital for further confirmation. Abdominal sonography was repeated, which revealed a mass with an alternating concentric echogenic lesion. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) was performed under the initial impression of gastric cancer with central necrosis and showed a tortuous distortion of gastric folds down from the lesser curvature side to the duodenal bulb with stenosis of the gastric outlet. EGD was barely passed through to the 2nd portion of the duodenum and a friable ulcerated mass was found. Several differential diagnoses were suspected, including gastroduodenal intussusception, gastric cancer invasion to the duodenum, or pancreatic cancer with adherence to the gastric antrum and duodenum. Abdominal computed tomography for further evaluation was arranged and showed gastroduodenal intussusception with a long stalk polypoid mass 5.9 cm in the duodenal bulb. Under the impression of gastroduodenal intussusception, ESD was performed at the base of the gastroduodenal intussusception; unfortunately, a gastric perforation was found after complete resection was accomplished, so gastrorrhaphy was performed for the perforation and retrieval of the huge polypoid lesion. The gastric tumor was pathologically proved to be a GIST. After the operation, there was no digestive disturbance and the patient was discharged uneventfully on the 10th day following the operation.
We present the second case of gastroduodenal intussusception caused by GIST treated by ESD. It is also the first case report of gastroduodenal intussusception by GIST in Taiwan, and endoscopic reduction or resection is an alternative treatment for elderly patients who are not candidates for surgery.
Core Tip: This is the first case report of gastroduodenal intussusception caused by gastrointestinal stromal tumor in Taiwan and endoscopic reduction or resection is an alternative treatment for elderly patients who are not candidates for surgery.
- Citation: Hsieh YL, Hsu WH, Lee CC, Wu CC, Wu DC, Wu JY. Gastroduodenal intussusception caused by gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumor: A case report and review of the literature. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(4): 838-846
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i4/838.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i4.838
Gastric outlet obstruction (GOO) is a clinical syndrome characterized by epigastric abdominal pain and postprandial vomiting due to mechanical obstruction. Benign disease such as peptic ulcer disease was responsible for 90% of cases until the late 1970s[1]. With the decline in the incidence of peptic ulcer disease, it is estimated that 50-80% of all cases of GOO are attributable to malignancies. Distal gastric cancer remains a relatively common cause of malignant GOO, accounting for up to 35% of GOO cases[2]. Gastro-duodenal intussusception is a rare cause of GOO in adults, and it is typically caused by a pathological leading point, malignant in over one half of cases[3]. Herein, we report an 84-year-old woman with gastroduodenal intussusception caused by a gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST).
An 84-year-old woman presented with symptoms of postprandial fullness with nausea and occasional vomiting for a month.
The patient suffered from persistent hematemesis and tarry stool complicated with orthostatic hypotension over the past 2-3 years. She complained about abdominal distress, abdominal fullness, nausea, and vomiting in recent one month. She first visited a local clinic, where abdominal sonography showed a liver tumor.
The patient had a history of hypertension, chronic kidney disease, and hepatitis B virus infection.
The patient denied any personal history of alcohol, betel nuts, and cigarette consumption. She also denied travel, contact, and cluster history in recent 6 mo. As a housewife, she did not have any occupational history. Regarding her family history, she had one elder brother and four younger sisters. All of them did not have any malignancy history.
On the physical examination, the patient’s consciousness was alert (E4V5M6); her conjunctiva was not pale; she had anicteric sclera; her chest had symmetric movement with respiration; Her breath sound was bilaterally clear; and she had regular heart beat, flat abdomen, normoactive bowel sound, no muscle guarding, no tenderness, no rebound pain, and no pitting edema.
The results of laboratory examinations are shown in Table 1.
