Published online Nov 6, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i13.659
Peer-review started: August 7, 2018
First decision: August 24, 2018
Revised: September 10, 2018
Accepted: October 9, 2018
Article in press: October 9, 2018
Published online: November 6, 2018
Processing time: 92 Days and 0 Hours
Herein we report a case of acute liver failure (ALF) and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) induced by varicella infection, successfully rescued by a combination therapy of acyclovir, supportive care, and immunosuppression with dexamethasone and etoposide. A previously healthy 16-year-old boy presented with generalized rash, fever, severe abdominal pain, and abnormal liver function within 4 d. Chickenpox was suspected, and acyclovir and intravenous immunoglobulin were started on admission. However, the patient’s condition deteriorated overnight with soaring transaminases, severe coagulopathy and encephalopathy. On the fourth day of admission, pancytopenia emerged, accompanied by hypofibrinogenemia and hyperferritinemia. The patient was diagnosed with ALF. He also met the diagnostic criteria of HLH according to the HLH-2004 guideline. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplifications of varicella-zoster virus (VZV) were positive, confirming that VZV was a causative trigger for ALF and HLH. In view of the devastating immune activation in HLH, immunosuppression therapy with dexamethasone and etoposide was administered, in addition to high dose acyclovir. The patient’s symptoms improved dramatically and he finally made a full recovery. To our knowledge, this is only the second report of a successful rescue of ALF associated with HLH, without resorting to liver transplantation. The first case was reported in a neonate infected by herpes simplex virus-1. However, survival data in older children and adults are lacking, most of whom died or underwent liver transplantation. Our report emphasizes the clinical vigilance for the possible presence of HLH, and the necessity of extensive investigation for underlying etiologies in patients presenting with indeterminate ALF. Early initiation of specific therapy targeting the underlying etiology, and watchful immunosuppression such as dexamethasone and etoposide, together with supportive therapy, are of crucial importance in this life-threatening disorder.
Core tip: Herein we report a case of acute liver failure (ALF) and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) induced by varicella infection, successfully rescued by a combination therapy of acyclovir and immunosuppression with dexamethasone and etoposide. Accumulating evidence pointed towards a similar immune dysregulation pattern in ALF and HLH. Given the rarity, high mortality, and complexity of HLH in the context of ALF, it is important to maintain a high suspicion for HLH in ALF with or without an identified trigger. Patients might benefit from therapies targeted to halt any underlying trigger and control the overactive immune system.
- Citation: Zhang LN, Guo W, Zhu JH, Guo Y. Successful rescue of acute liver failure and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis following varicella infection: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2018; 6(13): 659-665
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v6/i13/659.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v6.i13.659
Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), also known as hemophagocytic syndrome, is a devastating disorder characterized by defects in natural killer cell and cytotoxic T-cell function, and inappropriate activation of macrophages, leading to hemophagocytosis with resultant cytopenias and a plasma “cytokine storm”[1-3]. Patients with HLH almost always have evidence of liver inflammation, commonly being mild to moderate elevations of transaminases. Acute liver failure (ALF) associated with HLH is rarely reported and generally recognized to be extremely fatal[4-8]. Currently, there is a paucity of information on the successful treatment of ALF associated with HLH[9]. Herein we report a 16-year-old boy with chickenpox who developed ALF and concomitant HLH, successfully rescued by a combination therapy of acyclovir, and immunosuppression with dexamethasone and etoposide, fortunately avoiding liver transplantation.
