Published online Jun 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i17.4238
Peer-review started: January 24, 2021
First decision: March 8, 2021
Revised: March 21, 2021
Accepted: April 9, 2021
Article in press: April 9, 2021
Published online: June 16, 2021
Processing time: 122 Days and 0.9 Hours
Eosinophilic gastroenteritis (EGE) is a rare disease that presents many unspecific gastroenterological symptoms. The disease includes three types depending on the depth of eosinophil infiltration in the gastrointestinal tract. The serosal type is the most rare, presenting as ascites.
A 34-year-old man presented with abdominal pain, diarrhea without bloody stool, or nausea. Laboratory test results revealed a peripheral blood eosinophil count (4.85 × 109/L), which was remarkedly elevated. Computed tomography scan demonstrated extensive intestinal wall edema thickening in the duodenum, jejunum, ascending colon and transverse colon; multiple exudative effusion surrounding the intestinal tract, and ascites in the abdominal cavity. A series of examinations excluded eosinophil elevation in secondary diseases. Endoscopic multipoint biopsy detected eosinophilic infiltration in the mucous layer of the transverse colon, with ≥ 50 eosinophils/high power field. All symptoms vanished after a few days of steroid therapy and ascites disappeared within 2 wk.
EGE should be considered in patients with abdominal pain, ascites, and eosinophilia. Multiple point biopsies are essential for diagnosis.
Core Tip: Eosinophilic gastroenteritis (EGE) is a rare disease that presents many unspecific gastroenterological symptoms. We present a case with abdominal pain, ascites, and eosinophilia after raw and cold seafood. The patient was eventually diagnosed with EGE based on biopsy findings. The case highlights the ultimate importance of multiple point biopsies in diagnosis and the effectiveness of corticosteroid therapy in EGE patients.
- Citation: Tian XQ, Chen X, Chen SL. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis with abdominal pain and ascites: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(17): 4238-4243
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i17/4238.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i17.4238
Eosinophilic gastroenteritis (EGE) is a rare inflammatory disease with many unspecific presentations, depending on the depth of eosinophil infiltration in gastrointestinal (GI) tract[1]. EGE can affect the entire GI tract, with the antrum and duodenum being the most common sites. Symptoms correlate with the affected segment and layer of the GI wall. The diagnosis of EGE requires high sensitivity for this disease in the clinic. EGE is diagnosed according to GI mucosa pathology.
Here, we report a case of EGE that presented with abdominal pain and diarrhea.
A 34-year-old man was admitted to the emergency department due to abdominal pain and diarrhea for 1 d.
One day earlier, the patient had eaten raw and cold seafood with several friends. He reported the aggravation of abdominal pain for 6 h. He denied other symptoms including fever, vomiting, hematochezia, skin rash, as well as recent medication intake.
He had a history of recurrent iritis, spondylarthritis, and chronic viral hepatitis B. He denied a previous history of asthma and seasonal allergic rhinitis.
The patient had no special family history.
On physical examination, the patient’s temperature was 37.3 °C, heart rate was 98 beats per min, respiratory rate was 18 breaths per min, blood pressure was 128/80 mmHg, and oxygen saturation in room air was 99%. There was abdominal tenderness and no rebound pain. The cardiopulmonary examination was normal. The clinical neurological examination was also normal.
Blood tests revealed leukocytosis (14560/μL) with 15.6% of eosinophils (2270/μL), which was marginally elevated. C-reactive protein was only slightly elevated (8.13 mg/L). There was no elevation of hepatobiliary and pancreatic enzyme levels. His feces test was negative for occult blood and multiple enteric pathogens. The parasitological exams in his stool and blood were also negative. Serum IgE level was normal. T-spot test was within normal ranges. To exclude other systemic diseases, the rheumatological index, serum protein electrophoresis, and immunostationary electrophoresis were tested, which were negative. To rule out blood diseases, peripheral blood smear and FIP1L1-PDGFRa fusion gene qualitative test were performed, which were both negative. Laboratory test of ascitic fluid was suggested as exudate with a low serum albumin-ascitic gradient, as well as bacterial culture and tuberculosis was negative.