| Result | Reference range | |
| WBC | 9.37 | 4.4-11.3 × 109 L |
| Hb | 9.1 | 12.3-15.3 g/dL |
| Plt | 302 | (160-370) × 1000/uL |
| CRP | 2.04 | mg/L |
| Crea | 1.53 | mg/dL |
| BUN | 25.9 | mg/dL |
| Na | 139 | mmol/L |
| K | 3.9 | mmol/L |
| GOT | 16 | IU/L |
| GPT | 11 | IU/L |
| INR | 0.97 | |
| PTT | 24.3 | sec |
| CEA | 3.58 |
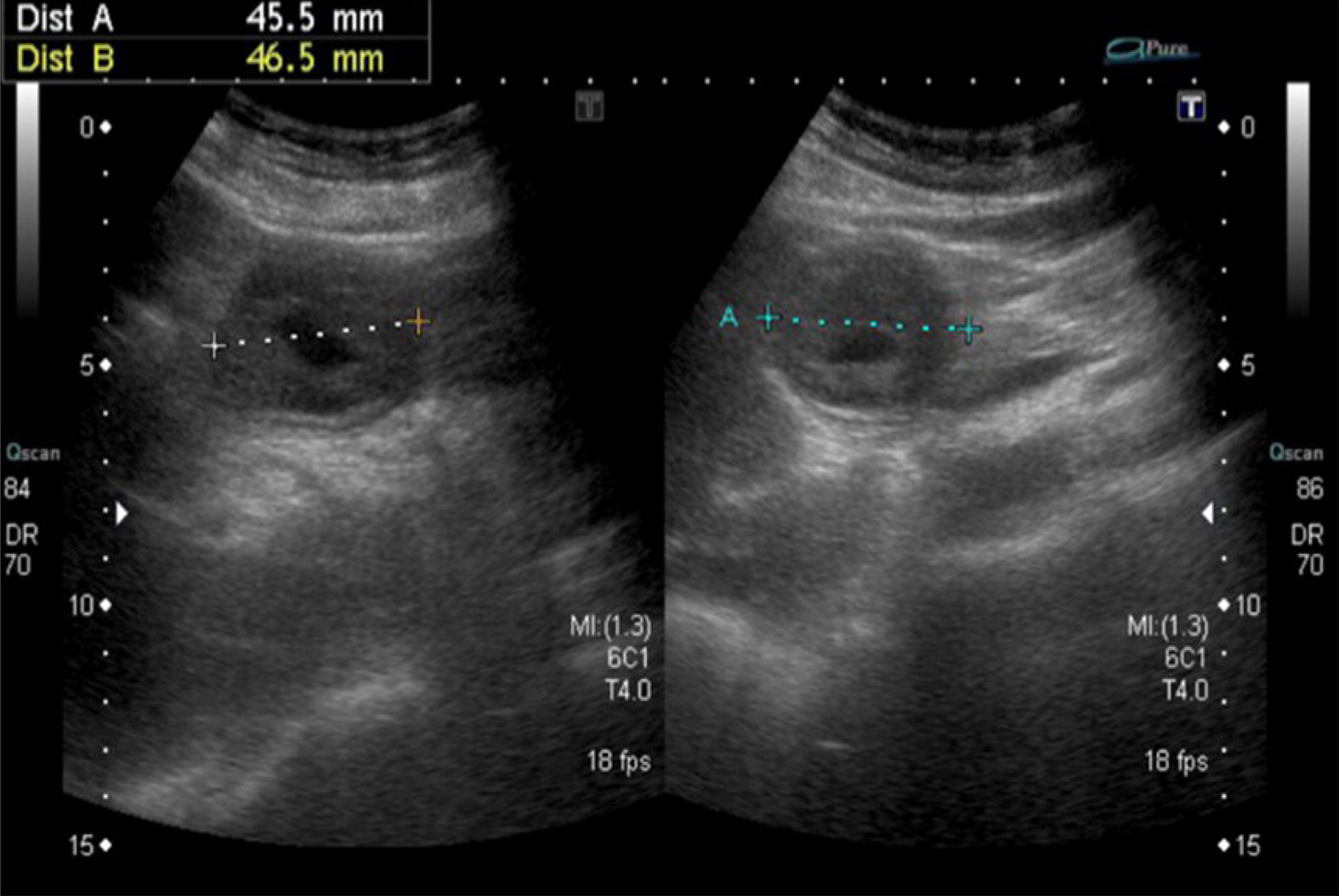
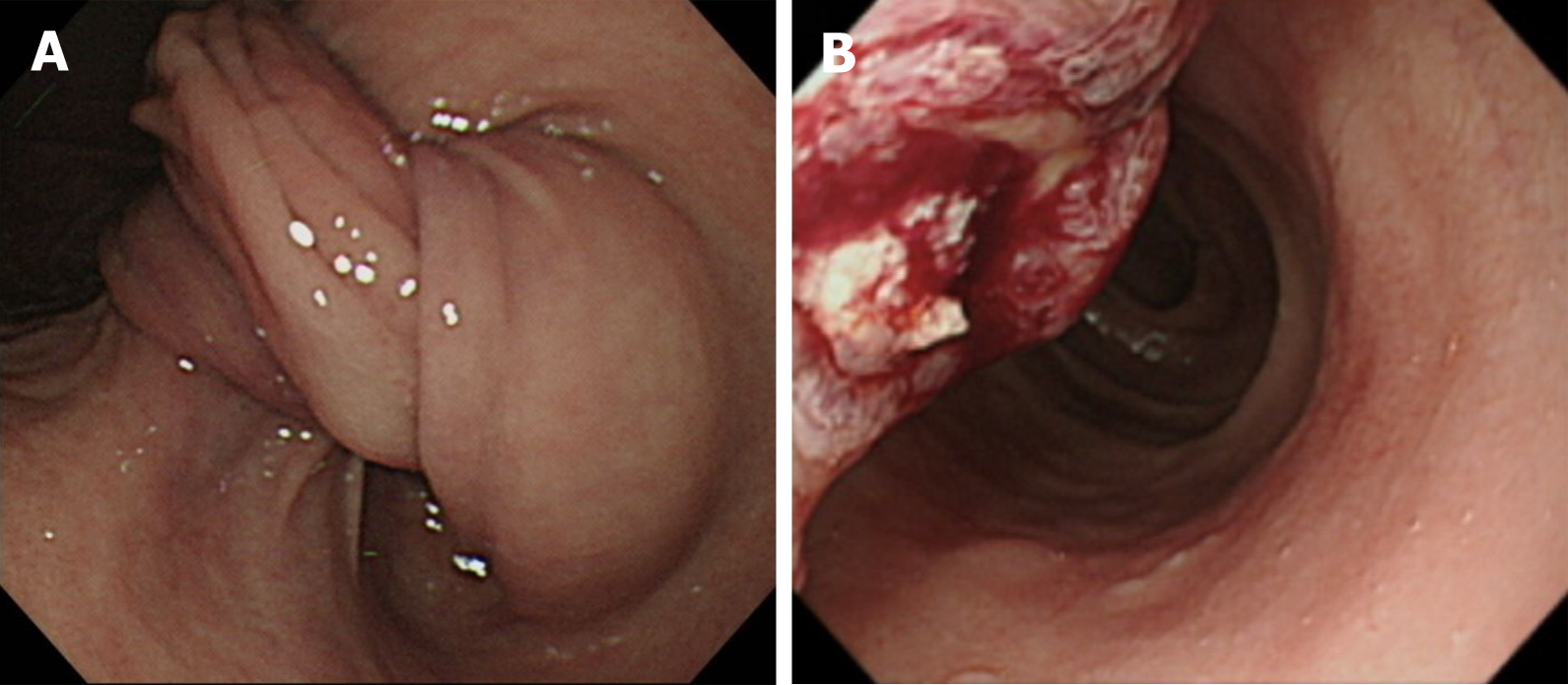
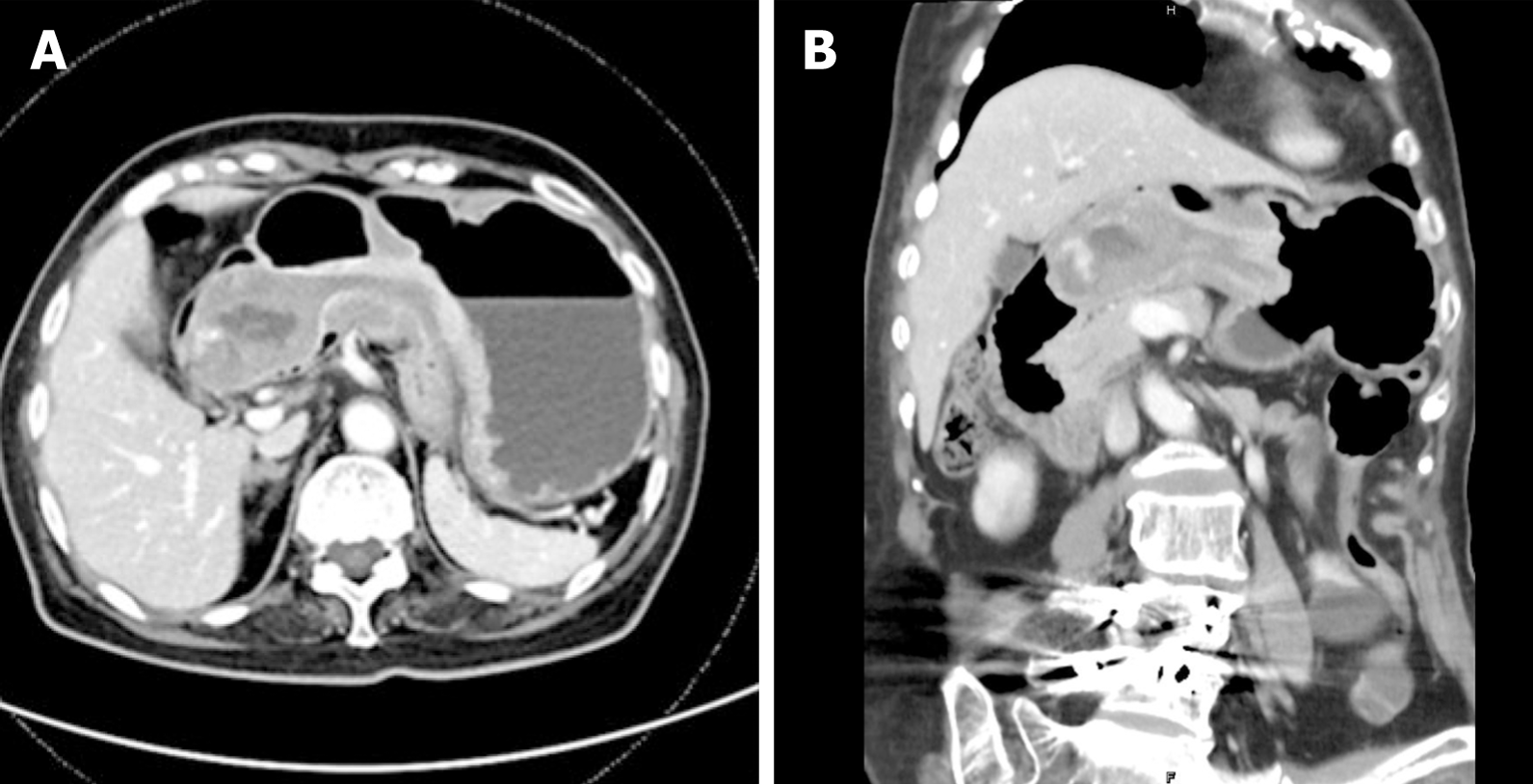
Abdominal sonography was repeated, which revealed a mass with an alternating concentric echogenic lesion (Figure 1). EGD was performed under the initial impression of gastric cancer with central necrosis and showed a tortuous distortion of gastric folds down from the lesser curvature side to the duodenal bulb with stenosis of the gastric outlet (Figure 2A). EGD was barely passed through to the 2nd portion of the duodenum and a friable ulcerated mass was found (Figure 2B). Several differential diagnoses were suspected, including gastroduodenal intussusception, gastric cancer invasion to the duodenum, or pancreatic cancer with adherence to the gastric antrum and duodenum. Abdominal computed tomography for further evaluation was arranged and showed gastroduodenal intussusception with a long stalk polypoid mass (5.9 cm) in the duodenal bulb (Figure 3).
