Published online Jan 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i1.175
Peer-review started: May 25, 2020
First decision: June 12, 2020
Revised: September 15, 2020
Accepted: November 21, 2020
Article in press: November 21, 2020
Published online: January 6, 2021
Processing time: 221 Days and 0.8 Hours
Low grade fibromyxoid sarcoma (LGFMS) is a rare and benign mesenchymal tumor with indolent course, most commonly found in young or middle-aged men. The majority of the LGFMSs are located in the trunk and deep soft tissue of the lower extremities. They appear as well circumscribed, although not encapsulated, which often leads to incomplete surgical resection. Despite their seemingly benign appearance, these tumors have aggressive behavior with high metastatic and recurrence rates. Accurate histopathologic examination of the specimen and its immunohistochemical analysis are mandatory for a precise diagnosis.
We report a case of a 38 year-old-man who presented with jaundice and upper abdominal discomfort. Multi-detector computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging showed a large left liver tumor mass, extending to the hepatoduodenal ligament. Left hepatectomy was performed with resection and reconstruction of hepatic artery and preservation of middle hepatic vein. Histopathologic examination confirmed the tumor being a low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma. Three and a half years after surgery, the patient died after being diagnosed with spine metastasis.
Due to poor response to all modalities of adjuvant treatment, we consider that the focus of treatment should be on surgery as the only option for curing the disease.
Core Tip: Low grade fibromyxoid sarcoma (LGFMS) is very rare mesenchymal tumors with indolent course but aggressive biological behavior. There are no effective diagnostic procedures to achieve an accurate preoperative diagnosis. Symptoms are usually caused by compression on adjacent organs and structures. This report describes the case of a large left liver LGFMS in male patient, extending to the hepatoduodenal ligament, which was detected with abdominal ultrasound and confirmed by multi-detector computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Left hepatectomy was performed and the tumor was completely removed at laparotomy.
- Citation: Dugalic V, Ignjatovic II, Kovac JD, Ilic N, Sopta J, Ostojic SR, Vasin D, Bogdanovic MD, Dumic I, Milovanovic T. Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma of the liver: A case report . World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(1): 175-182
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i1/175.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i1.175
Low grade fibromyxoid sarcoma (LGFMS) is a rare, deceptively benign, mesenchymal tumor. It was first described by Evans in 1987[1]. All the reports of this tumor come from Asia and the western countries[2]. LGFMS accounts for less than 1% of all malignancies and typically develop in young or middle-aged men, with most common localization (in 50%) on the trunk and the lower extremities[3]. Other, frequently involved sites include the axilla, chest wall, inguinal region, and buttocks[4]. Intraabdominal LGFMSs are very rare, such as those in the retroperitoneum, small bowel mesentery, large bowel, falciform ligament and pancreas[2,5-8]. Three cases of pelvic LGFMS have been described previously[9]. In spite of their seemingly benign appearance, LGFMSs show aggressive behavior with high rates of tumor recurrence following surgery and high metastatic potential. These tumors are detected with standard imaging modalities such as ultrasound, multi-detector computed tomo-graphy (MDCT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). However, laboratory and imaging findings are nonspecific, and definitive diagnosis is obtained only after histopathologic and immunohistochemical (IHC) examination. In this report, we present a case of a large left liver LGFMS in a male patient, which was visualized by ultrasound, MDCT and MRI and completely surgically removed at laparotomy.
A 38-year-old man complained of upper abdominal pain and discomfort.
A 38-years-old man was admitted with jaundice, upper abdominal pain and discomfort.
The patient suffered from depression but was healthy otherwise, without medical problems.
The patient suffered from depression but was healthy otherwise, without medical problems.
Physical examination revealed a firm mass under the right costal margin.
On admission, serum bilirubin levels were elevated (180 U/L). Tumor markers, carcinoembryonic antigen and alpha fetoprotein were within normal range, while CA19-9 was moderately elevated (83 U/L).
Abdominal ultrasound showed a large tumor mass (10 cm × 7.6 cm), with irregular calcification, in the projection of the left liver lobe, extending to the liver hilum, with infiltration of the common hepatic duct and bile duct confluence.