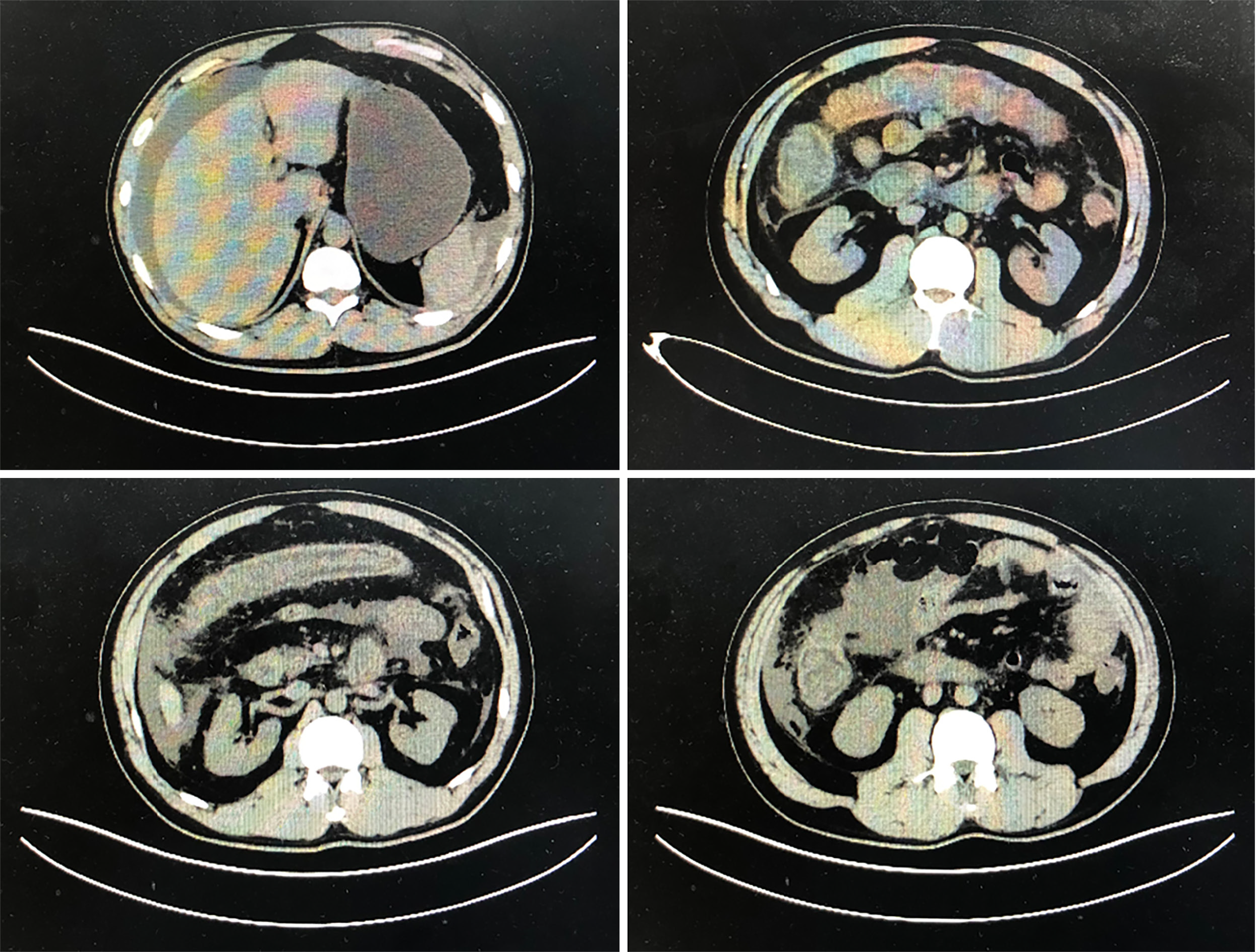
Computed tomography scan demonstrated extensive intestinal wall edema thickening in the duodenum, jejunum, ascending colon and transverse colon; multiple exudative effusion surrounding the intestinal tract; and ascites in the abdominal cavity (Figure 1).