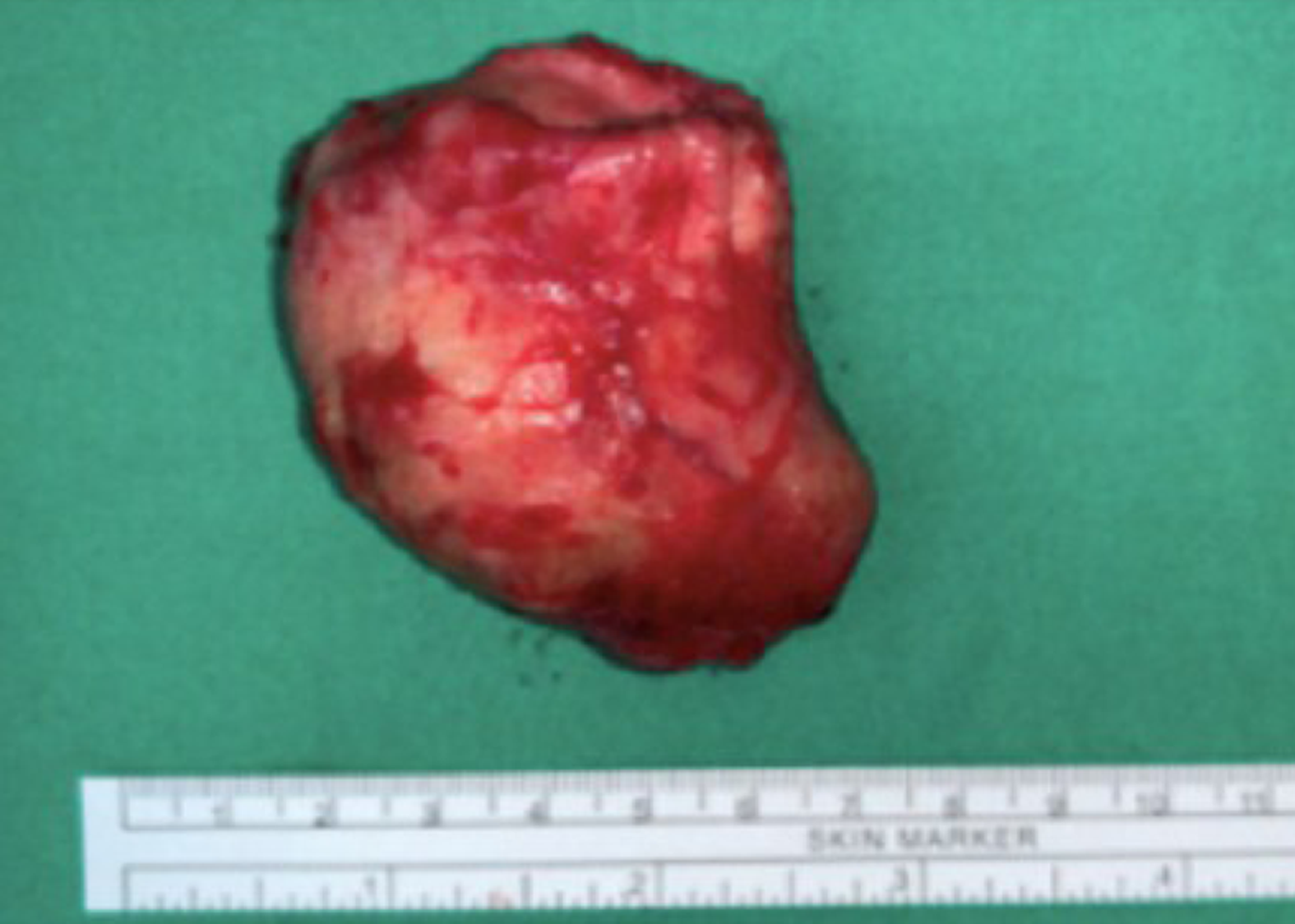
Under the impression of gastroduodenal intussusception, endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) was performed at the base of the gastroduodenal intussusception; unfortunately, a gastric perforation was found after complete resection was accomplished, so gastrorrhaphy was performed for the perforation and retrieval of the huge polypoid lesion (Figure 4).