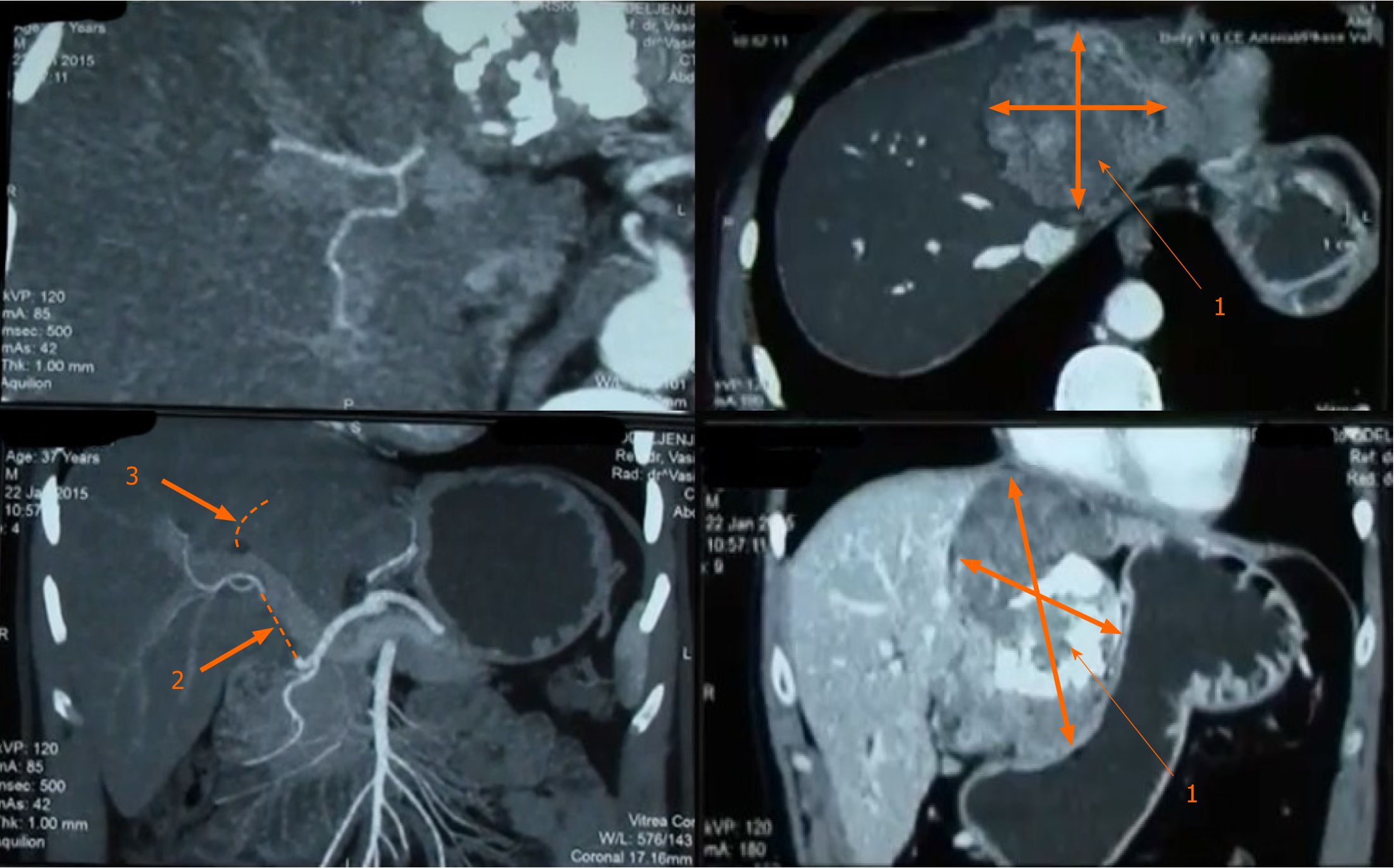
MDCT revealed, well circumscribed and encapsulated tumor mass (10 cm × 9 cm × 7 cm), in the epigastric region. The tumor was predominantly located in the left liver lobe. In its caudal aspect tumor mass extended to the hepatoduodenal ligament with infiltration of the left bile duct and bile duct confluence, common bile duct, left branch of the portal vein, and hepatic artery, from the bifurcation of gastroduodenal artery to the level of right second branching. The tumor was in close contact with the pancreas and the stomach, but without any evidence of infiltration. Hepatic artery was infiltrated in the length of 6cm, from the level of its origin from gastroduodenal artery (Figure 1). MRI with magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography finding was in concordance with MDCT.
An upper endoscopy showed extramural compression on the lesser curve of the stomach, without infiltration of gastric mucosa. Endoscopic ultrasound guided fine needle aspiration was performed and histopatological findings were highly suggestive of a low grade mesenchymal tumor.
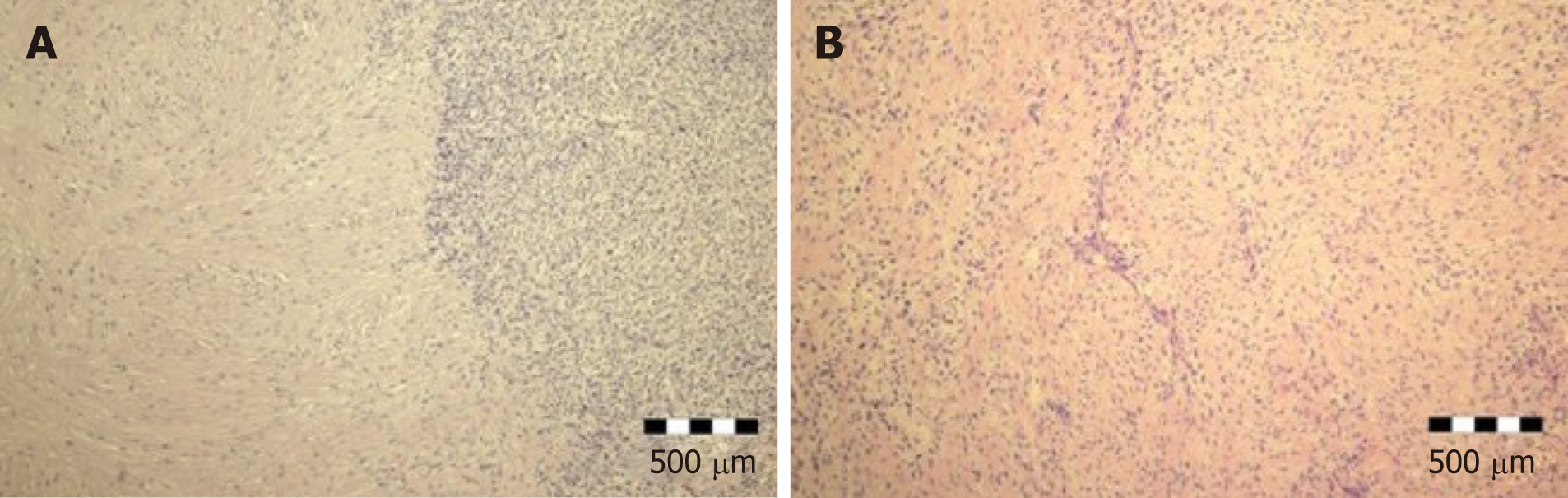
Tumor was graded as T3, with no lymph node metastasis (N0, 0/12). There was venular (V1) but no perineural involvement (PN0). Residual status was classified as R0. Histological examination of the tumor demonstrated a nodular biphasic growth pattern. Fibrous and myxoid areas with moderate to low cellularity were present. There were bland-appearing spindle cells, with no or slight nuclear pleomorphism, and rare mitotic figures. Intense hypocellular fibrotic areas, with thick collagen bundles, were also described. Fibromyxoid matrix was present focally, arranged in giant pseudo-rosettes (Figure 2).