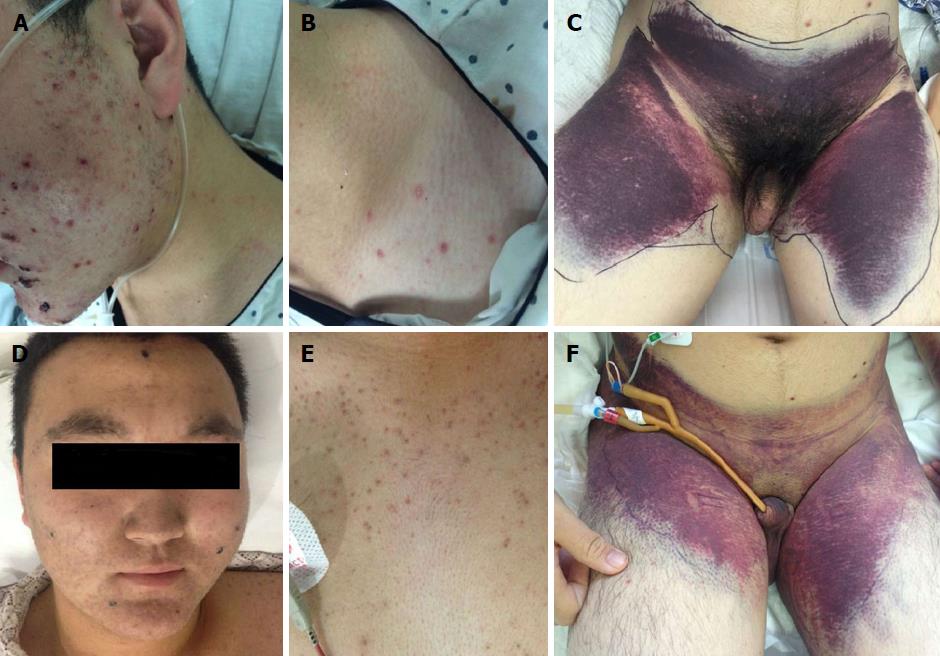
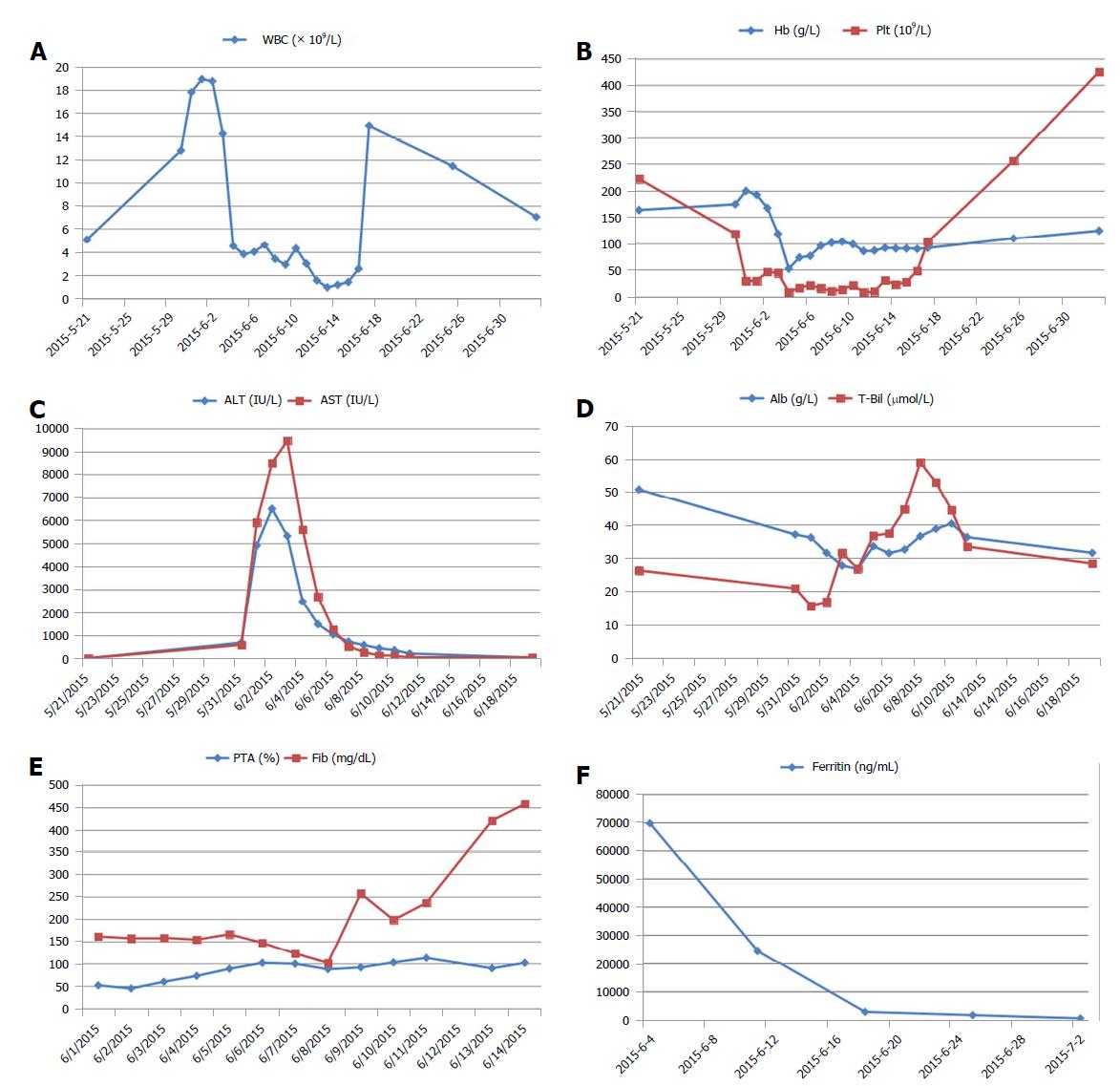
A previously healthy 16-year-old boy presented with generalized rash and severe abdominal pain, followed by fever and abnormal liver function within 4 d. Chickenpox was suspected, and intravenous acyclovir was started at a dose of 10 mg/kg/d. On admission, the patient was stable, alert, and oriented to person and place. The temperature was 38.5°C, the blood pressure 125/65 mmHg, the pulse 105 beats per minute, the respiratory rate 22 breaths per minute, and the oxygen saturation 99% while he was breathing ambient air. There were papulovesicular rashes on the face and trunk, with various stages of development including maculopapules, vesicles, pustules, and crusts (Figure 1A and B). Extensive ecchymosis was noted on the lower abdomen and thighs (Figure 1C). The patient’s liver function deteriorated overnight with coagulopathy and grade 2 encephalopathy. The white blood cell count was 14.3×109/L; hemoglobin 118 g/L; platelet count 44×109/L; alanine transaminase 6499 IU/L, aspartate transaminase 8496 IU/L; total bilirubin 16.8 μmol/L; albumin 31.6 g/L; lactate dehydrogenase 12290 IU/L; international normalized ratio 1.65; and prothrombin activity 45%. An ultrasound of the abdomen showed splenomegaly, but neither hepatomegaly nor ascites.
The patient was diagnosed with ALF. A thorough investigation for an etiology was performed. Markers for hepatitis A, B, C, and E virus infection and for human immunodeficiency virus infection were negative. Antinuclear, anti-smooth muscle and anti-mitochondrial antibodies were negative. There had been no recent travel, illicit drug or alcohol use, or herbal medicine intake. In view of the recent onset rash, we tested the blood and blister liquid for herpes group viruses. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplifications of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), herpes simplex virus (HSV1, HSV2), cytomegalovirus (CMV), and human herpes virus 6 were negative, but varicella-zoster virus (VZV) PCR amplifications were positive, both in the blood and blister liquid. The patient recalled that one month before admission, a number of his schoolmates had developed chickenpox.
The patient was thus deemed as having varicella-induced ALF, and underwent a combination therapy of acyclovir (10 mg/kg every 8 h, for 10 d), intravenous immunoglobulin, and multiple transfusions of platelets and fresh-frozen plasma. On the 4th day of admission, his liver enzymes started to decline (Figure 2C) but pancytopenia developed (Figure 2A and B). This prompted us to consider HLH. Further investigation revealed markedly high serum ferritin (69670 ng/mL) and hypofibrinogenemia (148 mg/dL), though bone marrow biopsy showed no evidence of hemophagocytosis. He met the diagnostic criteria for HLH according to the HLH-2004 guideline (Table 1)[1], and was treated with dexamethasone and etoposide on the 5th day. Imipenem was added in this high-risk neutropenic patient, and de-escalation strategy was applied in the following days. His abdominal pain abated dramatically by the 8th day, the ecchymosis gradually resolved (Figure 1F), and the skin lesions regressed (Figure 1D and E). Meanwhile, the laboratory values continued to improve (Figure 2). The recovery was uneventful, and he was discharged from the hospital. The patient remained healthy without a recurrence of HLH during a 3-year follow-up.