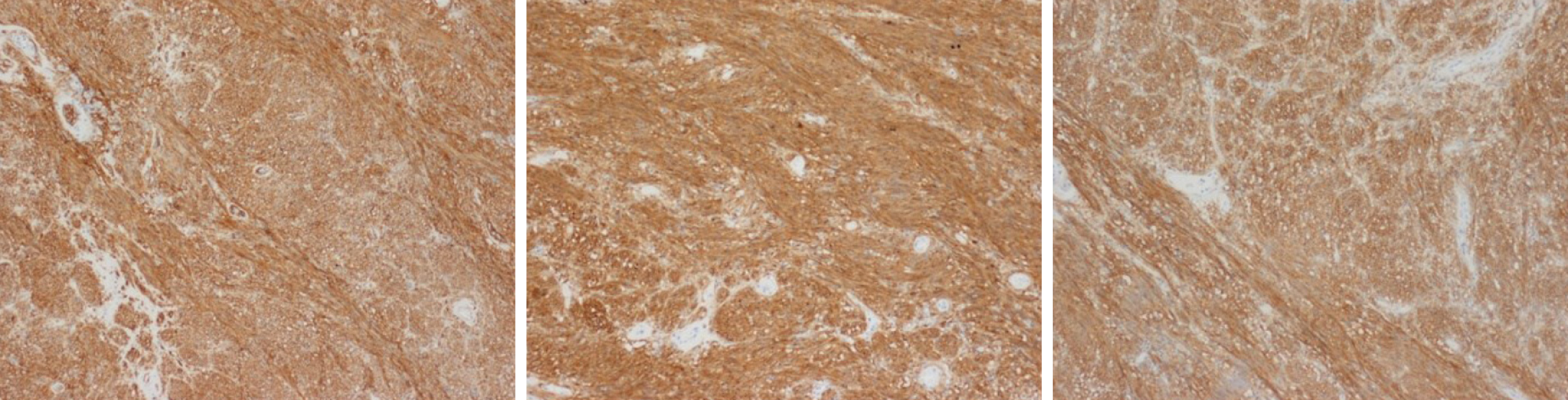
The gastric tumor was pathologically diagnosed as a GIST (Figure 5).
Endoscopic resection and laparotomy were performed for gastric tumor removal and gastrorrhaphy.
The patient had a complete remission.
Regarding gastrointestinal obstruction in adults, symptoms are variable depending on the locations of obstruction, which range from small bowel obstruction followed by large intestine and gastric outlet complications[4]. It is mostly caused by reasons such as adhesion, malignancy, and volvulus. In adults, intussusception accounts merely for 1% of mechanical gastrointestinal obstructions, representing a very rare cause[5]. The symptoms of intussusception are nausea, vomiting, gastrointestinal bleeding, change in bowel habits, constipation, or abdominal pain[6]. Ischemic change and peritonitis seldom occur but represent major critical complications of intussusception. In adults, intussusception is usually the result of lesions, including scar-like tissue in the intestine (adhesions) and prior surgery such as gastrointestinal bypass surgery for weight control, polyp, or tumor. The presenting case suffering from partial gastric outlet obstruction by gastroduodenal intussusception was managed by ESD and gastrorrhaphy proved that is was caused by a GIST.
GIST accounts for around 0.2% of all gastrointestinal tumors and occurs anywhere along the gastrointestinal tract, but most commonly in the stomach (40%-60%) and jejunum/ileum (25%-30%)[7]. GIST is typically asymptomatic or has nonspecific symptoms (i.e., early satiety and bloating), unless they ulcerate, bleed, or grow large enough to cause pain or obstruction. Conceivably, gastroduodenal intussusception caused by GIST most commonly presents with nonspecific symptoms of acute or intermittent abdominal pain with vomiting lasting from days to several months[8]. By reviewing the relevant literature, we found 41 cases of gastroduodenal intussusception within the past 20 years (Table 2)[9-44]. Gastric GIST is the most common etiology and accounts for more than half of these cases, with the mean size of the GIST being 54.8 mm and the average age being 64.25 years (range, 29-95 years). Management of gastroduodenal intussusception included surgical intervention and endoscopic reduction in the past, and for the present case, endoscopic reduction of the inva-gination was tried but failed due to its large size (5.9 cm). Although gastroduodenal intussusception caused by gastric GIST is mostly treated by surgical resection, the first case of gastroduodenal intussusception caused by gastric GIST was treated by ESD in Japan in 2017[45], so ESD was also tried for this case with the result of complete resection although complicated with perforation. Finally, gastrorrhaphy repair and retrieval of the huge polypoid lesion were accomplished. Here we present the second case of gastroduodenal intussusception caused by GIST treated by ESD. It is also the first case report of gastroduodenal intussusception caused by GIST in Taiwan, and endoscopic reduction or resection is an alternative treatment for elderly patients who are not candidates for surgery.