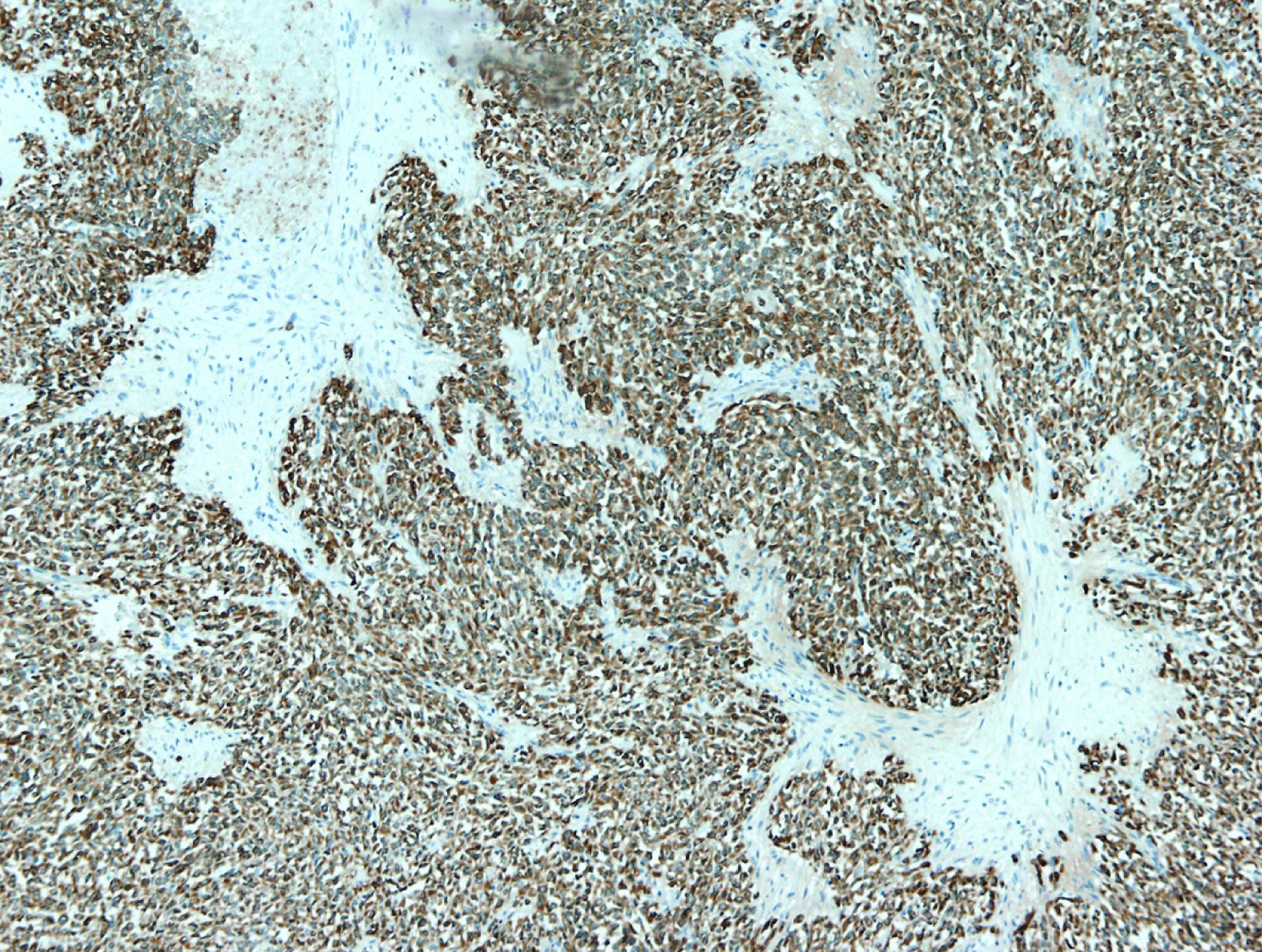
IHC showed that the tumor cells were diffusely and strongly positive for vimentin and MUC4 with CD99 and epithelial membrane antigen diffuse but slightly expressed (Figure 3). Cytokeratin, smooth muscle actin, S-100 protein and neuron specific enolase were negative. Proliferative index counted by Ki67 was 8% in hot spots. According to morphology, IHC and in concordance with preoperative imaging and intraoperative finding, the tumor was classified to be low grade fibromyxoid sarcoma of the liver.
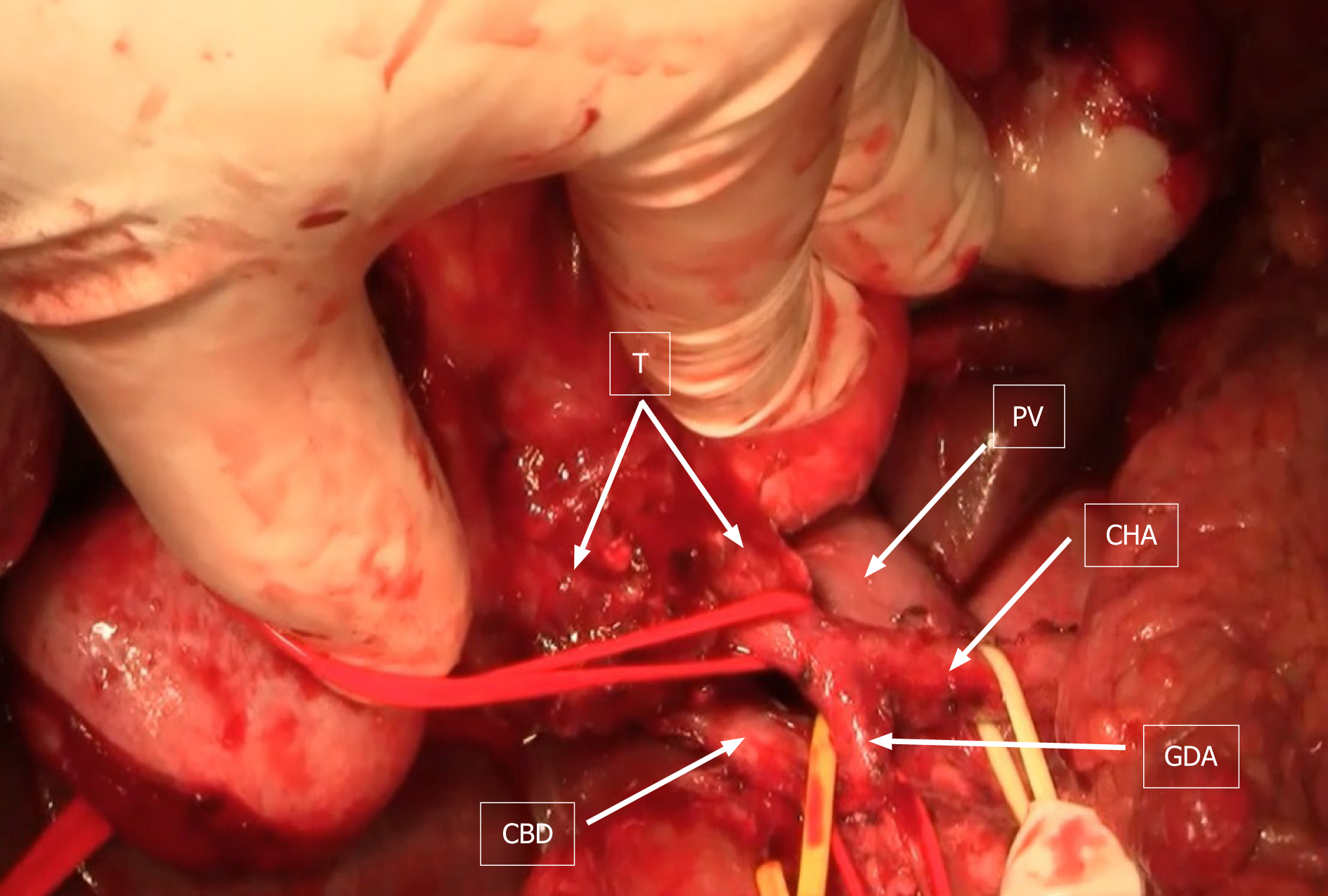
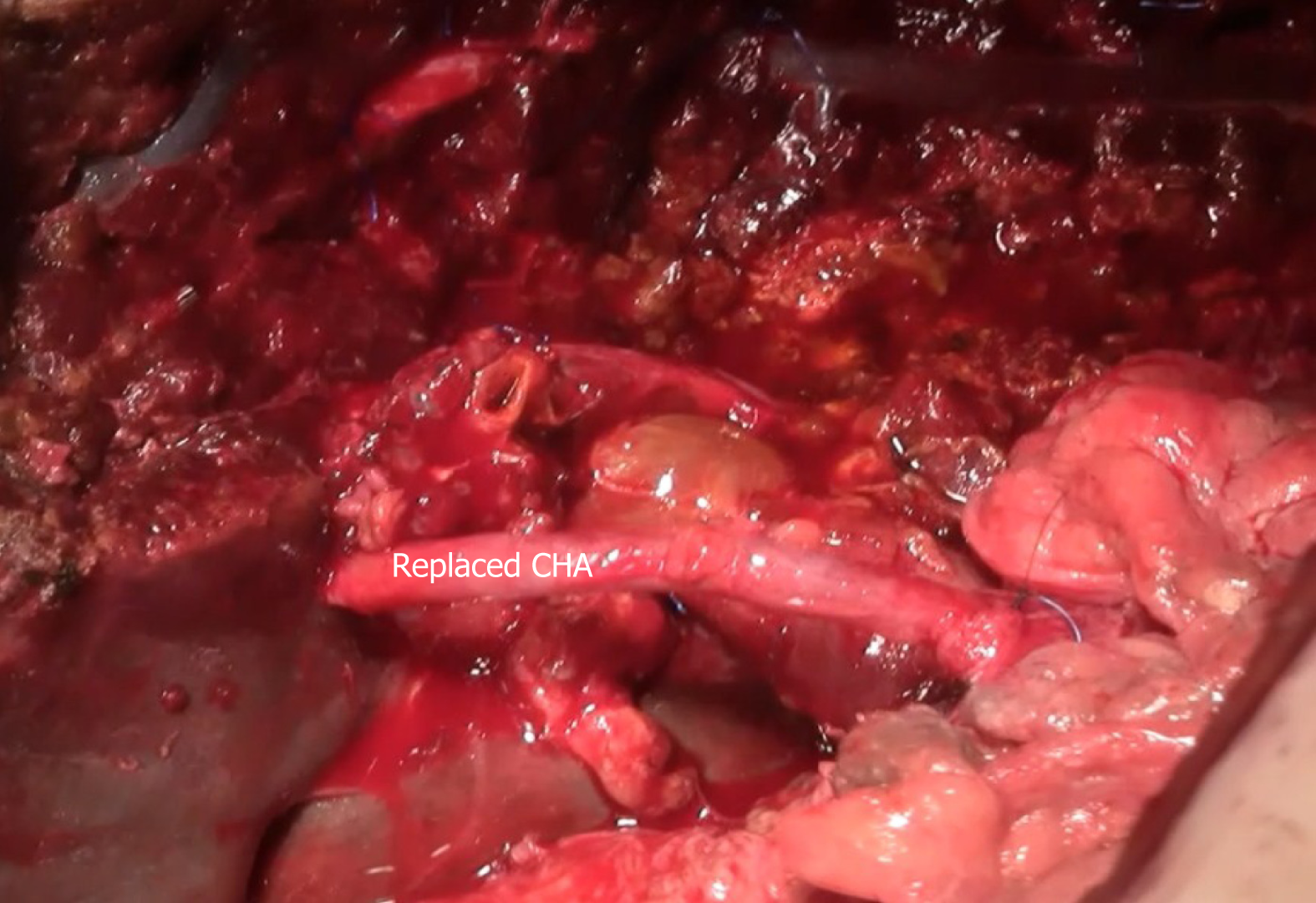
Subsequently, laparotomy was performed. At laparotomy, preoperative, imaging-techniques findings were confirmed (Figure 4). Left hepatectomy was performed with resection of hepatic artery and preservation of middle hepatic vein.
Hepatic artery was reconstructed with reverse saphenous vein graft interposition (Figure 5). After liver resection and reconstruction of the hepatic artery, hepatico-jejunostomy (end-to-side) with isolated jejunal Roux-en-Y loop, on the right hepatic bile duct, was created. Postoperative color-Doppler ultrasound of the vein graft showed