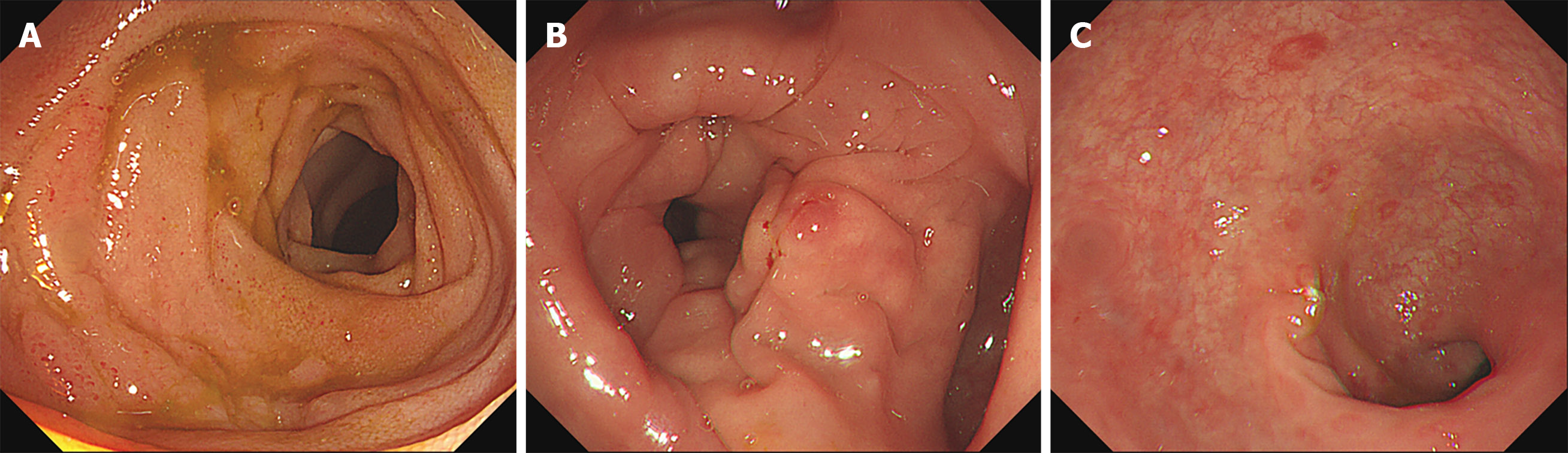
For further diagnosis, colonoscopy was performed. Terminal ileum and the entire colonic mucosa scattered in hyperemia and edema (Figure 2). Multiple point biopsies were taken respectively from the terminal ileum, ascending colon, transverse colon, and rectum. The gastroscopy showed “hyperemia of the body and antrum mucosa”; biopsies were taken from multiple sites including the esophagus, gastric body, gastric antrum, duodenal bulb, and descending duodenal part.