| Ref. | Year | Age | Sex | Diagnosis | Pathology report | Management | Size |
| Nakagawara et al[9] | 2000 | 50 | F | EGD | Gastric heterotopia | Endoscopic polypectomy | 30 mm × 36 mm |
| Sankaranunni et al[10] | 2001 | 48 | M | CT | Gastric lipoma | Laparotomy | NA |
| Harrison et al[11] | 2001 | 76 | M | EGD | Leiomyoma | Laparotomy | 50 mm × 42 mm |
| Mouës et al[12] | 2002 | EGD and CT | Gastric lipoma | Laparotomy | 50 mm × 100 mm | ||
| Crowther et al[13] | 2002 | 59 | F | CT | GIST | Partial gastrectomy | 60 mm |
| Vinces et al[14] | 2005 | 72 | M | Laparoscopy | Gastric lipoma | Exploratory laparotomy | NA |
| Vinces et al[14] | 2006 | Gastric lipoma | NA | ||||
| Juglard et al[15] | 2006 | Ménétrier’s disease | NA | ||||
| Adjepong et al[16] | 2006 | 84 | M | CT | GIST | Laparoscopic Billroth II partial gastrectomy | 40 mm × 30 mm |
| Samamé et al[17] | 2007 | GIST | NA | ||||
| Shum et al[18] | 2007 | 34 | F | CT | GIST | Partial gastrectomy | 50 mm × 50 mm |
| Shum et al[18] | 2008 | 67 | M | Ultrasound and EGD | Gastric carcinoma | Surgical resection | 45 mm × 40 mm |
| Alamili al[19] | 2008 | CT | Duodenal lipoma | Surgical resection | NA | ||
| Siam et al[20] | 2008 | 29 | M | EGD | GIST | Partial Gastrectomy | 60 mm × 60 mm |
| Su et al[21] | 2009 | 24 | M | EGD | Gastric carcinoma (PJS) | Surgical resection | 30 mm |
| Hillenbrand et al[22] | 2009 | 42 | F | CT | Post banded gastroplasty | Surgical reduction | |
| Chan et al[23] | 2009 | 34 | F | CT | GIST | Laparoscopic wedge resection | 65 mm × 44 mm |
| Eom al[24] | 2011 | 73 | F | CT and EGD | Gastric carcinoma | Subtotal gastrectomy | 78 mm × 75 mm |
| Euanorasetr et al[25] | 2011 | Gastric carcinoma | Subtotal gastrectomy | NA | |||
| Gyedu et al[26] | 2011 | 59 | F | CT and US | GIST | Partial gastrectomy | 70 mm × 60 mm |
| Seok et al[27] | 2012 | 51 | M | CT and EGD | GIST | Gastric partial resection | 55 mm × 42 mm |
| Seok et al[27] | 2012 | 62 | F | EGD and CT | GIST | Billroth II partial gastrectomy | 52 mm × 35 mm |
| Wilson et al[28] | 2012 | 78 | F | CT | GIST | Laparoscopic wedge resection | 44 mm × 33 mm |
| Chen et al[29] | 2013 | 63 | F | CT and EGD | Gastric hamartomatous polyp | Endoscopic mucosal resection | NA |
| Rittenhouse et al[30] | 2013 | 52 | F | CT | GIST | Laparoscopic wedge resection | 50 mm × 50 mm |
| Chahla et al[31] | 2014 | 76 | M | CT | Gastric hyperplastic polyp | Endoscopic resection | < 30 mm |
| Khanna et al[32] | 2014 | 33 | M | CT and EGD | Brunner’s gland hamartoma | Duodenostomy and polypectomy | 35 mm × 70 mm |
| Kadowaki et al[33] | 2014 | 77 | F | Laparotomy | Gastric collision tumor | Gastrotomy followed by duodenotomy | 120 mm |
| Yang et al[34] | 2015 | 63 | M | CT | Gastric schwannoma | Conventional laparotomy | 55 mm × 48 mm |
| M S et al[35] | 2015 | 74 | M | CT | GIST | Partial gastrectomy | NA |
| Indiran et al[36] | 2015 | GIST | NA | ||||
| Yildiz et al[37] | 2016 | 85 | F | CT | GIST | Subtotal gastrectomy | 60 mm × 50 mm |
| Komatsubara et al[38] | 2016 | 90 | F | EGD | GIST | Wedge resection | 50 mm × 45 mm |
| Yamauchi et al[9] | 2017 | 95 | F | CT | GIST | Endoscopic submucosaldissection | 42 mm × 39 mm |
| Jameel et al[39] | 2017 | 65 | F | EGD and CT | GIST | Laparoscopic resection | 60 mm × 60 mm |
| Casimiro Pérez et al[40] | 2018 | 55 | M | EGD and CT | Gastric submucosal lipoma | Laparoscopic transgastric excision | 63 mm × 55 mm |
| Zhou et al[41] | 2018 | 69 | M | EGD and CT | GIST | Laparoscopic resection | 45 mm × 40 mm |
| Ssentongo et al[42] | 2018 | 85 | F | CT | GIST | Wedge resection | 25 mm × 25 mm |
| De et al[43] | 2018 | 42 | F | EGD | GIST | Surgical resection | 80 mm × 70 mm |
| Đokić et al[8] | 2019 | 62 | M | CT and US | GIST | Laparotomy resection | 75 mm × 55 mm |
| Suda et al[44] | 2019 | 81 | F | EGD and CT | Gastric carcinoma | Laparoscopic gastrectomy | 55 mm |
| Our case | 2020 | 84 | M | US and EGD and CT | GIST | Endoscopic submucosaldissection and surgical repair | 59 mm |
We present the second case of gastroduodenal intussusception caused by GIST treated by endoscopic submucosal dissection. It is also the first case report of gastroduodenal intussusception caused by GIST in Taiwan, and endoscopic reduction or resection is an alternative treatment for elderly patients who are not candidates for surgery.