| Presence of 5 or more of the following: | The condition in our patient |
| Fever ≥ 38.5°C | Yes |
| Splenomegaly | Yes |
| Cytopenias affecting at least 2 of 3 of the peripheral blood lineages | Yes |
| Hemoglobin < 90 g/L | Yes |
| Platelets < 100 ×109/L | Yes |
| Neutrophils < 1.0 ×109/L | No |
| Hypertriglyceridemia (fasting, ≥ 265 mg/dL) and/or hypofibrinogenemia (≤ 150 mg/dL) | Yes |
| Hemophagocytosis in bone marrow, liver, spleen, or lymph nodes | Not found |
| Low or absent NK cell activity | NA |
| Ferritin ≥ 500 ng/mL | Yes |
| sIL-2R ≥ 2400 U/mL | NA |
Indeterminate ALF necessitates a broad evaluation for underlying etiologies; both infectious and noninfectious are included. Although screening for common forms of viral hepatitis, including hepatitis A to E is nearly universal, testing for viruses less frequently considered hepatropic may not always be complete[10,11]. For example, some cases of herpes virus-associated fulminant hepatitis were only confirmed by postmortem liver biopsy[12]. VZV is a hepatropic virus that belongs to the family of herpes viruses, and is the cause of chickenpox, a highly contagious but generally mild disease in childhood, which could be more severe in adults. Varicella-induced ALF is rare but potentially fatal, and should always be suspected in the presence of ALF and vesicular skin rash[13]. Our patient was a 16-year-old adolescent who was previously in good health and had not ever before caught chickenpox. He presented with generalized vesicular rash and severe abdominal pain several days before ALF. Soon after, PCR amplifications of VZV were found to be positive in both specimens of blood and blister liquid, confirming that VZV was a causative factor in the development of ALF in this case. Furthermore, the patient rapidly developed pancytopenia, and hyperferritinemia, suggesting the coexistence of HLH, a devastating syndromic disorder, characterized by fever, splenomegaly, cytopenia and the finding of activated macrophages in hemopoietic organs[1-3]. Though not yet listed as part of the current diagnostic criteria, various degrees of liver inflammation are considered a typical feature of HLH[2,3]. ALF associated with HLH is extremely fatal and rarely reported. Very few patients have been documented to survive with their native liver. In recent years, HLH first presenting as ALF was becoming increasingly noticed while the mortality remained high[4-8]. HLH was thus considered an important differential diagnosis for ALF. Unexplained liver failure with concurrent cytopenias and elevated serum ferritin should suggest HLH[14,15].
A diagnosis of HLH can be made if a patient meet five of the following criteria: fever, splenomegaly, cytopenia, elevated serum concentrations of triglycerides, ferritin, or soluble interleukin-2 receptor (sIL-2R), hypofibrinogenemia, the presence of hemophagocytosis, or decreased or absent natural killer cell function (Table 1)[1]. HLH can be either primary, with a genetic etiology, or secondary, associated with a variety of triggers, including infection, malignancy, drugs, rheumatologic and metabolic disorders[2,3]. Among them, viral infection is the most frequent trigger, and herpes viruses (most commonly EBV, CMV, and VZV) account for 62% of reported viral cases of HLH[16]. Viral infection may trigger deficiency in cytolytic activity, which results in uncontrolled activation of macrophages, histiocytes and T cells. This in turn produces an exaggerated inflammatory response caused by hyper-secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor α, interferon-γ, interleukin 1, interleukin 4, interleukin 6, interleukin 8, interleukin 10, and interleukin 18[16,17]. This so-called “cytokine storm” can be pathogenically related to the development of the clinical and laboratory features of HLH and contributes to tissue damage and progressive systemic organ failure. The treatment of HLH is designed to halt any underlying trigger and control the overactive immune system[1-3]. If a malignancy or infection is identified, disease-specific treatment should be initiated immediately. Additional immunosuppressive therapy is almost always needed in severe cases and in those who fail to respond to disease-specific therapy within 2 to 3 d. The classic regimen containing etoposide and dexamethasone selectively depletes pathologic, activated T cells and suppresses inflammatory cytokine production, thus breaking the vicious cycle of immune dysregulation[3,18].