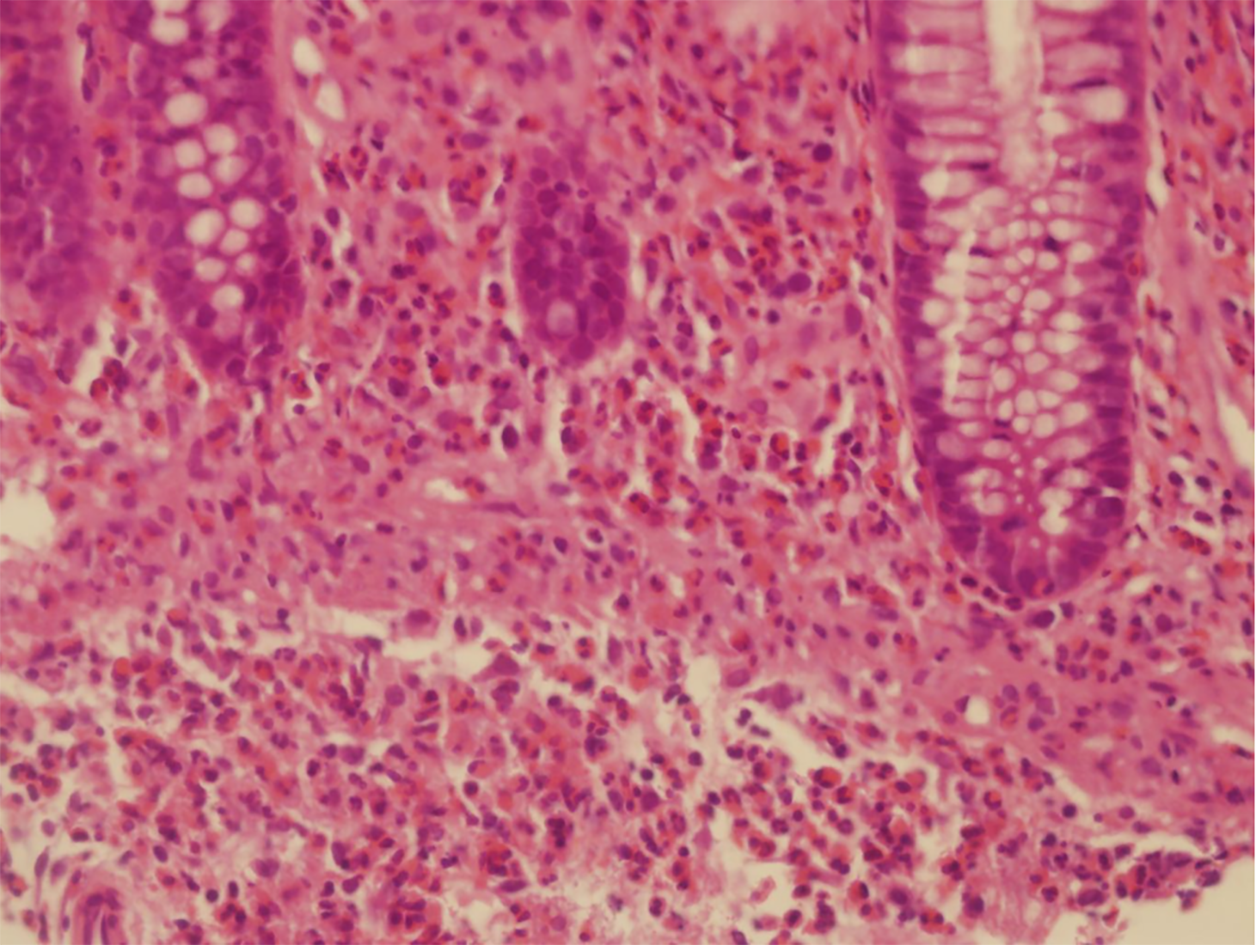
Multiple colon biopsies showed the following results: active enteritis with multiple lymphatic follicles forming in the terminal ileum; increased intraepithelial lympho
The final diagnosis of the presented case was EGE.
The patient was treated with 40 mg methylprednisolone/day. Following treatment, his abdominal pain vanished in a few days and ascites disappeared within 2 wk. The dose of prednisone was gradually reduced until it was discontinued after 6 mo.
To date, the patient had stopped taking corticosteroids for 6 mo and remains asympto
EGE is a rare disorder that presents with nonspecific clinical symptoms. Prevalence is from 8.4 to 28 per 100000, which is higher in children. Most adults are diagnosed between 30-years-old and 50-years-old[2]. Diagnosis requires a high degree of vigilance. More than 50% of the reported EGE cases have other allergic diseases including rhinitis, eczema, asthma, drug allergies, or food allergies[2,3]. A relationship with some autoimmune disorders has been described such as celiac disease, ulcerative colitis, and systemic lupus erythematosus[3]. It is essential to exclude other diseases such as parasitosis, tuberculosis, and cancer.