Manuscript source: Unsolicited manuscript
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country/Territory of origin: Taiwan
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B, B
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: D'Orazi V, Ozen H S-Editor: Zhang L L-Editor: Wang TQ P-Editor: Zhang YL
| 1. | Shone DN, Nikoomanesh P, Smith-Meek MM, Bender JS. Malignancy is the most common cause of gastric outlet obstruction in the era of H2 blockers. Am J Gastroenterol. 1995;90:1769-1770. [PubMed] |
| 2. | Chowdhury A, Dhali GK, Banerjee PK. Etiology of gastric outlet obstruction. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996;91:1679. [PubMed] |
| 3. | Marinis A, Yiallourou A, Samanides L, Dafnios N, Anastasopoulos G, Vassiliou I, Theodosopoulos T. Intussusception of the bowel in adults: a review. World J Gastroenterol. 2009;15:407-411. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 428] [Cited by in RCA: 507] [Article Influence: 31.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (2)] |
| 4. | Markogiannakis H, Messaris E, Dardamanis D, Pararas N, Tzertzemelis D, Giannopoulos P, Larentzakis A, Lagoudianakis E, Manouras A, Bramis I. Acute mechanical bowel obstruction: clinical presentation, etiology, management and outcome. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13:432-437. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 158] [Cited by in RCA: 152] [Article Influence: 8.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Azar T, Berger DL. Adult intussusception. Ann Surg. 1997;226:134-138. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 648] [Cited by in RCA: 666] [Article Influence: 23.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Weilbaecher D, Bolin JA, Hearn D, Ogden W 2nd. Intussusception in adults. Review of 160 cases. Am J Surg. 1971;121:531-535. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 239] [Cited by in RCA: 213] [Article Influence: 3.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Zakaria AH, Daradkeh S. Jejunojejunal intussusception induced by a gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Case Rep Surg. 2012;2012:173680. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Đokić M, Novak J, Petrič M, Ranković B, Štabuc M, Trotovšek B. Case report and literature review: patient with gastroduodenal intussusception due to the gastrointestinal stromal tumor of the lesser curvature of the gastric body. BMC Surg. 2019;19:158. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 9. | Nakagawara M, Kajimura M, Hanai H, Shimizu S, Kobayashi H. Gastroduodenal intussusception secondary to a giant solitary gastric heterotopia: a case report. Gastrointest Endosc. 2000;52:568-570. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Sankaranunni B, Ooi DS, Sircar T, Smith RC, Barry J. Gastric lipoma causing gastroduodenal intussusception. Int J Clin Pract. 2001;55:731-732. [PubMed] |
| 11. | Harrison JR, Ruchim M. Gastroduodenal intussusception. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001;53:632. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Mouës CM, Steenvoorde P, Viersma JH, van Groningen K, de Bruïne JF. Jejunal intussusception of a gastric lipoma: a review of literature. Dig Surg. 2002;19:418-420. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Crowther KS, Wyld L, Yamani Q, Jacob G. Case report: gastroduodenal intussusception of a gastrointestinal stromal tumour. Br J Radiol. 2002;75:987-989. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Vinces FY, Ciacci J, Sperling DC, Epstein S. Gastroduodenal intussusception secondary to a gastric lipoma. Can J Gastroenterol. 2005;19:107-108. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Juglard R, Rimbot A, Stéphant E, Paoletti H, Talarmin B, Arteaga C. [Gastroduodenal intussusception complicating Menetrier's disease]. J Radiol. 2006;87:69-71. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Adjepong SE, Parameswaran R, Perry A, Mathews R, Jones R, Butterworth JR, Sigurdsson A. Gastroduodenal intussusception due to gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) treated by laparoscopic billroth II distal gastrectomy. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2006;16:245-247. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Samamé J, Moreno JI, Maraschio MA. [Gastroduodenal intussusception due to gastrointestinal stromal tumor]. Cir Esp. 2007;82:131. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Shum JS, Lo SS, Ka SY, Yeung CW, Ho JT. Gastroduodenal intussusception. Abdom Imaging. 2007;32:698-700. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Alamili M, Berg JO, Lindström C, Jensen CV, Wettergren A. [Gastroduodenal intussusception causing gastric retention]. Ugeskr Laeger. 2008;170:753. [PubMed] |
| 20. | Siam FA, Siow SL. Stomach gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GIST) intussuscepted into duodenum: a case report. Malays J Med Sci. 2008;15:68-70. [PubMed] |
| 21. | Su PY, Yen HH, Chen CJ. Clinical challenges and images in GI. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome with gastroduodenal intussusception secondary to gastric cancer. Gastroenterology. 2009;136:774, 1125. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Hillenbrand A, Waidner U, Henne-Bruns D, Maria Wolf A, Buttenschoen K. After 3 years of starvation: duodenum swallowed remaining stomach. Obes Surg. 2009;19:664-666. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Chan CT, Wong SK, Ping Tai Y, Li MK. Endo-laparoscopic reduction and resection of gastroduodenal intussuception of gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST): a synchronous endoscopic and laparoscopic treatment. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2009;19:e100-e103. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Eom BW, Ryu KW, Lee JH, Lee JY, Lee JS, Kook MC, Kim YW. Gastrogastric intussusception secondary to a gastric carcinoma: Report of a case. Surg Today. 2011;41:1424-1427. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Euanorasetr C, Suwanthanma W. Transpyloric prolapse of a pedunculated polypoid gastric carcinoma: a case report and review of the literature. J Med Assoc Thai. 2011;94:1008-1012. [PubMed] |