regular blood flow. Patient’s postoperative recovery was prolonged due to the presence of an asymptomatic bile collection at the surgical site, which was eventually treated with percutaneous drainage. His liver function tests eventually normalized and he was discharged from the hospital three weeks after the surgery.
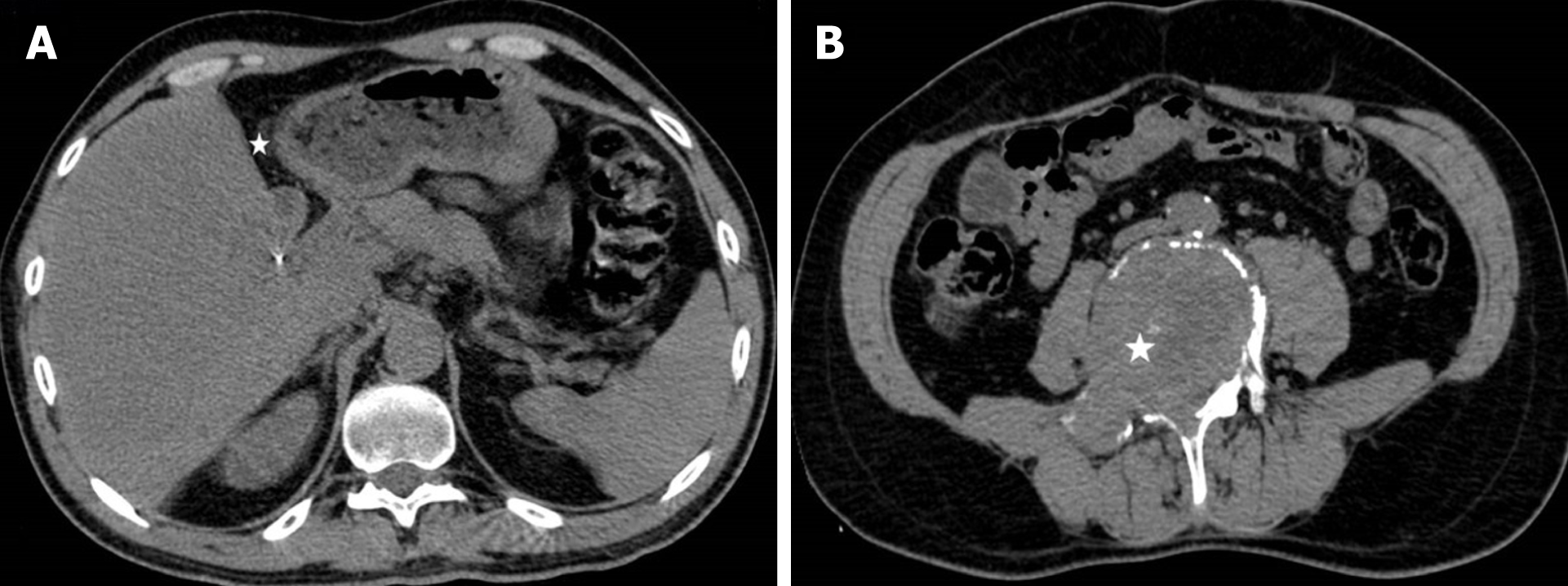
Regular follow-up was done every three months during the first two years after surgery, and bi-annually afterwards. This included full blood biochemical analysis and ultrasound/MDCT imaging. Two years following the surgery, there was no local recurrence or intraabdominal metastasis (Figure 6A).
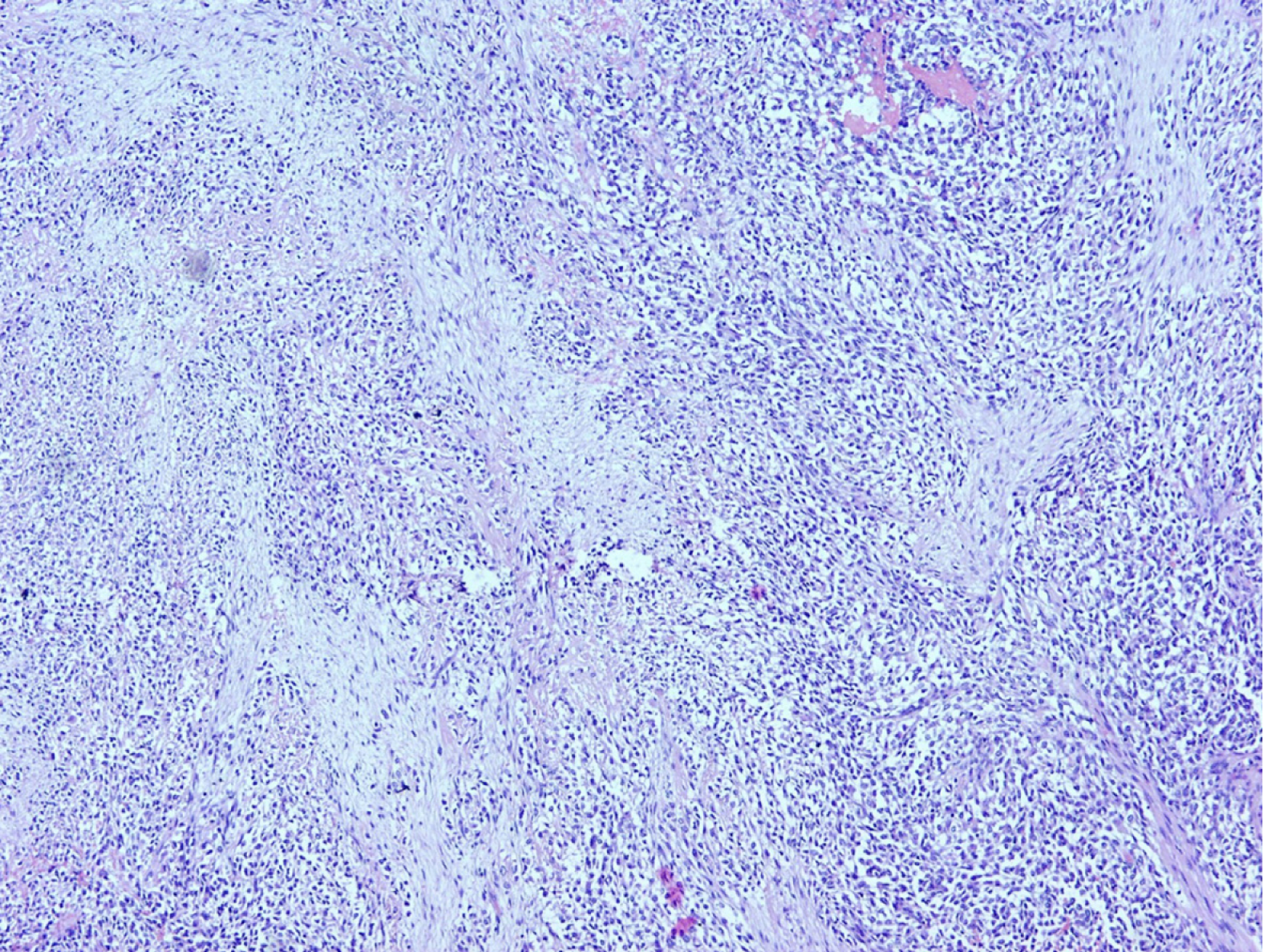
Unfortunately, two and a half years after surgery patient suffered pathological vertebral fracture and was subsequently diagnosed with lumbar vertebral metastasis (Figure 6B). He was treated with lumbar spine stabilization. Spine lesion biopsy was performed and was consistent with metastatic disease (Figure 7). The mitotic rate in metastatic tumor was 20%-25% in "hot spots". After the spine stabilisation surgery patient did not show on regular check-ups, preventing him from receiving potential adjuvant treatment. One year after, the patient died from septic complications of metastatic spine disease and the complications from venous thromboembolism.
LGFMS typically presents in young or middle aged men as a painless deep soft tissue mass. These tumors are slow growing and are often large at the time of diagnosis. The most common locations of these tumors include the deep soft tissues of the lower extremities, especially the thigh, axilla/chest wall area, shoulder area, buttocks, and the inguinal area[10]. Intra-abdominal LGFMS are exceptionally rare with only several cases published thus far. Some of the rare locations of LGFMS reported to date include those of the retroperitoneum, small bowel mesentery, large bowel, falciform ligament and pancreas[2,5-8]. Abdominal localization of the tumor is characterized by its slow progression and long recurrence-free intervals. There have been few reports of the LGFMSs of the renal capsule, paravertebral region, and broad ligament[10]. Mediastinal LGFMS is extremely rare, with only one case reported in the English literature[11]. Histopathologic analysis of the biopsy specimen in our patient, confirmed the diagnosis of low grade fibromyxoid sarcoma of the liver.
Following the review of EMBASE and MEDLINE databases we have found our case to be only the second case of liver LGFMS. The first case was described by Jin et al[12]. Although it most commonly occurs in middle-aged patients, LGFMS could develop at extremes of age with the youngest patient reported in the literature being 3 years old and the oldest patient being 78 years old[10,13].
Due to their large diameter, these tumors, become symptomatic when they compress adjacent organs and/or structures. Majority of the LGFMS appear well circumscribed, but they lack the capsule, which often renders surgical excision incomplete. Dilated, friable veins, are often present on the tumor surface. Prolonged INR may be present in laboratory findings as the result of consumption coagulopathy by the tumor. In our patients, surgical excision was complete (R0).
LGFMSs show tendency to recur with rates of local recurrence, as high as 65%. Recurrence free interval range from several months to up to 50 years after initial surgery. Prolonged survival is possible, moreover probable, even in the presence of metastatic disease. Most common site of metastatic disease is lungs which is not surprising given sarcomas’ tendency to spread hematogenously. Interestingly, our patient was diagnosed with lumbar spine metastasis in the absence of local recurrence, two and half years after surgery. The patient died one year after spine surgery due to septic complications of metastatic spine disease and the complications from venous thromboembolism.
The current standard treatment for patients with metastatic soft tissue sarcoma (excluding gastrointestinal stromal tumors, Ewing-like sarcomas, and other small blue round cell tumors) is systemic therapy with doxorubicin or ifosfamide, both resulting in poor survival rates[14]. Even the blandest LGMFS still carries a recurrent potential that cannot be predicted by either different grading schemes or other clinicopathologic parameters. However, disease-specific mortality rate is significantly related to tumor necrosis, large tumor volume, and decreased myxoid area. Tumors having necrosis or exceeding 5 cm are at significant risk of metastatic relapse[15]. Our patient did not have early distant metastases, since the spine metastasis was detected two and a half years after surgery. The main reason for distant spread in this case was large size of the tumor (over 10 cm), positive venular involvement (V1) and infiltration of the major blood vessels. Although, patient was presented to a multidisciplinary team (surgeon, pathologist, oncologist and radiologist) the decision was that no adjuvant therapy was needed, since there was no evidence of R1 resection or metastatic spread of the disease. In addition, in the present literature, there is no clear evidence of benefit of adjuvant therapy.
As with many other tumors, an accurate diagnosis rests on detailed histo-pathological examination. Most common histopathologic features include swirling pattern of tumor cells which form variable vascular arcades within alternate, myxoid, and cellular collagenous areas. These are composed of oval to spindle-shaped tumor cells, which can be seen in 50% to 88.2% of cases[10,16] . Tumor cells show a few or no mitosis. While there is no significant necrosis inside the tumor, foci of hemorrhage are usually present. It is important to distinguish LGFMS from myxofibrosarcoma, as they have different clinical course, and the later more frequently metastasize. Other malignancies to be excluded are malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor, spindle-cell liposarcoma, and malignant fibrohistiocytic tumor[2]. LGFMSs are often mistaken for benign tumors such as mixoid neurofibroma, desmoid fibromatosis, perineurinoma and nodular fasciitis. Proper histopathologic evaluation of the tumor and IHC is necessary for making an accurate diagnosis. IHC classically shows positive staining with vimentin, and, rarely, immunoreactivity could be seen for smooth muscle actin, desmin, cytokeratin and CD34. MUC4 was found to be a diagnostically useful biomarker for LGFMS and it can be used as an excellent screening tool[17]. Cytogenetic analyses have identified a recurrent balanced translocation t (7; 16) (q32-34; p11), later shown to result in a novel fusion genes, FUS/CREB3L2 and FUS-CREB3L1, which can be used as an excellent tool in differentiating LGFMS from other similar entities[18]. Li et al[19] published a study of 10 genetically confirmed cases in a Chinese population.
Due to its poor response to all modalities of adjuvant therapy, the focus of treatment should be on surgery as the only option for the cure. Achieving the tumor-free resection margins, gives patients the best chance for prolonged survival, and minimize the possibility of the tumor recurrence. As we demonstrated in this case, radical surgery with clear margins does not always preclude the occurrence of metastatic disease. Even in the absence of local tumor recurrence and relatively long disease free interval metastatic disease might occur in distant places necessitating another surgery with its associated complications.
Manuscript source: Unsolicited manuscript
Corresponding Author's Membership in Professional Societies: Association of Serbian Gastroenterologists.
Specialty type: Surgery
Country/Territory of origin: Serbia
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B, B
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): E
P-Reviewer: Fahrner R, Han JH, Suc B, Zhang YT S-Editor: Zhang H L-Editor: A P-Editor: Zhang YL
| 1. | Evans HL. Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma. A report of two metastasizing neoplasms having a deceptively benign appearance. Am J Clin Pathol. 1987;88:615-619. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 273] [Cited by in RCA: 266] [Article Influence: 7.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Alatise OI, Oke OA, Olaofe OO, Omoniyi-Esan GO, Adesunkanmi AR. A huge low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma of small bowel mesentery simulating hyper immune splenomegaly syndrome: a case report and review of literature. Afr Health Sci. 2013;13:736-740. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Citores-Pascual MA, Tinoco-Carrasco C, Arenal-Vera JJ, Benito-Fernández C, Torres-Nieto Mde L, Zamora-Martínez T. [Low grade fibromixoid sarcoma: a purpose of 3 cases and review of the bibliography]. Cir Cir. 2013;81:333-339. [PubMed] |
| 4. | Goodlad JR, Mentzel T, Fletcher CD. Low grade fibromyxoid sarcoma: clinicopathological analysis of eleven new cases in support of a distinct entity. Histopathology. 1995;26:229-237. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 163] [Cited by in RCA: 145] [Article Influence: 4.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Harish K, Ashok AC, Alva NK. Low grade fibromyxoid sarcoma of the falciform ligament: a case report. BMC Surg. 2003;3:7. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 26] [Cited by in RCA: 26] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Winfield HL, De Las Casas LE, Greenfield WW, Santin AD, McKenney JK. Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma presenting clinically as a primary ovarian neoplasm: a case report. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 2007;26:173-176. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 24] [Cited by in RCA: 26] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Park IJ, Kim HC, Yu CS, Kim JS, Jang SJ, Kim JC. Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma of the colon. Dig Liver Dis. 2007;39:274-277. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 23] [Cited by in RCA: 22] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Colović R, Grubor N, Misev M, Jovanović M, Radak V. [Fibromyxoid sarcoma of the pancreas]. Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2008;136:158-161. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Ud Din N, Ahmad Z, Zreik R, Horvai A, Folpe AL, Fritchie K. Abdominopelvic and Retroperitoneal Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcoma: A Clinicopathologic Study of 13 Cases. Am J Clin Pathol. 2018;149:128-134. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Folpe AL, Lane KL, Paull G, Weiss SW. Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma and hyalinizing spindle cell tumor with giant rosettes: a clinicopathologic study of 73 cases supporting their identity and assessing the impact of high-grade areas. Am J Surg Pathol. 2000;24:1353-1360. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 251] [Cited by in RCA: 226] [Article Influence: 9.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Takanami I, Takeuchi K, Naruke M. Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma arising in the mediastinum. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1999;118:970-971. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 35] [Cited by in RCA: 31] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Jin B, Du G, Li T. Right Upper Abdominal Distension and Discomfort Caused by a Massive Hepatic Tumor. Gastroenterology. 2017;153:e24-e26. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Canpolat C, Evans HL, Corpron C, Andrassy RJ, Chan K, Eifel P, Elidemir O, Raney B. Fibromyxoid sarcoma in a four-year-old child: case report and review of the literature. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1996;27:561-564. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Grimme FAB, Seesing MFJ, van Hillegersberg R, van Coevorden F, de Jong KP, Nagtegaal ID, Verhoef C, de Wilt JHW; On behalf of the Dutch Liver Surgery Working Group. Liver Resection for Hepatic Metastases from Soft Tissue Sarcoma: A Nationwide Study. Dig Surg. 2019;36:479-486. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 2.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Huang HY, Lal P, Qin J, Brennan MF, Antonescu CR. Low-grade myxofibrosarcoma: a clinicopathologic analysis of 49 cases treated at a single institution with simultaneous assessment of the efficacy of 3-tier and 4-tier grading systems. Hum Pathol. 2004;35:612-621. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 170] [Cited by in RCA: 142] [Article Influence: 6.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Rekhi B, Deshmukh M, Jambhekar NA. Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma: a clinicopathologic study of 18 cases, including histopathologic relationship with sclerosing epithelioid fibrosarcoma in a subset of cases. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2011;15:303-311. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 39] [Cited by in RCA: 46] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Mustafa S, VandenBussche CJ, Ali SZ, Siddiqui MT, Wakely PE Jr. Cytomorphologic findings of low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma. J Am Soc Cytopathol. 2020;9:191-201. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Vernon SE, Bejarano PA. Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma: a brief review. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2006; 130: 1358-1360 [PMID: 16948525 DOI: 10. 1043/1543-2165(2006)130. |
| 19. | Li M, Chen H, Shi D, Chen M, Zhang Z, Zhang H. Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma: a clinicopathologic and molecular study of 10 genetically confirmed cases. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018;11:5860-5868. [PubMed] |