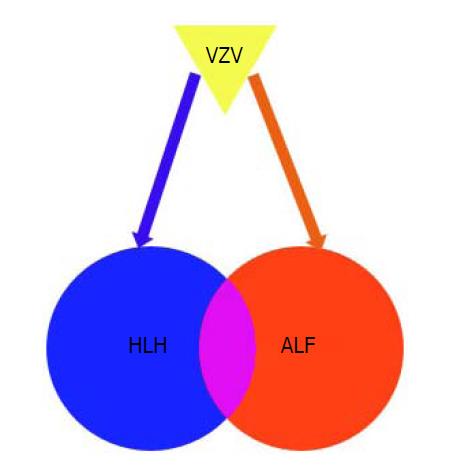
Recent studies have suggested that patients with ALF have an immune dysregulation pattern similar to observations in HLH[11,19]. Some patients with ALF present with elevated ferritin and sIL-2R levels, low fibrinogen, and numerous infiltrating CD8+ T cells on liver biopsy, which are compatible with those found in HLH[19,20]. However, they do not manifest the full spectrum of criteria required for diagnosis of HLH. In contrast, HLH diagnosis in the context of ALF is exceptionally complicated: some of the HLH-2004 criteria such as splenomegaly, fever, and cytopenia could appear in non-HLH-related ALF, and the HLH-2004 criteria are not validated in the setting of ALF. It may be inferred that at least a subset of ALF cases may manifest with the HLH spectrum in a shared pathophysiology predominantly affecting the liver (Figure 3).
To our knowledge, this is only the second report of a successful rescue of ALF associated with HLH, without resorting to liver transplantation. The first case was a neonate with ALF and HLH triggered by HSV-1, who was successfully treated by high-dose acyclovir and immunosuppression therapy[9]. However, survival data in older children and adults are lacking, most of whom died or underwent liver transplantation[4-8]. Although liver transplantation provides a treatment option for patients who fail to recover with medical management, the mortality is high. In addition, it has significant inherent risks including surgical complications and long-term immunosuppression[19]. Herein we presented an adolescent with ALF and HLH induced by VZV, successfully rescued by a combination therapy of acyclovir, supportive care, and short-term immunosuppression with dexamethasone and etoposide, fortunately avoiding liver transplantation. Our patient showed the highest ALT and AST level ever documented, indicating massive liver necrosis. Severe coagulopathy and encephalopathy also occurred. However, he finally made a full recovery and remained well during a 3-year follow-up period. In fact, there was another patient who survived from HLH and liver dysfunction secondary to rubella and varicella virus dual infection, but her liver damage did not reach the standard of ALF[21].
The limitation of our study was that we did not check sIL-2R or natural killer cell function. Since these investigations were time-consuming to perform and report, it was not feasible to rely completely on them in order to establish the diagnosis of HLH. Of note, our patient showed a markedly elevated serum ferritin of 69670 ng/mL. The differential diagnosis for such a high level of ferritin could be limited to few clinical circumstances, such as Still’s disease, HLH, and systemic histoplasmosis[15]. Other chronic inflammatory disorders may elevate ferritin levels appreciably, but not to this degree. Despite the disease’s name, hemophagocytosis is neither sensitive nor specific for HLH. Hemophagocytosis may not appear in initial biopsies and yet may linger in later biopsies even when other disease parameters begin to improve[2,3]. In fact, we did not find hemophagocytosis in the bone marrow of this patient, which might be ascribed to relatively low sensitivity in early biopsies. It is important to keep in mind the constellation of items listed in the diagnostic criteria of HLH. Although the individual sign or symptom of HLH may occur in a variety of clinical circumstances, the combination of these features, indicating a unique pattern of pathologic inflammation, is sensitive and specific for corroborating the diagnosis.