| 26. | Gyedu A, Reich SB, Hoyte-Williams PE. Gastrointestinal stromal tumour presenting acutely as gastroduodenal intussusception. Acta Chir Belg. 2011;111:327-328. [PubMed] |
| 27. | Seok HS, Shon CI, Seo HI, Choi YG, Chung WG, Won HS. [Gastroduodenal intussusception due to pedunculated polypoid gastrointestinal stromal tumor]. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2012;59:372-376. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Wilson MH, Ayoub F, McGreal P, Collins C. Gastrointestinal stromal tumour presenting as gastroduodenal intussusception. BMJ Case Rep. 2012;2012. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Chen YY, Chen TW, Chen YF. Asymptomatic multiple gastric and duodenal tumors. Sporadic gastric hamartomatous polyps with gastroduodenal intussusception and adenocarcinoma transformation. Gastroenterology. 2013;145:e7-e8. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Rittenhouse DW, Lim PW, Shirley LA, Chojnacki KA. Gastroduodenal intussusception of a gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST): case report and review of the literature. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2013;23:e70-e73. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Chahla E, Kim MA, Beal BT, Alkaade S, Garrett RW, Omran L, Ogawa MT, Taylor JR. Gastroduodenal Intussusception, Intermittent Biliary Obstruction and Biochemical Pancreatitis due to a Gastric Hyperplastic Polyp. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2014;8:371-376. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Khanna M, Ramanathan S, Ahmed A, Kumar D. Gastroduodenal intussusception secondary to a pedunculated Brunner's gland hamartoma: CT and endoscopic features. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2014;45 Suppl 1:257-260. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Kadowaki Y, Nishimura T, Komoto S, Yuasa T, Tamura R, Okamoto T, Ishido N. Gastroduodenal intussusception caused by a gastric collision tumor consisting of adenocarcinoma and neuroendocrine carcinoma. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2014;8:89-94. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Yang JH, Zhang M, Zhao ZH, Shu Y, Hong J, Cao YJ. Gastroduodenal intussusception due to gastric schwannoma treated by Billroth II distal gastrectomy: one case report. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21:2225-2228. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 35. | M S PB, Reddy CK, Augustine AJ, Sagari SG. Gastroduodenal intussusception due to pedunculated polypoid gastrointestinal stromal tumour (gist ): a rare case. J Clin Diagn Res. 2015;9:PD05-PD06. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 36. | Indiran V, Vinoth Kumar R, Maduraimuthu P. Gastrointestinal stromal tumor presenting as gastroduodenal intussusception. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2015;34:347-348. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 37. | Yildiz MS, Doğan A, Koparan IH, Adin ME. Acute Pancreatitis and Gastroduodenal Intussusception Induced by an Underlying Gastric Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor: A Case Report. J Gastric Cancer. 2016;16:54-57. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 38. | Komatsubara T, Zuiki T, Lefor AK, Hirota N, Oki J. Unusual gastroduodenal intussusception secondary to a gastrointestinal stromal tumor of the gastric fundus. IJS Open. 2016;5:33-36. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 39. | Jameel ARA, Segamalai D, Murugaiyan G, Shanmugasundaram R, Obla NB. Gastroduodenal Intussusception due to Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumour (GIST). J Clin Diagn Res. 2017;11:PD09-PD10. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 40. | Casimiro Pérez JA, Fernández Quesada C, Rodríguez Méndez Á, Sánchez Guedez I. Gastroduodenal invagination secondary to gastric submucosal lipoma treated by laparoscopic transgastric excision. Cir Esp. 2018;96:235. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 41. | Zhou Y, Wu XD, Shi Q, Xu CH, Jia J. Gastroduodenal intussusception and pylorus obstruction induced by a c-KIT-negative gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumor: case report and review of the literature. Z Gastroenterol. 2018;56:374-379. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 42. | Ssentongo P, Egan M, Arkorful TE, Dorvlo T, Scott O, Oh JS, Amponsah-Manu F. Adult Intussusception due to Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor: A Rare Case Report, Comprehensive Literature Review, and Diagnostic Challenges in Low-Resource Countries. Case Rep Surg. 2018;2018:1395230. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 43. | De U, Basu S. Gastroduodenal intussusception due to gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Clin Case Rep. 2018;6:2276-2278. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 44. | Suda T, Hodo Y, Shirota Y. Gastroduodenal intussusception of a gastric carcinoma. Dig Endosc. 2019;31:e38-e39. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 45. | Yamauchi K, Iwamuro M, Ishii E, Narita M, Hirata N, Okada H. Gastroduodenal Intussusception with a Gastric Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor Treated by Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection. Intern Med. 2017;56:1515-1519. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |