Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Apr 6, 2020; 8(7): 1319-1325
Published online Apr 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i7.1319
Published online Apr 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i7.1319
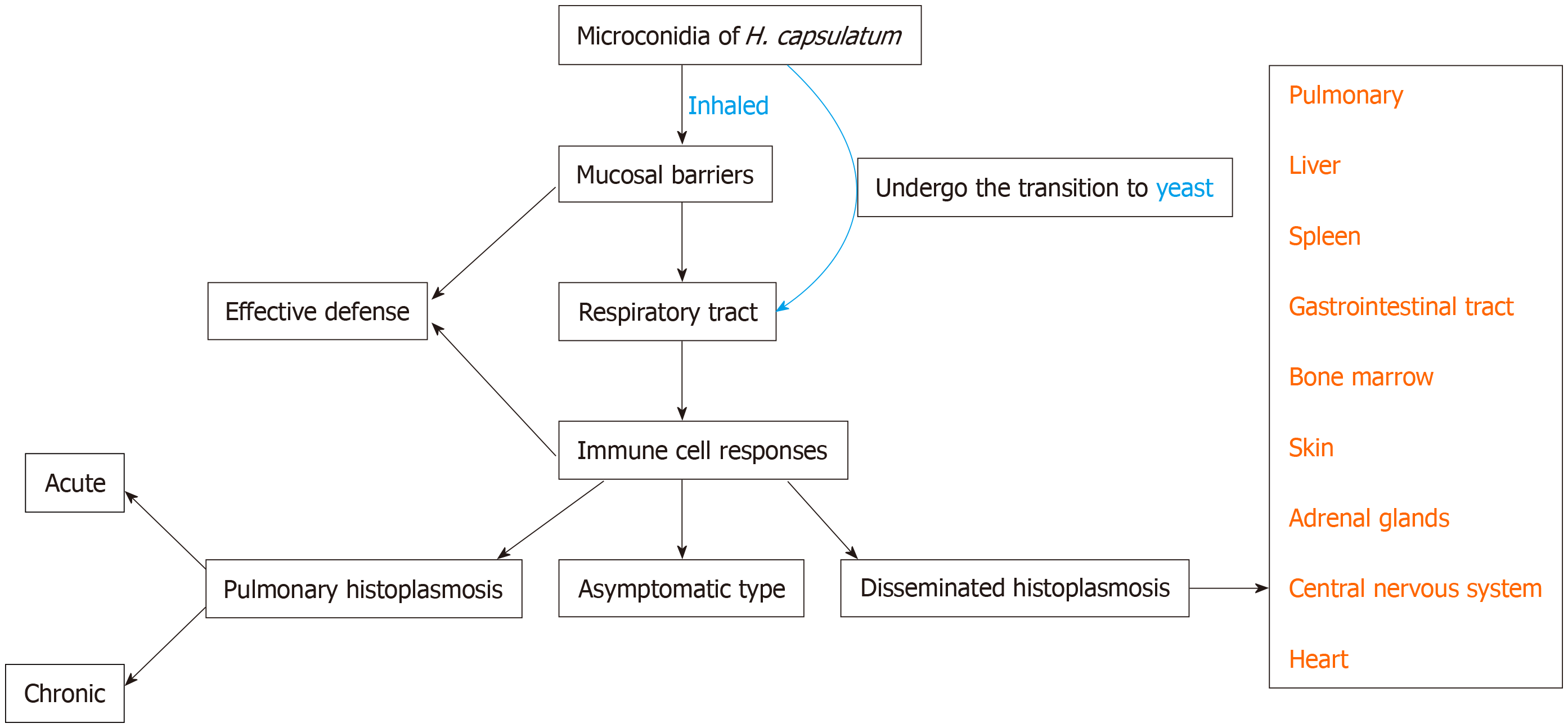
Figure 3 A simplified flow diagram of the histoplasmosis.
When microconidia can effectively be inhaled and travel as far as the host alveoli, it can undergo the transition to yeast. Only when the H. capsulatum overcomes the mucosal barriers, effectively avoid host immune cell and effector responses, and multiply, can it cause host injury.
- Citation: Li JA, Cheng YY, Cui ZT, Jiang W, Zhang WQ, Du ZH, Gao B, Xie YY, Meng HM. Disseminated histoplasmosis in primary Sjögren syndrome: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(7): 1319-1325
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i7/1319.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i7.1319