The clinical manifestations of EGE depend on the location, range, and depth of eosinophilic infiltration of the GI wall. EGE was classified into three types according to the depth of eosinophilic infiltration: mucosal, muscular, and serosal. The disease with the mucosal layer infiltration is the most frequent type. This type present with nonspecific symptoms include general abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. The severe patient may present with GI bleeding, iron deficiency anemia, and protein-losing enteropathy. The second type is eosinophilic infiltration in the muscular layer, causing thickening of the digestive tract wall and intestinal obstruc
As absence of unified diagnostic criteria, the cutoff value for eosinophil counts should be individualized to the different biopsy sites[6]. To confirm the histological pathological diagnosis, many researchers have suggested that at least 20 eosinophils/ HPF are considered necessary[7].
Treatment with corticosteroids are generally effective in EGE patients. Prednisolone dose typically starts at 40 mg/d for 7-14 d, then gradually decreases. Second-line therapies include antihistamines, mast cell stabilizers (sodium cromoglycate), leukotriene antagonists (montelukast), elimination diet (elimination of milk, soy, wheat, eggs, peanuts, and seafood), immunomodulators (azathioprine), tumor necrosis factors inhibitors (infliximab), mepolizumab, and IgE monoclonal antibody (omalizumab)[8].
The course and prognosis of different patients are variable. Some patients do not relapse, while other patients have recurring symptoms and require repeated or long-termed steroid therapy. In these patients, the second-line therapies mentioned above may be considered[9].
According to this case, EGE should be considered in patients with abdominal pain, ascites, and eosinophilia in blood routine examination, especially after a special diet. Multiple point biopsies are essential for diagnosis. Treatment with corticosteroids is generally effective in EGE patients.
Manuscript source: Unsolicited manuscript
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): 0
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Baryshnikova NV S-Editor: Liu M L-Editor: Filipodia P-Editor: Li X
| 1. | Tien FM, Wu JF, Jeng YM, Hsu HY, Ni YH, Chang MH, Lin DT, Chen HL. Clinical features and treatment responses of children with eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Pediatr Neonatol. 2011;52:272-278. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 42] [Cited by in RCA: 46] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Abou Rached A, El Hajj W. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis: Approach to diagnosis and management. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. 2016;7:513-523. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 58] [Cited by in RCA: 84] [Article Influence: 9.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (4)] |
| 3. | Shih HM, Bair MJ, Chen HL, Lin IT. Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis : Brief Review. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2016;79:239-244. [PubMed] |
| 4. | Uppal V, Kreiger P, Kutsch E. Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis and Colitis: a Comprehensive Review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016;50:175-188. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 83] [Cited by in RCA: 101] [Article Influence: 11.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Quack I, Sellin L, Buchner NJ, Theegarten D, Rump LC, Henning BF. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis in a young girl--long term remission under Montelukast. BMC Gastroenterol. 2005;5:24. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 46] [Cited by in RCA: 45] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Matsushita T, Maruyama R, Ishikawa N, Harada Y, Araki A, Chen D, Tauchi-Nishi P, Yuki T, Kinoshita Y. The number and distribution of eosinophils in the adult human gastrointestinal tract: a study and comparison of racial and environmental factors. Am J Surg Pathol. 2015;39:521-527. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 52] [Cited by in RCA: 65] [Article Influence: 6.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Kinoshita Y, Ishimura N, Oshima N, Mikami H, Okimoto E, Jiao DJ, Ishihara S. Recent Progress in the Research of Eosinophilic Esophagitis and Gastroenteritis. Digestion. 2016;93:7-12. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 24] [Cited by in RCA: 23] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Alhmoud T, Hanson JA, Parasher G. Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis: An Underdiagnosed Condition. Dig Dis Sci. 2016;61:2585-2592. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 25] [Cited by in RCA: 34] [Article Influence: 3.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Straumann A. Idiopathic eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases in adults. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2008;22:481-496. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 37] [Cited by in RCA: 40] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (2)] |