In summary, we reported a case of ALF and HLH following varicella infection, successfully rescued by a combination therapy of acyclovir, supportive care, and immunosuppression with dexamethasone and etoposide. Given the rarity, high mortality, and complexity of HLH in the context of ALF, it is important to maintain a high suspicion for HLH in ALF with or without an identified etiology. Extensive investigation for underlying etiologies of HLH and ALF should be initiated as early as possible. This is essentially important for those with curable etiologies, such as varicella infection, as in this case. Early initiation of specific therapy targeting the underlying etiology, and watchful immunosuppression such as dexamethasone and etoposide, together with supportive therapy, are of crucial importance in this life-threatening disorder.
We thank Professor Zhao Wang, Department of Hematology, Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University, and Professor Le-Ping Zhang, Department of Pediatrics, Peking University People’s Hospital, for their help with the evaluation and management of the patient.
A previously healthy 16-year-old boy developed acute liver failure (ALF) and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) soon after varicella infection.
Generalized skin rash with various stages of development including maculopapules, vesicles, pustules, and crusts were typical features of chickenpox [primary infection of varicella-zoster virus(VZV)].
The differential diagnosis for extremely high level of ferritin (> 50000 ng/mL) could be limited to few clinical circumstances, such as Still’s disease, HLH, and systemic histoplasmosis.
A sudden onset of liver injury with soared transaminases and decreased prothrombin activity pointed to ALF. Pancytopenia, hypofibrinogenemia, and hyperferritinemia were clues for HLH. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplifications of VZV confirmed varicella infection.
An ultrasound of the abdomen showed splenomegaly, but neither hepatomegaly nor ascites.
Not applicable.
The patient underwent a combination therapy of acyclovir (10 mg/kg every 8 h), supportive care, and immunosuppression with dexamethasone and etoposide.
ALF associated with HLH is extremely fatal and rarely reported. In recent years, HLH first presenting as ALF was becoming increasingly noticed while the mortality remained high.
HLH, also known as hemophagocytic syndrome, is a devastating disorder characterized by fever, splenomegaly, cytopenia and the finding of activated macrophages in hemopoietic organs.
Accumulating evidence pointed towards a similar immune dysregulation pattern in ALF and HLH. It is important to maintain a high suspicion for HLH in ALF with or without an identified trigger. Patients might benefit from therapies targeted to halt any underlying trigger and control the overactive immune system.
CARE Checklist (2013) statement: This manuscript has completed the CARE Checklist (2013).
Manuscript source: Unsolicited manuscript
Specialty type: Medicine, research and experimental
Country of origin: China
Peer-review report classification
Grade A (Excellent): A
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P- Reviewer: Shinjoh M, Lei YC S- Editor: Dou Y L- Editor: A E- Editor: Song H
| 1. | Henter JI, Horne A, Aricó M, Egeler RM, Filipovich AH, Imashuku S, Ladisch S, McClain K, Webb D, Winiarski J. HLH-2004: Diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2007;48:124-131. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3075] [Cited by in RCA: 3579] [Article Influence: 198.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 2. | Jordan MB, Allen CE, Weitzman S, Filipovich AH, McClain KL. How I treat hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Blood. 2011;118:4041-4052. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 747] [Cited by in RCA: 793] [Article Influence: 56.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Schram AM, Berliner N. How I treat hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in the adult patient. Blood. 2015;125:2908-2914. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 212] [Cited by in RCA: 272] [Article Influence: 27.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Schneier A, Stueck AE, Petersen B, Thung SN, Perumalswami P. An Unusual Cause of Acute Liver Failure: Three Cases of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Presenting at a Transplant Center. Semin Liver Dis. 2016;36:99-105. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Amir AZ, Ling SC, Naqvi A, Weitzman S, Fecteau A, Grant D, Ghanekar A, Cattral M, Nalli N, Cutz E. Liver transplantation for children with acute liver failure associated with secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Liver Transpl. 2016;22:1245-1253. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 31] [Cited by in RCA: 27] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Lin S, Li Y, Long J, Liu Q, Yang F, He Y. Acute liver failure caused by hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in adults: A case report and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95:e5431. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 30] [Cited by in RCA: 27] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Patel R, Patel H, Mulvoy W, Kapoor S. Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma with Secondary Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Presenting as Acute Liver Failure. ACG Case Rep J. 2017;4:e68. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Kumar M, Kothari N, Gupta BD, Gupta N. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis presenting with acute liver failure and central nervous system involvement in early infancy. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2018;61:281-283. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Yamada K, Yamamoto Y, Uchiyama A, Ito R, Aoki Y, Uchida Y, Nagasawa H, Kimura H, Ichiyama T, Fukao T. Successful treatment of neonatal herpes simplex-type 1 infection complicated by hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and acute liver failure. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2008;214:1-5. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 26] [Cited by in RCA: 26] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Bernal W, Lee WM, Wendon J, Larsen FS, Williams R. Acute liver failure: A curable disease by 2024? J Hepatol. 2015;62:S112-S120. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 158] [Cited by in RCA: 180] [Article Influence: 18.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Alonso EM, Horslen SP, Behrens EM, Doo E. Pediatric acute liver failure of undetermined cause: A research workshop. Hepatology. 2017;65:1026-1037. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 45] [Cited by in RCA: 59] [Article Influence: 7.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Yokoi Y, Kaneko T, Sawayanagi T, Takano Y, Watahiki Y. Fatal fulminant herpes simplex hepatitis following surgery in an adult. World J Clin Cases. 2018;6:11-19. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Dits H, Frans E, Wilmer A, Van Ranst M, Fevery J, Bobbaers H. Varicella-zoster virus infection associated with acute liver failure. Clin Infect Dis. 1998;27:209-210. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 27] [Cited by in RCA: 28] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Allen CE, Yu X, Kozinetz CA, McClain KL. Highly elevated ferritin levels and the diagnosis of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2008;50:1227-1235. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 381] [Cited by in RCA: 430] [Article Influence: 25.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Tierney LM Jr, Thabet A, Nishino H. Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Case 10-2011. A woman with fever, confusion, liver failure, anemia, and thrombocytopenia. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:1259-1270. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Ramos-Casals M, Brito-Zerón P, López-Guillermo A, Khamashta MA, Bosch X. Adult haemophagocytic syndrome. Lancet. 2014;383:1503-1516. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 788] [Cited by in RCA: 954] [Article Influence: 86.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Canna SW, Behrens EM. Not all hemophagocytes are created equally: appreciating the heterogeneity of the hemophagocytic syndromes. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2012;24:113-118. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 47] [Cited by in RCA: 50] [Article Influence: 3.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Johnson TS, Terrell CE, Millen SH, Katz JD, Hildeman DA, Jordan MB. Etoposide selectively ablates activated T cells to control the immunoregulatory disorder hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. J Immunol. 2014;192:84-91. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 106] [Cited by in RCA: 154] [Article Influence: 12.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | DiPaola F, Grimley M, Bucuvalas J. Pediatric acute liver failure and immune dysregulation. J Pediatr. 2014;164:407-409. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 1.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | McKenzie RB, Berquist WE, Nadeau KC, Louie CY, Chen SF, Sibley RK, Glader BE, Wong WB, Hofmann LV, Esquivel CO. Novel protocol including liver biopsy to identify and treat CD8+ T-cell predominant acute hepatitis and liver failure. Pediatr Transplant. 2014;18:503-509. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Takeoka Y, Hino M, Oiso N, Nishi S, Koh KR, Yamane T, Ohta K, Nakamae H, Aoyama Y, Hirose A. Virus-associated hemophagocytic syndrome due to rubella virus and varicella-zoster virus dual infection in patient with adult idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Ann Hematol. 2001;80:361-364. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |